Mapping the Arabidopsis organelle proteome - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2006 Apr 25;103(17):6518-23.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506958103. Epub 2006 Apr 17.
Svenja Hester, Ian P Shadforth, John Runions, Thilo Weimar, Sally L Hanton, Julian L Griffin, Conrad Bessant, Federica Brandizzi, Chris Hawes, Rod B Watson, Paul Dupree, Kathryn S Lilley
Affiliations
- PMID: 16618929
- PMCID: PMC1458916
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506958103
Mapping the Arabidopsis organelle proteome
Tom P J Dunkley et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006.
Abstract
A challenging task in the study of the secretory pathway is the identification and localization of new proteins to increase our understanding of the functions of different organelles. Previous proteomic studies of the endomembrane system have been hindered by contaminating proteins, making it impossible to assign proteins to organelles. Here we have used the localization of organelle proteins by the isotope tagging technique in conjunction with isotope tags for relative and absolute quantitation and 2D liquid chromatography for the simultaneous assignment of proteins to multiple subcellular compartments. With this approach, the density gradient distributions of 689 proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana were determined, enabling confident and simultaneous localization of 527 proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuolar membrane, plasma membrane, or mitochondria and plastids. This parallel analysis of endomembrane components has enabled protein steady-state distributions to be determined. Consequently, genuine organelle residents have been distinguished from contaminating proteins and proteins in transit through the secretory pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
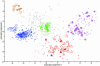
Fig. 1.
PCA scores plot showing clustering of proteins according to their density gradient distributions and, therefore, localizations. iTRAQ reporter ion ratios were imported into
simca
10, logged, and preprocessed with unit-variance scaling before performing PCA analysis. Filled shapes indicate known organelle residents (marker proteins). Open shapes (or stars in the case of mitochondria/plastid) indicate proteins with predicted localizations that were confirmed based on their proximity to the corresponding marker proteins on the PCA scores plot. Small dots indicate proteins, without known or predicted localizations, that were assigned to an organelle by using PLS-DA, in conjunction with limited manual analysis. Small crosses indicate proteins that were not assigned to an organelle. Inverted triangles, vacuolar membrane; squares, ER; diamonds, PM; circles, known mitochondria/plastids; stars, predicted mitochondria/plastids; triangles, Golgi apparatus.
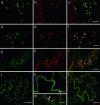
Fig. 2.
Fluorescent protein fusions to uncharacterized proteins to confirm LOPIT targeting predictions. (a_–_f) Golgi apparatus. Colocalization of uncharacterized protein with known Golgi apparatus markers is shown. (a) At1g04910-GFP marks small motile organelles. (b) ST-mRFP marks the Golgi apparatus. (c) Colocalization of the markers in a and b. (d) At1g31850 GMT1GFP marks small motile organelles. (e) ERD2-YFP marks Golgi apparatus strongly as bright spots and the ER weakly. (f) Colocalization of the markers in d and e. (Scale bars: 5 μm.) (g_–_i) ER localization. Colocalization of uncharacterized protein with known ER marker. (g) At3g44330-GFP marks a reticulate structure in the periphery of the cell. (h) YFP-HDEL marks the ER. (i) Colocalization of the markers in g and h. (Scale bars: 10 μm.) (j and k) Plasma membrane localization. (j) At1g14870-GFP. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (k) Higher magnification of g. (Scale bars: 10 μm.) (l and m) Vacuolar membrane localization. (l) At2g47800-GFP. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (m) Higher magnification of l. Note that membrane position toward the center of the cell relative to a chloroplast (arrowhead) confirms its identity as a vacuolar membrane. (Scale bar: 5 μm.)
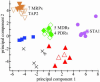
Fig. 3.
PCA score plot showing positions of the ABC transporters, vacuolar sorting receptors, the unclassified V-ATPase V0a homolog, and GMT1 and GMT2 relative to the organelle marker proteins (filled shapes). Inverted triangles, vacuolar membrane and vacuolar ABC transporters; diamonds, PM and PM ABC transporters; circles, mitochondria/plastids; star, mitochondrial ABC transporter; diagonal crosses, vacuolar sorting receptors; horizontal cross, V-ATPase subunit V0a; triangles, Golgi apparatus, GMT1, and GMT2; squares, ER.
Similar articles
- Localization of organelle proteins by isotope tagging (LOPIT).
Dunkley TP, Watson R, Griffin JL, Dupree P, Lilley KS. Dunkley TP, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004 Nov;3(11):1128-34. doi: 10.1074/mcp.T400009-MCP200. Epub 2004 Aug 4. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004. PMID: 15295017 - The use of isotope-coded affinity tags (ICAT) to study organelle proteomes in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Dunkley TP, Dupree P, Watson RB, Lilley KS. Dunkley TP, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Jun;32(Pt3):520-3. doi: 10.1042/BST0320520. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15157176 Review. - Identification of Regulatory and Cargo Proteins of Endosomal and Secretory Pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana by Proteomic Dissection.
Heard W, Sklenář J, Tomé DF, Robatzek S, Jones AM. Heard W, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015 Jul;14(7):1796-813. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.050286. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25900983 Free PMC article. - The organelle proteome of the DT40 lymphocyte cell line.
Hall SL, Hester S, Griffin JL, Lilley KS, Jackson AP. Hall SL, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Jun;8(6):1295-305. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800394-MCP200. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19181659 Free PMC article. - Plant organelle proteomics.
Lilley KS, Dupree P. Lilley KS, et al. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007 Dec;10(6):594-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.08.006. Epub 2007 Oct 2. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 17913569 Review.
Cited by
- AT_CHLORO: A Chloroplast Protein Database Dedicated to Sub-Plastidial Localization.
Bruley C, Dupierris V, Salvi D, Rolland N, Ferro M. Bruley C, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2012 Sep 11;3:205. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00205. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22973284 Free PMC article. - Multifunctional Microtubule-Associated Proteins in Plants.
Krtková J, Benáková M, Schwarzerová K. Krtková J, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2016 Apr 21;7:474. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00474. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27148302 Free PMC article. Review. - Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the GUX Gene Family in Eucalyptus grandis.
Li L, Tang J, Wu A, Fan C, Li H. Li L, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 27;25(15):8199. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158199. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125768 Free PMC article. - Functional Redundancy and Divergence within the Arabidopsis RETICULATA-RELATED Gene Family.
Pérez-Pérez JM, Esteve-Bruna D, González-Bayón R, Kangasjärvi S, Caldana C, Hannah MA, Willmitzer L, Ponce MR, Micol JL. Pérez-Pérez JM, et al. Plant Physiol. 2013 Jun;162(2):589-603. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.217323. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23596191 Free PMC article. - SUBA: the Arabidopsis Subcellular Database.
Heazlewood JL, Verboom RE, Tonti-Filippini J, Small I, Millar AH. Heazlewood JL, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D213-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl863. Epub 2006 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17071959 Free PMC article.
References
- Dunkley T. P., Dupree P., Watson R. B., Lilley K. S. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004;32:520–523. - PubMed
- Gabaldon T., Huynen M. A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1659:212–220. - PubMed
- Hanton S. L., Bortolotti L. E., Renna L., Stefano G., Brandizzi F. Traffic. 2005;6:267–277. - PubMed
- Dunkley T. P. J., Watson R., Griffin J. L., Dupree P., Lilley K. S. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2004;3:1128–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases