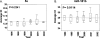Systematic analysis of microRNA expression of RNA extracted from fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples - PubMed (original) (raw)
Systematic analysis of microRNA expression of RNA extracted from fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples
Yaguang Xi et al. RNA. 2007 Oct.
Abstract
microRNAs (miRNAs) are noncoding small RNAs that regulate gene expression at the translational level by mainly interacting with 3' UTRs of their target mRNAs. Archived formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) specimens represent excellent resources for biomarker discovery. Currently there is a lack of systematic analysis on the stability of miRNAs and optimized conditions for expression analysis using FFPE samples. In this study, the expression of miRNAs from FFPE samples was analyzed using high-throughput locked nucleic acid-based miRNA arrays. The effect of formalin fixation on the stability of miRNAs was also investigated using miRNA real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis. The stability of miRNAs of archived colorectal cancer FFPE specimens was characterized with samples dating back up to 10 yr. Our results showed that the expression profiles of miRNAs were in good correlation between 1 mug of fresh frozen and 1-5 mug of FFPE samples (correlation coefficient R (2) = 0.86-0.89). Different formalin fixation times did not change the stability of miRNAs based on real-time qRT-PCR analysis. There are no significant differences of representative miRNA expression among 40 colorectal cancer FFPE specimens. This study provides a foundation for miRNA investigation using FFPE samples in cancer and other types of diseases.
Figures
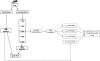
FIGURE 1.
Schematic illustrations of sample processing and miRNA expression analysis from mouse liver tissue.
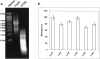
FIGURE 2.
Effect of formalin fixation on miRNA expression. (A) Representative RNA agarose gel image (lane 1, RNA ladder; lane 2, fresh frozen sample; lane 3, FFPE sample). (B) The expression of _hsa_-miR-16 and RUN6B was analyzed using real-time QRT-PCR analysis from formalin-fixed mouse liver samples.
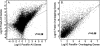
FIGURE 3.
Correlation analysis of the global miRNAs expression between fresh frozen and FFPE samples. (A–C) The comparisons of different input RNA amounts (1, 3, and 5 μg) of FFPE samples versus 1 μg fresh frozen sample.
FIGURE 4.
(A–C) Correlation analysis of the global miRNAs expression between different amounts of total RNA input (1, 3, and 5 μg) from FFPE samples.
FIGURE 5.
Correlation analysis of the messenger RNA expression between fresh frozen and FFPE samples. (A) Global mRNAs expression comparison. (B) Overlapping mRNAs expression comparison.
FIGURE 6.
Quantitative real-time PCR expression analysis of 5S (A) and miR-181b (B) from archived clinical colon cancer specimens. The line represents the trend of median expression levels of miRNAs in FFPE samples from different years. _P_-value was calculated by Wilcoxon's signed-rank sum test.
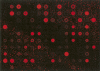
FIGURE 7.
Representative miRNA array image from a 10-yr-old FFPE colon cancer sample.
Similar articles
- miRNA analysis of prostate cancer by quantitative real time PCR: comparison between formalin-fixed paraffin embedded and fresh-frozen tissue.
Leite KR, Canavez JM, Reis ST, Tomiyama AH, Piantino CB, Sañudo A, Camara-Lopes LH, Srougi M. Leite KR, et al. Urol Oncol. 2011 Sep-Oct;29(5):533-7. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2009.05.008. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Urol Oncol. 2011. PMID: 19734068 - MicroRNA Stability in FFPE Tissue Samples: Dependence on GC Content.
Kakimoto Y, Tanaka M, Kamiguchi H, Ochiai E, Osawa M. Kakimoto Y, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Sep 20;11(9):e0163125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163125. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27649415 Free PMC article. - An array-based analysis of microRNA expression comparing matched frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human tissue samples.
Zhang X, Chen J, Radcliffe T, Lebrun DP, Tron VA, Feilotter H. Zhang X, et al. J Mol Diagn. 2008 Nov;10(6):513-9. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2008.080077. Epub 2008 Oct 2. J Mol Diagn. 2008. PMID: 18832457 Free PMC article. - Excavation of a buried treasure--DNA, mRNA, miRNA and protein analysis in formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissues.
Klopfleisch R, Weiss AT, Gruber AD. Klopfleisch R, et al. Histol Histopathol. 2011 Jun;26(6):797-810. doi: 10.14670/HH-26.797. Histol Histopathol. 2011. PMID: 21472693 Review. - Accuracy of Molecular Data Generated with FFPE Biospecimens: Lessons from the Literature.
Greytak SR, Engel KB, Bass BP, Moore HM. Greytak SR, et al. Cancer Res. 2015 Apr 15;75(8):1541-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2378. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25836717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Expression profiling of cancerous and normal breast tissues identifies microRNAs that are differentially expressed in serum from patients with (metastatic) breast cancer and healthy volunteers.
van Schooneveld E, Wouters MC, Van der Auwera I, Peeters DJ, Wildiers H, Van Dam PA, Vergote I, Vermeulen PB, Dirix LY, Van Laere SJ. van Schooneveld E, et al. Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 21;14(1):R34. doi: 10.1186/bcr3127. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22353773 Free PMC article. - Downregulated miR-506 expression facilitates pancreatic cancer progression and chemoresistance via SPHK1/Akt/NF-κB signaling.
Li J, Wu H, Li W, Yin L, Guo S, Xu X, Ouyang Y, Zhao Z, Liu S, Tian Y, Tian Z, Ju J, Ni B, Wang H. Li J, et al. Oncogene. 2016 Oct 20;35(42):5501-5514. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.90. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27065335 Free PMC article. - Cyclin G2, a novel target of sulindac to inhibit cell cycle progression in colorectal cancer.
Zhao H, Yi B, Liang Z, Phillips C, Lin HY, Riker AI, Xi Y. Zhao H, et al. Genes Dis. 2020 Nov 16;8(3):320-330. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.11.006. eCollection 2021 May. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 33997179 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA expression in alpha and beta cells of human pancreatic islets.
Klein D, Misawa R, Bravo-Egana V, Vargas N, Rosero S, Piroso J, Ichii H, Umland O, Zhijie J, Tsinoremas N, Ricordi C, Inverardi L, Domínguez-Bendala J, Pastori RL. Klein D, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055064. Epub 2013 Jan 29. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383059 Free PMC article. - Prediction of desmoid tumor progression using miRNA expression profiling.
Dufresne A, Paturel M, Alberti L, Philippon H, Duc A, Decouvelaere AV, Cassier P, Blay JY. Dufresne A, et al. Cancer Sci. 2015 May;106(5):650-5. doi: 10.1111/cas.12640. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25707497 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous