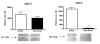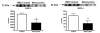Delayed minocycline inhibits ischemia-activated matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 after experimental stroke - PubMed (original) (raw)
Delayed minocycline inhibits ischemia-activated matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 after experimental stroke
Livia S Machado et al. BMC Neurosci. 2006.
Abstract
Background: Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9) are increased in the brain after experimental ischemic stroke in rats. These two proteases are involved with the degradation of the basal lamina and loss of stability of the blood brain barrier that occurs after ischemia and that is associated with thrombolytic therapy in ischemic stroke. Minocycline is a lipophilic tetracycline and is neuroprotective in several models of brain injury. Minocycline inhibits inflammation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation. In this study we investigated whether delayed minocycline inhibits brain MMPs activated by ischemia in a model of temporary occlusion in Wistar rats.
Results: Both MMP-2 and MMP-9 were elevated in the ischemic tissue as compared to the contra-lateral hemisphere after 3 hours occlusion and 21 hours survival (p < 0.0001 for MMP-9). Intraperitoneal minocycline at 45 mg/kg concentration twice a day (first dose immediately after the onset of reperfusion) significantly reduced gelatinolytic activity of ischemia-elevated MMP-2 and MMP-9 (p < 0.0003). Treatment also reduced protein concentration of both enzymes (p < 0.038 for MMP-9 and p < 0.018 for MMP-2). In vitro incubation of minocycline in concentrations as low as 0.1 mug/ml with recombinant MMP-2 and MMP-9 impaired enzymatic activity and MMP-9 was more sensitive at lower minocycline concentrations (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Minocycline inhibits enzymatic activity of gelatin proteases activated by ischemia after experimental stroke and is likely to be selective for MMP-9 at low doses. Minocycline is a potential new therapeutic agent to acute treatment of ischemic stroke.
Figures
Figure 1
The ischemic hemisphere has increased MMP-9 (significant increase) and MMP-2 activity as compared to the contra-lateral non ischemic control hemisphere in non-treated animals. Sample sizes: n = 8 for both PBS and minocycline treated groups (p < 0.0001 for MMP-9 increase). Each band represents one different replicate sample. Molecular weights were determined with the use of pre-stained protein standards.
Figure 2
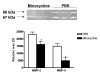
Intra-peritoneal minocycline 45 mg/kg treatment twice a day (first dose immediately after reperfusion), significantly reduced the ischemia-induced increase in MMP-2 and MMP-9 gelatinolytic activities (represented by the active form bands; 67 and 86 kDa respectively). Sample sizes: PBS n = 6; Minocycline n = 8 (p < 0.0003). Each band represents one different replicate sample.
Figure 3
Intra-peritoneal minocycline 45 mg/kg treatment twice a day (first dose immediately after reperfusion), significantly reduced the ischemia-induced increase in MMP-2 and MMP-9 total protein concentrations as compared to PBS treated control animals. Sample sizes: PBS n = 6; Minocycline n = 6 (p < 0.038 for MMP-9 and p < 0.018 for MMP-2). Each band represents one different replicate sample.
Figure 4
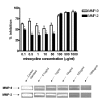
Minocycline concentrations ranging within 0.1 and 1000 μg/ml inhibits the activity of 0.05 ng recombinant human MMP-2 and MMP-9 as compared to the control enzymatic activity. At low concentrations, MMP-9 inhibition is greater than that of MMP-2 (p < 0.05).
Similar articles
- Extension of the thrombolytic time window with minocycline in experimental stroke.
Murata Y, Rosell A, Scannevin RH, Rhodes KJ, Wang X, Lo EH. Murata Y, et al. Stroke. 2008 Dec;39(12):3372-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.514026. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Stroke. 2008. PMID: 18927459 Free PMC article. - Minocycline and hypothermia for reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat: effects on BBB breakdown and MMP expression in the acute and subacute phase.
Nagel S, Su Y, Horstmann S, Heiland S, Gardner H, Koziol J, Martinez-Torres FJ, Wagner S. Nagel S, et al. Brain Res. 2008 Jan 10;1188:198-206. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.10.052. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18031717 - Closure of the blood-brain barrier by matrix metalloproteinase inhibition reduces rtPA-mediated mortality in cerebral ischemia with delayed reperfusion.
Pfefferkorn T, Rosenberg GA. Pfefferkorn T, et al. Stroke. 2003 Aug;34(8):2025-30. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000083051.93319.28. Epub 2003 Jul 10. Stroke. 2003. PMID: 12855824 - Diverse roles of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation and cerebral ischemia.
Candelario-Jalil E, Yang Y, Rosenberg GA. Candelario-Jalil E, et al. Neuroscience. 2009 Feb 6;158(3):983-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.025. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18621108 Free PMC article. Review. - Metalloproteinase and stroke infarct size: role for anti-inflammatory treatment?
Morancho A, Rosell A, García-Bonilla L, Montaner J. Morancho A, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Oct;1207:123-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05734.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20955435 Review.
Cited by
- Effects of minocycline plus tissue plasminogen activator combination therapy after focal embolic stroke in type 1 diabetic rats.
Fan X, Lo EH, Wang X. Fan X, et al. Stroke. 2013 Mar;44(3):745-52. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000309. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23422086 Free PMC article. - The Dual Role of Microglia in Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction after Stroke.
Kang R, Gamdzyk M, Lenahan C, Tang J, Tan S, Zhang JH. Kang R, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(12):1237-1249. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200529150907. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32469699 Free PMC article. Review. - Nonantibiotic Properties of Tetracyclines in Rosacea and Their Clinical Implications.
Del Rosso JQ, Webster G, Weiss JS, Bhatia ND, Gold LS, Kircik L. Del Rosso JQ, et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021 Aug;14(8):14-21. Epub 2021 Aug 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34840653 Free PMC article. Review. - Minocycline development for acute ischemic stroke.
Fagan SC, Cronic LE, Hess DC. Fagan SC, et al. Transl Stroke Res. 2011 Jun 1;2(2):202-8. doi: 10.1007/s12975-011-0072-6. Transl Stroke Res. 2011. PMID: 21909339 Free PMC article. - Extension of the thrombolytic time window with minocycline in experimental stroke.
Murata Y, Rosell A, Scannevin RH, Rhodes KJ, Wang X, Lo EH. Murata Y, et al. Stroke. 2008 Dec;39(12):3372-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.514026. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Stroke. 2008. PMID: 18927459 Free PMC article.
References
- Gasche Y, Fujimura M, Morita-Fujimura Y, Copin JC, Kawase M, Massengale J, Chan PH. Early appearance of activated matrix metalloproteinase-9 after focal cerebral ischemia in mice: a possible role in blood-brain barrier dysfunction. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:1020–1028. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199909000-00010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK074385/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044216/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK074385/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS044216-04/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous