GOrilla: a tool for discovery and visualization of enriched GO terms in ranked gene lists - PubMed (original) (raw)
GOrilla: a tool for discovery and visualization of enriched GO terms in ranked gene lists
Eran Eden et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009.
Abstract
Background: Since the inception of the GO annotation project, a variety of tools have been developed that support exploring and searching the GO database. In particular, a variety of tools that perform GO enrichment analysis are currently available. Most of these tools require as input a target set of genes and a background set and seek enrichment in the target set compared to the background set. A few tools also exist that support analyzing ranked lists. The latter typically rely on simulations or on union-bound correction for assigning statistical significance to the results.
Results: GOrilla is a web-based application that identifies enriched GO terms in ranked lists of genes, without requiring the user to provide explicit target and background sets. This is particularly useful in many typical cases where genomic data may be naturally represented as a ranked list of genes (e.g. by level of expression or of differential expression). GOrilla employs a flexible threshold statistical approach to discover GO terms that are significantly enriched at the top of a ranked gene list. Building on a complete theoretical characterization of the underlying distribution, called mHG, GOrilla computes an exact p-value for the observed enrichment, taking threshold multiple testing into account without the need for simulations. This enables rigorous statistical analysis of thousand of genes and thousands of GO terms in order of seconds. The output of the enrichment analysis is visualized as a hierarchical structure, providing a clear view of the relations between enriched GO terms.
Conclusion: GOrilla is an efficient GO analysis tool with unique features that make a useful addition to the existing repertoire of GO enrichment tools. GOrilla's unique features and advantages over other threshold free enrichment tools include rigorous statistics, fast running time and an effective graphical representation. GOrilla is publicly available at: http://cbl-gorilla.cs.technion.ac.il
Figures
Figure 1
How to use the GOrilla web user interface. To use the GOrilla web interface, the user is required to perform the following four simple steps: (i) choose an organism; (ii) choose a running mode (either flexible threshold or fixed threshold mode) (iii) copy and paste a list (or upload a file) of genes in the case of a flexible threshold or two lists of genes – a target and a background – in the case of a fixed cutoff; (iv) choose an ontology.
Figure 2
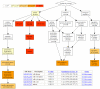
An example of the GOrilla analysis output. 14,565 genes from the van't Veer dataset were ranked according to their differential expression and given as input to GOrilla. The resulting enriched GO terms are visualized using a DAG graphical representation with color coding reflecting their degree of enrichment. Nodes in the graph are clickable and give additional information on the GO terms and genes attributing to the enrichment. N is the total number of genes; B is the total number of genes associated with a specific GO term; n is the flexible cutoff, i.e. the automatically determined number of genes in the 'target set' and b is the number of genes in the 'target set' that are associated with a specific GO term. Enrichment is defined as (b/n)/(B/N).
Similar articles
- GeneTools--application for functional annotation and statistical hypothesis testing.
Beisvag V, Jünge FK, Bergum H, Jølsum L, Lydersen S, Günther CC, Ramampiaro H, Langaas M, Sandvik AK, Laegreid A. Beisvag V, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Oct 24;7:470. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-470. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17062145 Free PMC article. - MILANO--custom annotation of microarray results using automatic literature searches.
Rubinstein R, Simon I. Rubinstein R, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Jan 20;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-12. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15661078 Free PMC article. - Gene Ontology analysis in multiple gene clusters under multiple hypothesis testing framework.
Zhong S, Xie D. Zhong S, et al. Artif Intell Med. 2007 Oct;41(2):105-15. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2007.08.002. Artif Intell Med. 2007. PMID: 17913480 - Cross-organism analysis using InterMine.
Lyne R, Sullivan J, Butano D, Contrino S, Heimbach J, Hu F, Kalderimis A, Lyne M, Smith RN, Štěpán R, Balakrishnan R, Binkley G, Harris T, Karra K, Moxon SA, Motenko H, Neuhauser S, Ruzicka L, Cherry M, Richardson J, Stein L, Westerfield M, Worthey E, Micklem G. Lyne R, et al. Genesis. 2015 Aug;53(8):547-60. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22869. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Genesis. 2015. PMID: 26097192 Free PMC article. Review. - A survey of metabolic databases emphasizing the MetaCyc family.
Karp PD, Caspi R. Karp PD, et al. Arch Toxicol. 2011 Sep;85(9):1015-33. doi: 10.1007/s00204-011-0705-2. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Arch Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21523460 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Comparative motif discovery combined with comparative transcriptomics yields accurate targetome and enhancer predictions.
Naval-Sánchez M, Potier D, Haagen L, Sánchez M, Munck S, Van de Sande B, Casares F, Christiaens V, Aerts S. Naval-Sánchez M, et al. Genome Res. 2013 Jan;23(1):74-88. doi: 10.1101/gr.140426.112. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23070853 Free PMC article. - Effects of non-vascularized adipose tissue transplantation on its genetic profile.
Schreiter JS, Kurow LO, Langer S, Steinert M, Massier L. Schreiter JS, et al. Adipocyte. 2021 Dec;10(1):131-141. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2021.1889815. Adipocyte. 2021. PMID: 33648423 Free PMC article. - Marine cyanobacterium Spirulina maxima as an alternate to the animal cell culture medium supplement.
Jeong Y, Choi WY, Park A, Lee YJ, Lee Y, Park GH, Lee SJ, Lee WK, Ryu YK, Kang DH. Jeong Y, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 1;11(1):4906. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84558-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649424 Free PMC article. - An integrated regulatory network reveals pervasive cross-regulation among transcription and splicing factors.
Kosti I, Radivojac P, Mandel-Gutfreund Y. Kosti I, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(7):e1002603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002603. Epub 2012 Jul 26. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22844237 Free PMC article. - Exposure to maternal high-fat diet induces extensive changes in the brain of adult offspring.
Fernandes DJ, Spring S, Roy AR, Qiu LR, Yee Y, Nieman BJ, Lerch JP, Palmert MR. Fernandes DJ, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Mar 2;11(1):149. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01274-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33654064 Free PMC article.
References
- Ashburner M, Ball C, Blake J, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry J, Davis A, Dolinski K, Dwight S, Eppig J, Harris M, Hill D, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese J, Richardson J, Ringwald M, Rubin G, Sherlock G. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–9. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Zeeberg B, Feng W, Wang G, Wang M, Fojo A, Sunshine M, Narasimhan S, Kane D, Reinhold W, Lababidi S, Bussey K, Riss J, Barrett J, Weinstein J. GoMiner: A Resource for Biological Interpretation of Genomic and Proteomic Data. Genome Biology. 2003;4:R28. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-4-r28. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous