Study of active controlled tocilizumab monotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate (SATORI): significant reduction in disease activity and serum vascular endothelial growth factor by IL-6 receptor inhibition therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Study of active controlled tocilizumab monotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate (SATORI): significant reduction in disease activity and serum vascular endothelial growth factor by IL-6 receptor inhibition therapy
Norihiro Nishimoto et al. Mod Rheumatol. 2009.
Abstract
We investigated the clinical efficacy and safety of tocilizumab (a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor antibody) monotherapy in active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with an inadequate response to low dose methotrexate (MTX). In a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial, 125 patients were allocated to receive either tocilizumab 8 mg/kg every 4 weeks plus MTX placebo (tocilizumab group) or tocilizumab placebo plus MTX 8 mg/week (control group) for 24 weeks. The clinical responses were measured using the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria and the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels were also monitored. At week 24, 25.0% in the control group and 80.3% in the tocilizumab group achieved ACR20 response. The tocilizumab group showed superior ACR response criteria over control at all time points. Additionally, serum VEGF levels were significantly decreased by tocilizumab treatment. The overall incidences of adverse events (AEs) were 72 and 92% (serious AEs: 4.7 and 6.6%; serious infections: 1.6 and 3.3%) in the control and the tocilizumab groups, respectively. All serious adverse events improved by adequate treatment. Tocilizumab monotherapy was well tolerated and provided an excellent clinical benefit in active RA patients with an inadequate response to low dose MTX.
Figures
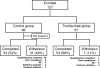
Fig. 1
Randomization, reasons for withdrawal, and numbers of patients who completed the trial. Tocilizumab humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody
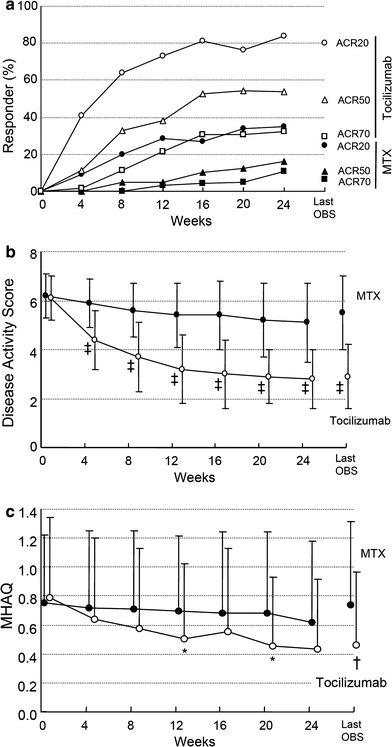
Fig. 2
Percentage of responders according to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) improvement criteria and the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) as well as mean change in Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ) scores. Percentage of responders according to the ACR improvement criteria (a) and the DAS28 (b) according to the ITT analysis over 24 weeks. Mean change in MHAQ scores from baseline to week 24 (c). Last OBS = last observation. *P < 0.05; †P < 0.01; ‡P < 0.001 versus MTX by paired _t_-test
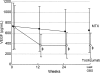
Fig. 3
Change from baseline in serum levels of VEGF. Values are the mean for each group at each time point. VEGF was measured at three points (0, 12 and 24 weeks) over the study period. Last OBS = last observation. ‡P < 0.001 versus MTX by paired _t_-test
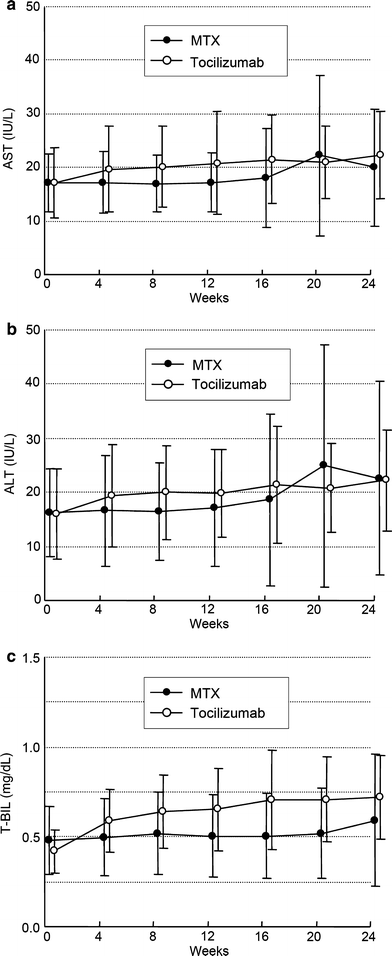
Fig. 4
Change from baseline in serum levels of aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), total bilirubin (T-BIL). Values are the mean for each group at each time point
Similar articles
- Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate.
Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, Pavelka K, Bröll J, Balint G, Emery P, Raemen F, Petersen J, Smolen J, Thomson D, Kishimoto T; CHARISMA Study Group. Maini RN, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Sep;54(9):2817-29. doi: 10.1002/art.22033. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16947782 Clinical Trial. - [The efficacy and safety of tocilizumab combined with disease-modifying anti-rheumatoid drugs in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis: a multi-center, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial].
Shi Q, Zhao Y, Bao CD, Li XF, Huang F, Zhu P, Li ZG, Gu JR, Zhang ZY, Zhao DB, Zhao SL, Jiang QD, Tian J, Zhang FC. Shi Q, et al. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;52(4):323-9. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23925361 Clinical Trial. Chinese. - Comparative Efficacy of Novel DMARDs as Monotherapy and in Combination with Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Inadequate Response to Conventional DMARDs: A Network Meta-Analysis.
Buckley F, Finckh A, Huizinga TW, Dejonckheere F, Jansen JP. Buckley F, et al. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2015 May;21(5):409-23. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2015.21.5.409. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25943002 Free PMC article. - Adalimumab: a review of its use in rheumatoid arthritis.
Bang LM, Keating GM. Bang LM, et al. BioDrugs. 2004;18(2):121-39. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200418020-00005. BioDrugs. 2004. PMID: 15046527 Review.
Cited by
- Tocilizumab, a humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Mihara M, Ohsugi Y, Kishimoto T. Mihara M, et al. Open Access Rheumatol. 2011 Feb 25;3:19-29. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S17118. eCollection 2011. Open Access Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 27790001 Free PMC article. Review. - Management of rheumatoid arthritis in People's Republic of China - focus on tocilizumab and patient considerations.
Wang G, Mu R, Xu H. Wang G, et al. Int J Gen Med. 2015 May 12;8:187-94. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S81633. eCollection 2015. Int J Gen Med. 2015. PMID: 25999757 Free PMC article. Review. - Monoclonal antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: comparative effectiveness of tocilizumab with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Tanaka T, Hishitani Y, Ogata A. Tanaka T, et al. Biologics. 2014 Apr 7;8:141-53. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S37509. eCollection 2014. Biologics. 2014. PMID: 24741293 Free PMC article. Review. - Efficacy and safety of CT-P47 versus reference tocilizumab: 32-week results of a randomised, active-controlled, double-blind, phase III study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, including 8 weeks of switching data from reference tocilizumab to CT-P47.
Smolen JS, Trefler J, Racewicz A, Jaworski J, Zielińska A, Krogulec M, Jeka S, Wojciechowski R, Kolossa K, Dudek A, Krajewska-Włodarczyk M, Hrycaj P, Klimiuk PA, Burmester GR, Kim S, Bae Y, Yang G, Jung Y, Hong J, Keystone E. Smolen JS, et al. RMD Open. 2024 Oct 18;10(4):e004514. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004514. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 39424404 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2271017', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2271017/'}\]}
- Harris ED Jr. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1277–89. - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/art.1780311003', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780311003'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3263133', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3263133/'}\]}
- Cush JJ, Lipsky PE. Phenotypic analysis of synovial tissue and peripheral blood lymphocytes isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:1230–8. - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.917', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.917'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8883427', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8883427/'}\]}
- Paleolog EM. Angiogenesis: a critical process in the pathogenesis of RA—a role for VEGF? Br J Rheumatol. 1996;35:917–9. - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8428365', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8428365/'}\]}
- Sato K, Tsuchiya M, Saldanha J, Koishihara Y, Ohsugi Y, Kishimoto T, et al. Reshaping a human antibody to inhibit the interleukin 6-dependent tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 1993;53:851–6. - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/art.10623', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10623'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12483717', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12483717/'}\]}
- Choy EHS, Isenberg DA, Garrood T, Farrow S, Ioannou Y, Bird H, et al. Therapeutic benefit of blocking interleukin–6 activity with an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:3143–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical