Parameter estimation in biochemical pathways: a comparison of global optimization methods - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
. 2003 Nov;13(11):2467-74.
doi: 10.1101/gr.1262503. Epub 2003 Oct 14.
Affiliations
- PMID: 14559783
- PMCID: PMC403766
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1262503
Comparative Study
Parameter estimation in biochemical pathways: a comparison of global optimization methods
Carmen G Moles et al. Genome Res. 2003 Nov.
Abstract
Here we address the problem of parameter estimation (inverse problem) of nonlinear dynamic biochemical pathways. This problem is stated as a nonlinear programming (NLP) problem subject to nonlinear differential-algebraic constraints. These problems are known to be frequently ill-conditioned and multimodal. Thus, traditional (gradient-based) local optimization methods fail to arrive at satisfactory solutions. To surmount this limitation, the use of several state-of-the-art deterministic and stochastic global optimization methods is explored. A case study considering the estimation of 36 parameters of a nonlinear biochemical dynamic model is taken as a benchmark. Only a certain type of stochastic algorithm, evolution strategies (ES), is able to solve this problem successfully. Although these stochastic methods cannot guarantee global optimality with certainty, their robustness, plus the fact that in inverse problems they have a known lower bound for the cost function, make them the best available candidates.
Figures
Figure 1
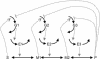
The model metabolic pathway used in these studies. Solid arrows represent mass flow, dashed arrows represent kinetic regulation; arrow ends represent activation, blunt ends inhibition. S and P are the pathway substrate and product and are held at constant concentrations; M1 and M2 are intermediate metabolites of the pathway; E1, E2, and E3 are the enzymes; G1, G2, and G3 are the mRNA species for the enzymes.
Figure 2
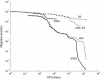
Convergence curves (objective function versus computation time, in seconds, using a PC/Pentium III 866 MHz).
Figure 3
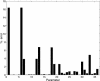
Histogram of the results obtained with the multistart local method.
Figure 4
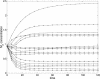
_M_2 predicted (continuous line) and experimental (marker) behavior for the 16 experiments.
Figure 5
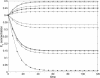
_E_1 predicted (continuous line) and experimental (marker) behavior for the 16 experiments.
Figure 6
Relative error (%) for the estimated parameters (for the best solution, obtained by SRES).
Similar articles
- Deterministic global optimization algorithm based on outer approximation for the parameter estimation of nonlinear dynamic biological systems.
Miró A, Pozo C, Guillén-Gosálbez G, Egea JA, Jiménez L. Miró A, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 May 10;13:90. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-90. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22574924 Free PMC article. - Biochemical systems identification by a random drift particle swarm optimization approach.
Sun J, Palade V, Cai Y, Fang W, Wu X. Sun J, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-S6-S1. Epub 2014 May 16. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 25078435 Free PMC article. - Novel metaheuristic for parameter estimation in nonlinear dynamic biological systems.
Rodriguez-Fernandez M, Egea JA, Banga JR. Rodriguez-Fernandez M, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Nov 2;7:483. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-483. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17081289 Free PMC article. - Parameter estimate of signal transduction pathways.
Arisi I, Cattaneo A, Rosato V. Arisi I, et al. BMC Neurosci. 2006 Oct 30;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-S1-S6. BMC Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17118160 Free PMC article. Review. - A comparison of deterministic and stochastic approaches for sensitivity analysis in computational systems biology.
Simoni G, Vo HT, Priami C, Marchetti L. Simoni G, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2020 Mar 23;21(2):527-540. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz014. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30753281 Review.
Cited by
- Optimization of time-course experiments for kinetic model discrimination.
Lages NF, Cordeiro C, Sousa Silva M, Ponces Freire A, Ferreira AE. Lages NF, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032749. Epub 2012 Mar 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22403703 Free PMC article. - Identifying effective evolutionary strategies-based protocol for uncovering reaction kinetic parameters under the effect of measurement noises.
Yeo HC, Vijay V, Selvarajoo K. Yeo HC, et al. BMC Biol. 2024 Oct 14;22(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02019-4. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39402553 Free PMC article. - An iterative identification procedure for dynamic modeling of biochemical networks.
Balsa-Canto E, Alonso AA, Banga JR. Balsa-Canto E, et al. BMC Syst Biol. 2010 Feb 17;4:11. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-11. BMC Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 20163703 Free PMC article. - Modeling and Optimization of a Molecular Biocontroller for the Regulation of Complex Metabolic Pathways.
Boada Y, Santos-Navarro FN, Picó J, Vignoni A. Boada Y, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 29;9:801032. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.801032. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35425808 Free PMC article. - Dynamic analysis of integrated signaling, metabolic, and regulatory networks.
Lee JM, Gianchandani EP, Eddy JA, Papin JA. Lee JM, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2008 May 23;4(5):e1000086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000086. PLoS Comput Biol. 2008. PMID: 18483615 Free PMC article.
References
- Ali, M.M., Storey, C., and Törn, A. 1997. Application of stochastic global optimization algorithms to practical problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 95: 545-563.
- Anonymous. 2000. Optimization toolbox user's guide. The Math Works Inc., Natick, MA.
- Bäck, T. 1996. Evolution strategies: An alternative evolutionary algorithm. In Artificial evolution (eds. J.M. Alliott et al.), pp. 3-20. Springer, Berlin.
- Balsa-Canto, E., Alonso, A.A., and Banga, J.R. 1998. Dynamic optimization of bioprocesses: Deterministic and stochastic strategies. In Proceedings of ACoFop IV (Automatic Control of Food and Biological Processes), (eds. C. Skjoldebremd and G. Trystrom), pp. 2-23. Göteborg, Sweden.
- Banga, J.R. and Casares, J.J. 1987. ICRS: Application to a wastewater treatment plant model. In IChemE Symposium Series No. 100, pp. 183-192. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK.
WEB SITE REFERENCES
- http://www.beowulf.org; technology for cluster computing.
- http://www.gepasi.org; Gepasi biochemical simulation package.
- http://www.globus.org; technology for grid computing.
- http://www.mathworks.com; Matlab.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources