Novel aspects of the roles of Rac1 GTPase in the cardiovascular system - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Novel aspects of the roles of Rac1 GTPase in the cardiovascular system
Naoki Sawada et al. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Apr.
Abstract
Rac1 GTPase is an established master regulator of cell motility through cortical actin re-organization and of reactive oxygen species generation through regulation of NADPH oxidase activity. Numerous molecular and cellular studies have implicated Rac1 in various cardiovascular pathologies: vascular smooth muscle proliferation, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, and endothelial cell shape change. The physiological relevance of these in vitro findings, however, is just beginning to be reassessed with the newly developed, conditional mouse mutagenesis technology. Conditional gene targeting has also revealed unexpected, cell type-specific roles of Rac1. The aim of this review is to summarize the recent advance made in Rac1 research in the cardiovascular system, with special focus on its novel roles in the regulation of endothelial function, angiogenesis, and endothelium-mediated neuroprotection.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; ROS; Rac1; actin cytoskeleton; angiogenesis; atrial fibrillation; cardiac hypertrophy; eNOS; endothelium-derived neurotrophic activity; heart failure.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
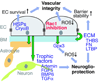
Figure 1
Proposed model of neuroprotection through targeting endothelial Rac1. BM: Basement membrane; EC: endothelial cell; ECM: Extracellular matrix; HSP: Heat shock protein; ROS: Reactive oxygen species. Adapted with permission from the reference [9].
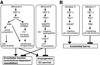
Figure 2
Context-dependent, Janus-faced functions of Rac1 in endothelial cell signaling. Different signaling axes encompassing distinct sets of upstream stimuli, GEF, Rac1 and effector(s) exert opposite effects on endothelial function, angiogenesis, EC survival (A), and endothelial barrier function (B).
Similar articles
- Phosphodiesterase 2 mediates redox-sensitive endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis by thrombin via Rac1 and NADPH oxidase 2.
Diebold I, Djordjevic T, Petry A, Hatzelmann A, Tenor H, Hess J, Görlach A. Diebold I, et al. Circ Res. 2009 May 22;104(10):1169-77. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.196592. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19390057 - Regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and postnatal angiogenesis by Rac1.
Sawada N, Salomone S, Kim HH, Kwiatkowski DJ, Liao JK. Sawada N, et al. Circ Res. 2008 Aug 15;103(4):360-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.178897. Epub 2008 Jul 3. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18599867 Free PMC article. - Rac1-mediated effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) in cardiovascular disease.
Adam O, Laufs U. Adam O, et al. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Mar 10;20(8):1238-50. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5526. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 23919665 Review. - Rac-1 as a new therapeutic target in cerebro- and cardio-vascular diseases.
Carrizzo A, Forte M, Lembo M, Formisano L, Puca AA, Vecchione C. Carrizzo A, et al. Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15(13):1231-46. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666141027110156. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25345393 Review. - Novel role of gp91(phox)-containing NAD(P)H oxidase in vascular endothelial growth factor-induced signaling and angiogenesis.
Ushio-Fukai M, Tang Y, Fukai T, Dikalov SI, Ma Y, Fujimoto M, Quinn MT, Pagano PJ, Johnson C, Alexander RW. Ushio-Fukai M, et al. Circ Res. 2002 Dec 13;91(12):1160-7. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000046227.65158.f8. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 12480817 Retracted.
Cited by
- Roles of small GTPases in cardiac hypertrophy (Review).
Wang X, Nie X, Wang H, Ren Z. Wang X, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2024 Nov;30(5):208. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13332. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39301654 Free PMC article. Review. - Fuel source shift or cost reduction: Context-dependent adaptation strategies in closely related Neodon fuscus and Lasiopodomys brandtii against hypoxia.
Li XJ, Qiao CC, Chen BJ, Li MY, Chen P, Huang ML, Chen CX, Liu Y, Cheng H, Jiang MW, Shi LY, Wang ZL. Li XJ, et al. Zool Res. 2022 Jul 18;43(4):497-513. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.011. Zool Res. 2022. PMID: 35585802 Free PMC article. - Structure-based design of CDC42 effector interaction inhibitors for the treatment of cancer.
Jahid S, Ortega JA, Vuong LM, Acquistapace IM, Hachey SJ, Flesher JL, La Serra MA, Brindani N, La Sala G, Manigrasso J, Arencibia JM, Bertozzi SM, Summa M, Bertorelli R, Armirotti A, Jin R, Liu Z, Chen CF, Edwards R, Hughes CCW, De Vivo M, Ganesan AK. Jahid S, et al. Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 5;39(1):110641. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110641. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35385746 Free PMC article. - Regulation of P2X1 receptors by modulators of the cAMP effectors PKA and EPAC.
Fong Z, Griffin CS, Large RJ, Hollywood MA, Thornbury KD, Sergeant GP. Fong Z, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 14;118(37):e2108094118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108094118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34508006 Free PMC article. - Activation of endothelial ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) improves post-stroke recovery and angiogenesis via activating Pak1 in mice.
Bu F, Min JW, Munshi Y, Lai YJ, Qi L, Urayama A, McCullough LD, Li J. Bu F, et al. Exp Neurol. 2019 Dec;322:113059. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113059. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31499064 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lezoualc'h F, Metrich M, Hmitou I, Duquesnes N, Morel E. Small GTP-binding proteins and their regulators in cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44:623–632. - PubMed
- Hordijk PL. Regulation of NADPH oxidases: the role of Rac proteins. Circ Res. 2006;98:453–462. - PubMed
- Tzima E. Role of small GTPases in endothelial cytoskeletal dynamics and the shear stress response. Circ Res. 2006;98:176–185. ● Comprehensive review summarizing how Rho and Ras GTPases mediate mechanotransduction in response to laminar flow.
- Gregg D, Rauscher FM, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ. Rac regulates cardiovascular superoxide through diverse molecular interactions: more than a binary GTP switch. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;285:C723–C734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 NS010828/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052233-12/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080187-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070274-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL052233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS010828-320036/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS010828/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS070001/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS010828/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS010828/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052233-13/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080187-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070274/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials