Effect of injectable and oral contraceptives on serum lipids - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effect of injectable and oral contraceptives on serum lipids
Abbey B Berenson et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2009 Oct.
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the effects of using depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) or oral contraceptives (OCs) containing 20 micrograms ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg desogestrel on serum lipid levels.
Methods: Serum lipids were measured at baseline and every 6 months thereafter for 3 years in 703 white, African-American, and Hispanic women using DMPA, OC, or nonhormonal birth control. Those who discontinued DMPA were followed for up to 2 additional years. Participants completed questionnaires containing demographic and behavioral measures every 6 months and underwent 24-hour dietary recalls annually. Mixed-model regression analyses and general-estimating-equations procedures were used to estimate changes over time in lipids by method along with their predictors.
Results: Users of OCs experienced significantly greater increases in levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol, very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol than did nonhormonal-contraceptive users (P<.001). However, no difference was noted in the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol:HDL ratio between OC users and nonhormonal-contraceptive users. Among DMPA users, HDL levels initially decreased for 6 months but then returned to baseline. The LDL:HDL ratio rose in the first 6 months of DMPA use but then dropped back to baseline over the next 24 months. After DMPA was discontinued, triglyceride, VLDL, and HDL levels were significantly higher in women who used OCs than in those who chose nonhormonal (P<.05) methods.
Conclusion: Use of very-low-dose OCs containing desogestrel can elevate lipid levels. Users of DMPA were at increased risk of developing an abnormally low HDL level as well as an abnormally high LDL level and an increase in the LDL:HDL cholesterol ratio, although these effects appeared to be temporary.
Level of evidence: II.
Figures
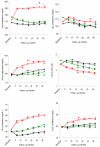
Figure 1
Mean change across 36 months of follow-up by contraceptive method for (A) total cholesterol, (B) serum triglyceride, (C) HDL cholesterol, (D) LDL cholesterol, (E) LDL-to-HDL ratio, and (F) VLDL Cholesterol. Solid lines represent the estimated mean (modeled) and dotted lines represent the unadjusted values. Green squares: nonhormonal contraception; black diamonds: depot medroxyprogesterone acetate; red circles: oral contraceptives.
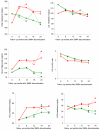
Figure 2
Mean change of lipid profile after depot medroxyprogesterone acetate discontinuation across 24 months for (A) total cholesterol, (B) serum triglyceride, (C) HDL cholesterol, (D) LDL cholesterol, (E) LDL-to-HDL ratio, and (F) VLDL Cholesterol. Solid lines represent the estimated mean (modeled) and dotted lines represent the unadjusted values. Green squares: depot medroxyprogesterone acetate to nonhormonal contraception; red circle: depot medroxyprogesterone acetate to oral contraceptives.
Similar articles
- Oral contraceptive tablets containing 20 and 30 micrograms of ethinyl estradiol with 150 micrograms desogestrel. Their influence on lipids, lipoproteins, sex hormone binding globulin and testosterone.
Akerlund M, Almström E, Högstedt S, Nabrink M. Akerlund M, et al. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1994 Feb;73(2):136-43. doi: 10.3109/00016349409013416. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1994. PMID: 8116352 Clinical Trial. - Associations of oral contraceptive use with serum lipids and lipoproteins in young women: the Bogalusa Heart Study.
Greenlund KJ, Webber LS, Srinivasan S, Wattigney W, Johnson C, Berenson GS. Greenlund KJ, et al. Ann Epidemiol. 1997 Nov;7(8):561-7. doi: 10.1016/s1047-2797(97)00119-1. Ann Epidemiol. 1997. PMID: 9408552 - Metabolic profile of six oral contraceptives containing norgestimate, gestodene, and desogestrel.
Teichmann A. Teichmann A. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud. 1995;40 Suppl 2:98-104. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud. 1995. PMID: 8574257 Clinical Trial. - Lipid metabolism effects with desogestrel-containing oral contraceptives.
Burkman RT. Burkman RT. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Mar;168(3 Pt 2):1033-40. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90334-f. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993. PMID: 8447357 Review. - Oral contraceptives and lipids.
Fotherby K. Fotherby K. BMJ. 1989 Apr 22;298(6680):1049-50. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6680.1049. BMJ. 1989. PMID: 2497884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Effect of hormonal contraceptives on vitamin B12 level and the association of the latter with bone mineral density.
Berenson AB, Rahman M. Berenson AB, et al. Contraception. 2012 Nov;86(5):481-7. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2012.02.015. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Contraception. 2012. PMID: 22464408 Free PMC article. - Use of the Levonorgestrel Intrauterine Device in Women With Type 2 Diabetes.
Lang B, Josephy T, Micks E, McCoy E, Prager S. Lang B, et al. Clin Diabetes. 2018 Jul;36(3):251-256. doi: 10.2337/cd17-0028. Clin Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 30078945 Free PMC article. - Effect of hormonal contraceptives on lipid profile and the risk indices for cardiovascular disease in a Ghanaian community.
Asare GA, Santa S, Ngala RA, Asiedu B, Afriyie D, Amoah AG. Asare GA, et al. Int J Womens Health. 2014 Jun 3;6:597-603. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S59852. eCollection 2014. Int J Womens Health. 2014. PMID: 24940082 Free PMC article. - Oestrogen and anti-androgen therapy for transgender women.
Tangpricha V, den Heijer M. Tangpricha V, et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017 Apr;5(4):291-300. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30319-9. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27916515 Free PMC article. Review. - Hormonal contraception in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: choices, challenges, and noncontraceptive benefits.
de Melo AS, Dos Reis RM, Ferriani RA, Vieira CS. de Melo AS, et al. Open Access J Contracept. 2017 Feb 2;8:13-23. doi: 10.2147/OAJC.S85543. eCollection 2017. Open Access J Contracept. 2017. PMID: 29386951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Fahmy K, Khairy M, Allam G, Gobran F, Alloush M. Effect of depo-medroxyprogesterone acetate on coagulation factors and serum lipids in Egyptian women. Contraception. 1991;44:431–44. - PubMed
- Mia AR, Siddiqui NI, Islam MN, Khan MR, Shampa SS, Rukunuzzaman M. Effects of prolonged use of injectable hormonal contraceptive on serum lipid profile. Mymensingh Med J. 2005;14:19–21. - PubMed
- WHO Task Force on Long-acting Systemic Agents for Fertility Regulation A multicentre comparative study of serum lipids and apolipoproteins in long-term users of DMPA and a control group of IUD users. Contraception. 1993;47:177–91. - PubMed
- Oyelola OO. Fasting plasma lipids, lipoproteins and apolipoproteins in Nigerian women using combined oral and progestin-only injectable contraceptives. Contraception. 1993;47:445–54. - PubMed
- Tankeyoon M, Dusitsin N, Poshyachinda V, Larsson-Cohn U. A study of glucose tolerance, serum transaminase and lipids in women using depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate and a combination-type oral contraceptive. Contraception. 1976;14:199–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HD039883-03S3/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039883-01A1/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000073-438696/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659-04/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000073-42A10528/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659-05/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039883-05/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000073/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039883-02S1/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659-02/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24HD043659/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039883-03/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039883/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659-06/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000073-41S10528/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000073-447287/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659-07/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00073/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659-03/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000073-455386/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039883-02/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD039883/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039883-04/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD043659/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials