Wnt signal transduction pathways - PubMed (original) (raw)
Wnt signal transduction pathways
Yuko Komiya et al. Organogenesis. 2008 Apr.
Abstract
The Wnt signaling pathway is an ancient and evolutionarily conserved pathway that regulates crucial aspects of cell fate determination, cell migration, cell polarity, neural patterning and organogenesis during embryonic development. The Wnts are secreted glycoproteins and comprise a large family of nineteen proteins in humans hinting to a daunting complexity of signaling regulation, function and biological output. To date major signaling branches downstream of the Fz receptor have been identified including a canonical or Wnt/beta-catenin dependent pathway and the non-canonical or beta-catenin-independent pathway which can be further divided into the Planar Cell Polarity and the Wnt/Ca(2+) pathways, and these branches are being actively dissected at the molecular and biochemical levels. In this review, we will summarize the most recent advances in our understanding of these Wnt signaling pathways and the role of these pathways in regulating key events during embryonic patterning and morphogenesis.
Keywords: Planar Cell Polarity; Wnt; canonical; dishevelled; frizzled; non-canonical; β-catenin.
Figures
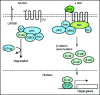
Figure 1
A schematic representation of the canonical Wnt signal transduction cascade. Left, in the absence of Wnt ligand, a complex of Axin, APC, GSK3-β, CK1 and β-catenin is located in the cytosol. β-catenin is dually phosphorylated by CK1 and GSK3-β and targeted degraded by the proteosomal machinery mediated by β-TrCP. Right, with Wnt stimulation, signaling through the Fz receptor and LRP5/6 co-receptor complex induces the dual phosphorylation of LRP6 by CK1 and GSK3-β and this allows for the translocation of a protein complex containing Axin from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. Dsh is also recruited to the membrane and binds to Fz and Axin binds to phosphorylated LRP5/6. This complex formed at the membrane at Fz/LRP5/6 induces the stabilization of β-cat via either sequestration and/or degradation of Axin. β-catenin translocates into the nucleus where it complexes with Lef/Tcf family members to mediate transcriptional induction of target genes.
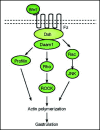
Figure 2
A schematic representation of the Planar Cell Polarity transduction cascade. Wnt signaling is transduced through Fz independent of LRP5/6 leading to the activation of Dsh. Dsh through Daam1 mediates activation of Rho which in turn activates Rho kinase (ROCK). Daam1 also mediates actin polymerization through the actin binding protein Profilin. Dsh also mediates activation of Rac, which in turn activates JNK. The signaling from Rock, JNK and Profilin are integrated for cytoskeletal changes for cell polarization and motility during gastrulation.
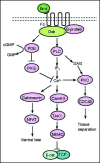
Figure 3
A schematic representation of the Wnt/Ca2+ signal transduction cascade. Wnt signaling via Fz mediates activation of Dsh via activation of G-proteins. Dishevelled activates the phosphodiesterase PDE which inhibits PKG and in turn inhibits Ca2+ release. Dsh through PLC activates IP3, which leads to release of intracellular Ca2+, which in turn activates CamK11 and calcineurin. Calcineurin activate NF-AT to regulate ventral cell fates. CamK11 activates TAK and NLK, which inhibit β-catenin/TCF function to negatively regulate dorsal axis formation. DAG through PKC activates CDC42 to mediate tissue separation and cell movements during gastrulation.
Similar articles
- The complex relationship of Wnt-signaling pathways and cilia.
Vuong LT, Mlodzik M. Vuong LT, et al. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023;155:95-125. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38043953 Free PMC article. - Wnt signaling pathway: A comprehensive review.
Hayat R, Manzoor M, Hussain A. Hayat R, et al. Cell Biol Int. 2022 Jun;46(6):863-877. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11797. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Cell Biol Int. 2022. PMID: 35297539 Review. - New steps in the Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway.
Sakanaka C, Sun TQ, Williams LT. Sakanaka C, et al. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000;55:225-36. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000. PMID: 11036939 Review. - CKIepsilon/discs overgrown promotes both Wnt-Fz/beta-catenin and Fz/PCP signaling in Drosophila.
Klein TJ, Jenny A, Djiane A, Mlodzik M. Klein TJ, et al. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 11;16(13):1337-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.06.030. Curr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16824922 - β-Arrestin interacts with the beta/gamma subunits of trimeric G-proteins and dishevelled in the Wnt/Ca(2+) pathway in xenopus gastrulation.
Seitz K, Dürsch V, Harnoš J, Bryja V, Gentzel M, Schambony A. Seitz K, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 29;9(1):e87132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087132. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24489854 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Neural crest specification by noncanonical Wnt signaling and PAR-1.
Ossipova O, Sokol SY. Ossipova O, et al. Development. 2011 Dec;138(24):5441-50. doi: 10.1242/dev.067280. Development. 2011. PMID: 22110058 Free PMC article. - Non-canonical WNT5a regulates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in the mouse ovarian surface epithelium.
Abedini A, Sayed C, Carter LE, Boerboom D, Vanderhyden BC. Abedini A, et al. Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 16;10(1):9695. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66559-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32546756 Free PMC article. - The Role of the Microenvironment in Controlling the Fate of Bioprinted Stem Cells.
West-Livingston LN, Park J, Lee SJ, Atala A, Yoo JJ. West-Livingston LN, et al. Chem Rev. 2020 Oct 14;120(19):11056-11092. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00126. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Chem Rev. 2020. PMID: 32558555 Free PMC article. Review. - Signaling in colon cancer stem cells.
Roy S, Majumdar AP. Roy S, et al. J Mol Signal. 2012 Aug 6;7(1):11. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-7-11. J Mol Signal. 2012. PMID: 22866952 Free PMC article. - Emerging Roles of Wnt Ligands in Human Colorectal Cancer.
Nie X, Liu H, Liu L, Wang YD, Chen WD. Nie X, et al. Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 14;10:1341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01341. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32923386 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Wodarz A, Nusse R. Mechanisms of Wnt signaling in development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1998;14:59–88. - PubMed
- Yamaguchi TP. Heads or tails: Wnts and anterior-posterior patterning. Curr Biol. 2001;11:713–724. - PubMed
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt Signaling Pathway in Development and Disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004 - PubMed
- He X, Semenov M, Tamai K, Zeng X. LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: arrows point the way. Development. 2004;131:1663–1677. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources