The monofunctional glycosyltransferase of Escherichia coli localizes to the cell division site and interacts with penicillin-binding protein 3, FtsW, and FtsN - PubMed (original) (raw)
The monofunctional glycosyltransferase of Escherichia coli localizes to the cell division site and interacts with penicillin-binding protein 3, FtsW, and FtsN
Adeline Derouaux et al. J Bacteriol. 2008 Mar.
Abstract
The monofunctional peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase (MtgA) catalyzes glycan chain elongation of the bacterial cell wall. Here we show that MtgA localizes at the division site of Escherichia coli cells that are deficient in PBP1b and produce a thermosensitive PBP1a and is able to interact with three constituents of the divisome, PBP3, FtsW, and FtsN, suggesting that MtgA may play a role in peptidoglycan assembly during the cell cycle in collaboration with other proteins.
Figures
FIG. 1.
Localization of GFP-MtgA in wild-type ponA+ ponB+ strain LMC500 (A) and ponA(ts) ponB strain EJ801 (B) grown in LB medium at 28°C, both harboring pDML2005. The arrows point to cells with fluorescent signals at the division site. Photographs were taken with a cooled AxioCam MRm (Zeiss) mounted on an Zeiss Axio Imager.Z1 fluorescent microscope through a EC Plan-Neofluar 100 × 1.3 oil immersion objective in bright field and fluorescence using filter set 37 (400- to 500-nm band pass excitation and 460- to 560-nm band pass emission; Zeiss). Images were analyzed using the AxioVision Rel. 4.5 (Zeiss) software as previously described (24). Bar, 5 μm.
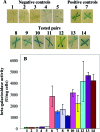
FIG. 2.
Interaction between MtgA and PBP3, FtsW, FtsN, or itself by the Cya bacterial two-hybrid assay. DHM1 transformants producing T18-T25 (1), T18-MtgA-T25 (2), T18-T25-MtgA (3), T18-MtgA-T25-Lpp-PBP3 (4), T18-Lpp-PBP3-T25-MtgA (5), T18-PBP1B-T25-PBP3 (6), T18-PBP3-T25-PBP1B (7), T18-MtgA-T25-PBP3 (8), T18-PBP3-T25-MtgA (9), T18-MtgA-T25-FtsN (10), T18-FstN-T25-MtgA (11), T18-MtgA-T25-FstW (12), T18-FtsW-T25-MtgA (13), and T18-MtgA-T25-MtgA (14) were used. (A) Transformants were grown at 30°C for 30 h on LB agar plates containing 0.5 mM IPTG, 40 μg/ml X-Gal, 50 μg/ml ampicillin, and 20 μg/ml chloramphenicol. (B) Quantitative analysis of the β-galactosidase activity from transformants grown in LB medium in the presence of 0.4 mM IPTG for 16 h at 30°C was carried out as described previously (17). Data are averages of three independent experiments.
Similar articles
- Regulation of the Peptidoglycan Polymerase Activity of PBP1b by Antagonist Actions of the Core Divisome Proteins FtsBLQ and FtsN.
Boes A, Olatunji S, Breukink E, Terrak M. Boes A, et al. mBio. 2019 Jan 8;10(1):e01912-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01912-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30622193 Free PMC article. - The bacterial cell division protein fragment EFtsN binds to and activates the major peptidoglycan synthase PBP1b.
Boes A, Kerff F, Herman R, Touze T, Breukink E, Terrak M. Boes A, et al. J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 25;295(52):18256-18265. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015951. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33109614 Free PMC article. - Direct interactions of early and late assembling division proteins in Escherichia coli cells resolved by FRET.
Alexeeva S, Gadella TW Jr, Verheul J, Verhoeven GS, den Blaauwen T. Alexeeva S, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jul;77(2):384-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07211.x. Epub 2010 May 19. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20497333 - Super-resolution images of peptidoglycan remodelling enzymes at the division site of Escherichia coli.
Söderström B, Chan H, Daley DO. Söderström B, et al. Curr Genet. 2019 Feb;65(1):99-101. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0869-x. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30056491 Free PMC article. Review. - Activities and regulation of peptidoglycan synthases.
Egan AJ, Biboy J, van't Veer I, Breukink E, Vollmer W. Egan AJ, et al. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Oct 5;370(1679):20150031. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0031. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26370943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A Dynamic Network of Proteins Facilitate Cell Envelope Biogenesis in Gram-Negative Bacteria.
Graham CLB, Newman H, Gillett FN, Smart K, Briggs N, Banzhaf M, Roper DI. Graham CLB, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 27;22(23):12831. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312831. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884635 Free PMC article. Review. - Exploring the Meta-regulon of the CRP/FNR Family of Global Transcriptional Regulators in a Partial-Nitritation Anammox Microbiome.
Beach NK, Myers KS, Owen BR, Seib M, Donohue TJ, Noguera DR. Beach NK, et al. mSystems. 2021 Oct 26;6(5):e0090621. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00906-21. Epub 2021 Oct 12. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34636676 Free PMC article. - Unipolar Peptidoglycan Synthesis in the Rhizobiales Requires an Essential Class A Penicillin-Binding Protein.
Williams MA, Aliashkevich A, Krol E, Kuru E, Bouchier JM, Rittichier J, Brun YV, VanNieuwenhze MS, Becker A, Cava F, Brown PJB. Williams MA, et al. mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0234621. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02346-21. Epub 2021 Sep 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34544272 Free PMC article. - Real-time monitoring of peptidoglycan synthesis by membrane-reconstituted penicillin-binding proteins.
Hernández-Rocamora VM, Baranova N, Peters K, Breukink E, Loose M, Vollmer W. Hernández-Rocamora VM, et al. Elife. 2021 Feb 24;10:e61525. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61525. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33625355 Free PMC article. - Peptidoglycan: Structure, Synthesis, and Regulation.
Garde S, Chodisetti PK, Reddy M. Garde S, et al. EcoSal Plus. 2021 Jan;9(2):eESP-0010-2020. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0010-2020. EcoSal Plus. 2021. PMID: 33470191 Free PMC article.
References
- Aarsman, M. E., A. Piette, C. Fraipont, T. M. Vinkenvleugel, M. Nguyen-Distèche, and T. den Blaauwen. 2005. Maturation of the Escherichia coli divisome occurs in two steps. Mol. Microbiol. 551631-1645. - PubMed
- Bertsche, U., E. Breukink, T. Kast, and W. Vollmer. 2005. In vitro murein peptidoglycan synthesis by dimers of the bifunctional transglycosylase-transpeptidase PBP1B from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 28038096-38101. - PubMed
- Bertsche, U., T. Kast, B. Wolf, C. Fraipont, M. E. Aarsman, K. Kannenberg, M. von Rechenberg, M. Nguyen-Disteche, T. den Blaauwen, J. V. Holtje, and W. Vollmer. 2006. Interaction between two murein (peptidoglycan) synthases, PBP3 and PBP1B, in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 61675-690. - PubMed
- Born, P., E. Breukink, and W. Vollmer. 2006. In vitro synthesis of cross-linked murein and its attachment to sacculi by PBP1A from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 28126985-26993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases