Type IX collagen gene mutations can result in multiple epiphyseal dysplasia that is associated with osteochondritis dissecans and a mild myopathy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
. 2010 Apr;152A(4):863-9.
doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33240.
Affiliations
- PMID: 20358595
- PMCID: PMC3557369
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33240
Free PMC article
Case Reports
Type IX collagen gene mutations can result in multiple epiphyseal dysplasia that is associated with osteochondritis dissecans and a mild myopathy
Gail C Jackson et al. Am J Med Genet A. 2010 Apr.
Free PMC article
Abstract
Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) is a clinically variable and genetically heterogeneous disease that is characterized by mild short stature and early onset osteoarthritis. Autosomal dominant forms are caused by mutations in the genes that encode type IX collagen, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, and matrilin-3: COL9A1, COL9A2, COL9A3, COMP, and MATN3, respectively. Splicing mutations have been identified in all three genes encoding type IX collagen and are restricted to specific exons encoding an equivalent region of the COL3 domain in all three alpha(IX) chains. MED has been associated with mild myopathy in some families, in particular one family with a COL9A3 mutation and two families with C-terminal COMP mutations. In this study we have identified COL9A2 mutations in two families with MED that also have osteochondritis dissecans and mild myopathy. This study therefore extends the range of gene-mutations that can cause MED-related myopathy. (c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
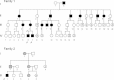
Fig 1
Pedigrees of two the families with MED presented in this study. An arrow indicates those individuals in which a COL9A2 mutation was identified. In Family 2 those individuals with semi-filled symbols were reported as affected by II-1, but this has not been independently confirmed by clinical or radiographic examination.
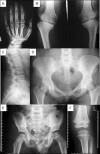
Fig 2
Radiographs of the proband (individual III-4, panels A–D) in Family 1 at 33 years of age and her eldest son (individual IV-6, panels E,F) at 3 years of age. The mother's radiographs showed (A) normal hand, (B) knees with bilateral genu varus, irregular joint surfaces, and decreased joint space, especially of the right knee, (C) lateral spine with irregular endplates of the vertebral bodies in the thoracolumbal region and (D) relatively normal hips. Radiographs of her 3-year-old son showing (E) hips and (F) the left knee. The radiographs were consistent with a diagnosis of mild MED, characterized by delayed ossification of the epiphyses. The hips were relatively spared but had small proximal femoral epiphyses, while the knees had small femoral and tibial epiphyses.
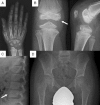
Fig 3
Radiographs of the proband in Family 2 (individual III-1) at age 9 years and 10 months of age showing (A) hand, (B) knee, (C) spine, and (D) hips. The radiographs were consistent with a diagnosis of MED, characterized by delayed and abnormal endochondral ossification. The hand showed marked carpal ossification delay with irregular carpal bones with a coarse internal structure. The distal epiphysis of the radius was also irregular and small. The knees had small and irregular femoral and tibial epiphyses and irregular metaphyses. The pelvis showed some flattening of the proximal femoral epiphyses but they were relatively spared. There was some irregularity of the vertebral end plates (arrow).
Similar articles
- A mutation in COL9A1 causes multiple epiphyseal dysplasia: further evidence for locus heterogeneity.
Czarny-Ratajczak M, Lohiniva J, Rogala P, Kozlowski K, Perälä M, Carter L, Spector TD, Kolodziej L, Seppänen U, Glazar R, Królewski J, Latos-Bielenska A, Ala-Kokko L. Czarny-Ratajczak M, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Nov;69(5):969-80. doi: 10.1086/324023. Epub 2001 Sep 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11565064 Free PMC article. - COL9A3: A third locus for multiple epiphyseal dysplasia.
Paassilta P, Lohiniva J, Annunen S, Bonaventure J, Le Merrer M, Pai L, Ala-Kokko L. Paassilta P, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Apr;64(4):1036-44. doi: 10.1086/302328. Am J Hum Genet. 1999. PMID: 10090888 Free PMC article. - A mutation in the alpha 3 chain of type IX collagen causes autosomal dominant multiple epiphyseal dysplasia with mild myopathy.
Bönnemann CG, Cox GF, Shapiro F, Wu JJ, Feener CA, Thompson TG, Anthony DC, Eyre DR, Darras BT, Kunkel LM. Bönnemann CG, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Feb 1;97(3):1212-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.3.1212. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10655510 Free PMC article. - Pseudoachondroplasia and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia: mutation review, molecular interactions, and genotype to phenotype correlations.
Briggs MD, Chapman KL. Briggs MD, et al. Hum Mutat. 2002 May;19(5):465-78. doi: 10.1002/humu.10066. Hum Mutat. 2002. PMID: 11968079 Review. - Pseudoachondroplasia and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia: New etiologic developments.
Unger S, Hecht JT. Unger S, et al. Am J Med Genet. 2001 Winter;106(4):244-50. Am J Med Genet. 2001. PMID: 11891674 Review.
Cited by
- Multifaceted Interweaving Between Extracellular Matrix, Insulin Resistance, and Skeletal Muscle.
Ahmad K, Lee EJ, Moon JS, Park SY, Choi I. Ahmad K, et al. Cells. 2018 Sep 22;7(10):148. doi: 10.3390/cells7100148. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30249008 Free PMC article. Review. - Osteochondritis Dissecans: Current Understanding of Epidemiology, Etiology, Management, and Outcomes.
Chau MM, Klimstra MA, Wise KL, Ellermann JM, Tóth F, Carlson CS, Nelson BJ, Tompkins MA. Chau MM, et al. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021 Jun 16;103(12):1132-1151. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.20.01399. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021. PMID: 34109940 Free PMC article. Review. - Pseudoachondroplasia and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia: a 7-year comprehensive analysis of the known disease genes identify novel and recurrent mutations and provides an accurate assessment of their relative contribution.
Jackson GC, Mittaz-Crettol L, Taylor JA, Mortier GR, Spranger J, Zabel B, Le Merrer M, Cormier-Daire V, Hall CM, Offiah A, Wright MJ, Savarirayan R, Nishimura G, Ramsden SC, Elles R, Bonafe L, Superti-Furga A, Unger S, Zankl A, Briggs MD. Jackson GC, et al. Hum Mutat. 2012 Jan;33(1):144-57. doi: 10.1002/humu.21611. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Hum Mutat. 2012. PMID: 21922596 Free PMC article. - Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: Etiology and Pathogenetic Mechanisms. A Systematic Review.
Andriolo L, Crawford DC, Reale D, Zaffagnini S, Candrian C, Cavicchioli A, Filardo G. Andriolo L, et al. Cartilage. 2020 Jul;11(3):273-290. doi: 10.1177/1947603518786557. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 29998741 Free PMC article. - The utility of mouse models to provide information regarding the pathomolecular mechanisms in human genetic skeletal diseases: The emerging role of endoplasmic reticulum stress (Review).
Briggs MD, Bell PA, Pirog KA. Briggs MD, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2015 Jun;35(6):1483-92. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2158. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25824717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bateman JF, Boot-Handford RP, Lamande SR. Genetic diseases of connective tissues: Cellular and extracellular effects of ECM mutations. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:173–183. - PubMed
- Briggs MD, Chapman KL. Pseudoachondroplasia and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia: Mutation review, molecular interactions, and genotype to phenotype correlations. Hum Mutat. 2002;19:465–478. - PubMed
- Fairbank T. Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex. Proc R Soc Med (Ortho Sec) 1947;39:315–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous