Hepatitis C virus protease NS3/4A cleaves mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein off the mitochondria to evade innate immunity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Hepatitis C virus protease NS3/4A cleaves mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein off the mitochondria to evade innate immunity
Xiao-Dong Li et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005.
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a global epidemic manifested mainly by chronic infection. One strategy that HCV employs to establish chronic infection is to use the viral Ser protease NS3/4A to cleave some unknown cellular targets involved in innate immunity. Here we show that the target of NS3/4A is the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein, MAVS, that activates NF-kappaB and IFN regulatory factor 3 to induce type-I interferons. NS3/4A cleaves MAVS at Cys-508, resulting in the dislocation of the N-terminal fragment of MAVS from the mitochondria. Remarkably, a point mutation of MAVS at Cys-508 renders MAVS resistant to cleavage by NS3/4A, thus maintaining the ability of MAVS to induce interferons in HCV replicon cells. NS3/4A binds to and colocalizes with MAVS in the mitochondrial membrane, and it can cleave MAVS directly in vitro. These results provide an example of host-pathogen interaction in which the virus evades innate immunity by dislodging a pivotal antiviral protein from the mitochondria and suggest that blocking the cleavage of MAVS by NS3/4A may be applied to the prevention and treatment of HCV.
Figures
Fig. 1.
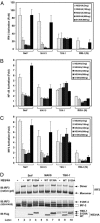
NS3/4A blocks IFN induction by MAVS. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with IFN-β-Luc and the expression vector for either the WT or S139A mutant of NS3/4A. The next day, cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding MAVS, TBK1, or RIG-I(N), or infected with SeV. The Luc activity was measured 24 h later and normalized for transfection efficiency. The error bar represents standard deviation from the mean value of duplicated experiments. (B) Similar to A, except that NF-κB Luc reporter was used in lieu of IFN-β-Luc. (C) Similar to A, except that cells were transfected with the UAS-Luc reporter together with the Gal4-IRF3 expression vector. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with the WT or S139A mutant of NS3/4A together with the expression vectors for MAVS (lanes 5–7) or TBK1 (lanes 8–10). In lanes 2–4, cells were infected with SeV for 24 h. Cell lysates were resolved by electrophoresis under native (Top) or denaturing condition (Middle) and then immunoblotted with an Ab against IRF3. The expression of NS3/4A and TBK1 also was analyzed by immunoblotting with a Flag Ab (Bottom).
Fig. 2.
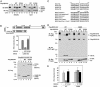
NS3/4A cleaves MAVS at Cys-508. (A) HEK293 (lanes 1–6) or Huh7 (lanes 7–12) cells were transfected with expression vectors for the WT (lanes 3,4, 9, and 10) or S139A mutant (lanes 5, 6, 11, and 12) of NS3/4A or vector (lanes 1, 2, 7, and 8). Cell lysates were separated into membrane pellet (P) or cytosolic supernatant (S) and then immunoblotted with an Ab against MAVS or Flag. The cleavage product of MAVS was indicated as MAVS*. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with the expression vectors for NS3/4A together with a MAVS mutant containing only the CARD and TM domains (miniMAVS; Top). The activation of IFN-β by the CARD-TM fragment of MAVS in the presence of WT or S139A mutant of NS3/4A was determined by measuring the expression of the IFN-β-Luc reporter (Middle). Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the Flag Ab that detects both NS3/4A and MAVS proteins (Bottom). (C) Alignment of the junction sequences of NS proteins of HCV and the putative cleavage site at the C terminus of MAVS from different species. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding the WT or C508R mutant of MAVS together with those encoding the WT or S139A mutant of NS3/4A. Cell lysates were separated by differential centrifugation into the membrane pellet and cytosolic supernatant, which were then resolved by 7% (Top and Bottom) or 4–20% (Middle) SDS/PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated Ab that detects the N terminus (Flag; Top) or C terminus (HA; Middle) of MAVS, or NS3/4A (Myc; Bottom). (E) HEK293 cells were transfected with MAVS and NS3/4A expression vectors as in D, except that IFN-β-Luc was also cotransfected to measure the induction of IFN-β by Luc assay.
Fig. 3.
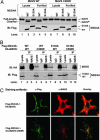
NS3/4A binds to and colocalizes with MAVS in the mitochondria, and it cleaves MAVS in vitro.(A) Flag-tagged WT or S139A mutant of NS3/4A was expressed in HEK293 cells and then purified by using Flag-Sepharose. The purified NS3/4A proteins (lanes 4, 5, 9, and 10) or lysates containing NS3/4A (lanes 1–3 and 6–8) were incubated with 35S-labeled MAVS or C508R mutant of MAVS, which was synthesized by in vitro translation and purified by using Flag-Sepharose. After incubation at 30°C for 2 h, proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by PhosphorImaging (Upper) or immunoblotting (Lower). The cleavage product of MAVS is indicated as MAVS*. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with expression vectors for Flag-NS3/4A and HA-MAVS as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the MAVS Ab (lanes 3, 6, 9, and 12) or control IgG (lanes 2, 5, 8, and 11). The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with an Ab against HA (Upper) or Flag (Lower). (C) Expression vectors for Flag-NS3/4A and HA-MAVS or C508R mutant were transfected into HeLa cells, and the localization of these proteins was stained by the indicated Abs and visualized by confocal microscopy.
Fig. 4.
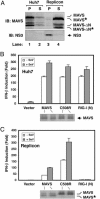
MAVS is cleaved at Cys-508 in a HCV replicon cell line. (A) Cell lysates from Huh7 (lanes 1 and 2) or Replicon cells (K2040; lanes 3 and 4) were separated by centrifugation into the membrane pellet (P) and cytosolic supernatant (S), which then were analyzed by immunoblotting with an Ab against MAVS or NS3. The cleavage products of MAVS are indicated as MAVS*. MAVS-ΔN, N-terminal truncated fragment of MAVS (see ref. 10); MAVS-ΔN*, N-terminal truncated fragment of MAVS in which the TM domain is also cleaved by NS3/4A. (B and C) Expression vectors for MAVS, C508 mutant of MAVS, or RIG-I(N) were cotransfected with the IFN-β-Luc reporter into Huh7 (B) or Replicon (C) cell lines. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were infected with SeV or mock infected for another 24 h before harvesting for Luc assay.
Comment in
- Interfering with interferons: Hepatitis C virus counters innate immunity.
Freundt EC, Lenardo MJ. Freundt EC, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Dec 6;102(49):17539-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509221102. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16314558 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Control of innate immune signaling and membrane targeting by the Hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease are governed by the NS3 helix α0.
Horner SM, Park HS, Gale M Jr. Horner SM, et al. J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(6):3112-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06727-11. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22238314 Free PMC article. - Hepacivirus NS3/4A Proteases Interfere with MAVS Signaling in both Their Cognate Animal Hosts and Humans: Implications for Zoonotic Transmission.
Anggakusuma, Brown RJP, Banda DH, Todt D, Vieyres G, Steinmann E, Pietschmann T. Anggakusuma, et al. J Virol. 2016 Nov 14;90(23):10670-10681. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01634-16. Print 2016 Dec 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27654291 Free PMC article. - Recruitment of an interferon molecular signaling complex to the mitochondrial membrane: disruption by hepatitis C virus NS3-4A protease.
Hiscott J, Lacoste J, Lin R. Hiscott J, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 30;72(11):1477-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.06.030. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16876765 - Nonstructural protein 3-4A: the Swiss army knife of hepatitis C virus.
Morikawa K, Lange CM, Gouttenoire J, Meylan E, Brass V, Penin F, Moradpour D. Morikawa K, et al. J Viral Hepat. 2011 May;18(5):305-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01451.x. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Viral Hepat. 2011. PMID: 21470343 Review. - [Chronic hepatitis C virus infection attenuates host antiviral innate immune response].
Oshiumi H, Matsumoto M, Seya T. Oshiumi H, et al. Nihon Rinsho. 2015 Feb;73(2):234-8. Nihon Rinsho. 2015. PMID: 25764676 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
- Hepatitis C virus and autophagy.
Wang L, Ou JH. Wang L, et al. Biol Chem. 2015 Nov;396(11):1215-22. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2015-0172. Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26024249 Free PMC article. Review. - Living in the liver: hepatic infections.
Protzer U, Maini MK, Knolle PA. Protzer U, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Feb 24;12(3):201-13. doi: 10.1038/nri3169. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22362353 Review. - Nonstructural 3 Protein of Hepatitis C Virus Modulates the Tribbles Homolog 3/Akt Signaling Pathway for Persistent Viral Infection.
Tran SC, Pham TM, Nguyen LN, Park EM, Lim YS, Hwang SB. Tran SC, et al. J Virol. 2016 Jul 27;90(16):7231-7247. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00326-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27252525 Free PMC article. - RNA binding by the NS3 protease of the hepatitis C virus.
Vaughan R, Li Y, Fan B, Ranjith-Kumar CT, Kao CC. Vaughan R, et al. Virus Res. 2012 Oct;169(1):80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.07.007. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22814430 Free PMC article. - Essential role of mda-5 in type I IFN responses to polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid and encephalomyocarditis picornavirus.
Gitlin L, Barchet W, Gilfillan S, Cella M, Beutler B, Flavell RA, Diamond MS, Colonna M. Gitlin L, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 30;103(22):8459-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603082103. Epub 2006 May 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16714379 Free PMC article.
References
- Lindenbach, B. D. & Rice, C. M. (2005) Nature 436, 933–938. - PubMed
- Chisari, F. V. (2005) Nature 436, 930–932. - PubMed
- Foy, E., Li, K., Wang, C., Sumpter, R., Jr., Ikeda, M., Lemon, S. M. & Gale, M., Jr. (2003) Science 300, 1145–1148. - PubMed
- Maniatis, T., Falvo, J. V., Kim, T. H., Kim, T. K., Lin, C. H., Parekh, B. S. & Wathelet, M. G. (1998) Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 63, 609–620. - PubMed
- McWhirter, S. M., Tenoever, B. R. & Maniatis, T. (2005) Cell 122, 645–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 GM068979/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019406/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI60919/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1-S10-RR19406/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous