Intensity of resistance exercise determines adipokine and resting energy expenditure responses in overweight elderly individuals - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2009 Dec;32(12):2161-7.
doi: 10.2337/dc08-1994. Epub 2009 Sep 3.
Affiliations
- PMID: 19729520
- PMCID: PMC2782969
- DOI: 10.2337/dc08-1994
Randomized Controlled Trial
Intensity of resistance exercise determines adipokine and resting energy expenditure responses in overweight elderly individuals
Ioannis G Fatouros et al. Diabetes Care. 2009 Dec.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the time course of leptin, adiponectin, and resting energy expenditure (REE) responses in overweight elderly males after acute resistance exercise protocols of various intensity configurations.
Research design and methods: Forty inactive men (65-82 years) were randomly assigned to one of four groups (n = 10/group): control, low-intensity resistance exercise, moderate-intensity resistance exercise, and high-intensity resistance exercise. Exercise energy cost, REE, leptin, adiponectin, cortisol, insulin, lactate, glucose, nonesterified fatty acids (NEFAs), and glycerol were determined at baseline, immediately after exercise, and during a 72-h recovery period.
Results: Exercise energy cost was lower in high-intensity than in low-intensity and moderate-intensity groups (221.6 +/- 8.8 vs. 295.6 +/- 10.7 and 281.6 +/- 9.8 kcal, P < 0.001). Lactate, glucose, NEFAs, and glycerol concentrations increased (P < 0.001) after exercise and returned to baseline thereafter in all groups. REE increased (P < 0.001) in all groups at 12 h in an intensity-dependent manner (P < 0.05). REE reached baseline after 48 h in the low- and moderate-intensity groups and after 72 h in the high-intensity group. Cortisol peaked in all active groups after exercise (P < 0.001) and remained elevated (P < 0.001) for 12 h. After adjustment for plasma volume shifts, leptin remained unaltered. Adiponectin concentration increased after 12 h and remained elevated for 24 h only in the high-intensity group (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Resistance exercise does not alter circulating leptin concentration but does increase REE and adiponectin in an intensity-dependent manner for as long as 48 and 24 h, respectively, in overweight elderly individuals. It appears that resistance exercise may represent an effective approach for weight management and metabolic control in overweight elderly individuals.
Figures
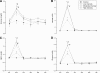
Figure 1
The effect of acute resistance exercise on concentrations of glucose (A), lactate (B), NEFA (C), and glycerol (D). Error bars represent SE. *Significantly different from the respective baseline (P < 0.05); #significant difference between the high-intensity group and the other groups (P < 0.05).
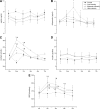
Figure 2
The effect of acute resistance exercise on concentrations of leptin (A), adiponectin (B), and cortisol (C), insulin (D), and REE (E). Error bars represent SE. *Significantly different from the respective baseline (P < 0.05); #significant difference between the high-intensity group and the other groups (P < 0.05).
Similar articles
- Leptin and adiponectin responses in overweight inactive elderly following resistance training and detraining are intensity related.
Fatouros IG, Tournis S, Leontsini D, Jamurtas AZ, Sxina M, Thomakos P, Manousaki M, Douroudos I, Taxildaris K, Mitrakou A. Fatouros IG, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Nov;90(11):5970-7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-0261. Epub 2005 Aug 9. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 16091494 Clinical Trial. - Exercise improves adiposopathy, insulin sensitivity and metabolic syndrome severity independent of intensity.
Heiston EM, Eichner NZ, Gilbertson NM, Malin SK. Heiston EM, et al. Exp Physiol. 2020 Apr;105(4):632-640. doi: 10.1113/EP088158. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Exp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32020676 - The Impact of Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract on Fat Oxidation, Body Composition and Cardio-Metabolic Health in Overweight, Recreationally Active Individuals.
Roberts JD, Willmott AGB, Beasley L, Boal M, Davies R, Martin L, Chichger H, Gautam L, Del Coso J. Roberts JD, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Feb 26;13(3):764. doi: 10.3390/nu13030764. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33652910 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The impact of exercise and dietary interventions on circulating leptin and adiponectin in individuals who are overweight and those with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Khalafi M, Hossein Sakhaei M, Kheradmand S, Symonds ME, Rosenkranz SK. Khalafi M, et al. Adv Nutr. 2023 Jan;14(1):128-146. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2022.10.001. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Adv Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36811585 Free PMC article. Review. - Exercise and Weight Management: The Role of Leptin-A Systematic Review and Update of Clinical Data from 2000-2022.
de Assis GG, Murawska-Ciałowicz E. de Assis GG, et al. J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 5;12(13):4490. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134490. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A single session of strength training changed plasma levels of resistin, but not leptin in overweight and obese men.
Fortes YM, Souza-Gomes AF, Moreira ARS, Campos LN, de Moura SS, Barroso LSS, de Faria MHS, de Barros Fernandes H, de Miranda AS, Martins-Costa HC, Simões E Silva AC, Moreira JM, Nunes-Silva A. Fortes YM, et al. Sports Med Health Sci. 2023 Dec 11;6(4):324-330. doi: 10.1016/j.smhs.2023.12.001. eCollection 2024 Dec. Sports Med Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 39309458 Free PMC article. - Concentrations of Selected Adipocytokines in the Blood Plasma in Proximal Suspensory Desmopathy of Horses, with a Focus on Their Physical Activity-A Pilot Study.
Nowicka B, Torres A, Polkowska I, Jackow-Nowicka J, Przewozny M, Jackow-Malinowska J. Nowicka B, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 22;25(1):205. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010205. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203376 Free PMC article. - Long-term exercise training and inflammatory biomarkers in healthy subjects: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Wang YH, Tan J, Zhou HH, Cao M, Zou Y. Wang YH, et al. Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 30;14:1253329. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1253329. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37720640 Free PMC article. Review. - Factors related to hypermetabolism in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Mansour A, Motamed S, Hekmatdoost A, Karimi S, Mohajeri-Tehrani MR, Abdollahi M, Jelodar R, Sajjadi-Jazi SM. Mansour A, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 4;13(1):3669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30945-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36871124 Free PMC article. - The Combinatory Effect of Spirulina Supplementation and Resistance Exercise on Plasma Contents of Adipolin, Apelin, Ghrelin, and Glucose in Overweight and Obese Men.
Mohammad M, Karim D, Mehdi M, Marziyeh S, Hadi S, Shila N. Mohammad M, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Jun 13;2022:9539286. doi: 10.1155/2022/9539286. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 35733519 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- American College of Sports Medicine. Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005
- Sigal RJ, Kenny GP, Wasserman DH, Castaneda-Sceppa C, White RD: Physical activity/exercise and type 2 diabetes: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 1433– 1438 - PubMed
- Simpson KA, Fiatarone-Singh MA: Effects of exercise on adiponectin: a systematic review. Obesity 2008; 16: 241– 256 - PubMed
- Tsuchida A, Yamauchi T, Ito Y: Insulin/Foxo1 pathway regulates expression levels of adiponectin receptors and adiponectin sensitivity. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 30817– 30822 - PubMed
- Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE: The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med 2001; 7: 947– 953 - PubMed