Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2010 May 6;362(18):1675-85.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907929. Epub 2010 Apr 28.
Naga Chalasani, Kris V Kowdley, Arthur McCullough, Anna Mae Diehl, Nathan M Bass, Brent A Neuschwander-Tetri, Joel E Lavine, James Tonascia, Aynur Unalp, Mark Van Natta, Jeanne Clark, Elizabeth M Brunt, David E Kleiner, Jay H Hoofnagle, Patricia R Robuck; NASH CRN
Collaborators, Affiliations
- PMID: 20427778
- PMCID: PMC2928471
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907929
Clinical Trial
Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Arun J Sanyal et al. N Engl J Med. 2010.
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is a common liver disease that can progress to cirrhosis. Currently, there is no established treatment for this disease.
Methods: We randomly assigned 247 adults with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and without diabetes to receive pioglitazone at a dose of 30 mg daily (80 subjects), vitamin E at a dose of 800 IU daily (84 subjects), or placebo (83 subjects), for 96 weeks. The primary outcome was an improvement in histologic features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, as assessed with the use of a composite of standardized scores for steatosis, lobular inflammation, hepatocellular ballooning, and fibrosis. Given the two planned primary comparisons, P values of less than 0.025 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results: Vitamin E therapy, as compared with placebo, was associated with a significantly higher rate of improvement in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (43% vs. 19%, P=0.001), but the difference in the rate of improvement with pioglitazone as compared with placebo was not significant (34% and 19%, respectively; P=0.04). Serum alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels were reduced with vitamin E and with pioglitazone, as compared with placebo (P<0.001 for both comparisons), and both agents were associated with reductions in hepatic steatosis (P=0.005 for vitamin E and P<0.001 for pioglitazone) and lobular inflammation (P=0.02 for vitamin E and P=0.004 for pioglitazone) but not with improvement in fibrosis scores (P=0.24 for vitamin E and P=0.12 for pioglitazone). Subjects who received pioglitazone gained more weight than did those who received vitamin E or placebo; the rates of other side effects were similar among the three groups.
Conclusions: Vitamin E was superior to placebo for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in adults without diabetes. There was no benefit of pioglitazone over placebo for the primary outcome; however, significant benefits of pioglitazone were observed for some of the secondary outcomes. (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00063622.)
2010 Massachusetts Medical Society
Figures
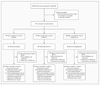
Figure 1. Screening, Randomization, and Follow-up of Study Subjects
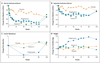
Figure 2. Changes from Baseline in Aminotransferase Levels, Insulin Resistance, and Weight, According to Study Group
Mean values are shown for changes from baseline (the value at follow-up minus the baseline value) in alanine aminotransferase levels, aspartate aminotransferase levels, insulin resistance, and weight among the 83 subjects in the placebo group, 84 subjects in the vitamin E group, and 80 subjects in the pioglitazone group. All available data were included in the calculation of means; data were missing for less than 10% of subjects. Insulin resistance was calculated according to the homeostasis model assessment, with the use of the following formula: (milligrams of glucose per deciliter × microunits of insulin per milliliter) ÷ 405.
Comment in
- Vitamin E for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: ready for prime time?
Dufour JF. Dufour JF. Hepatology. 2010 Aug;52(2):789-92. doi: 10.1002/hep.23817. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20683969 No abstract available. - Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Armstrong MJ, Houlihan DD, Rowe IA. Armstrong MJ, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 Sep 16;363(12):1185; author reply 1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1006581. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20843257 No abstract available. - ACP Journal Club: vitamin E, but not pioglitazone, improved nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in nondiabetic patients.
Sanyal AJ. Sanyal AJ. Ann Intern Med. 2010 Sep 21;153(6):JC3-12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-153-6-201009210-02012. Ann Intern Med. 2010. PMID: 20855789 No abstract available. - Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Violi F, Cangemi R. Violi F, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 Sep 16;363(12):1185-6; author reply 1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1006581. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20857543 No abstract available. - Clinical trial report: treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with vitamin E.
Bacon BR. Bacon BR. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011 Feb;13(1):1-2. doi: 10.1007/s11894-010-0162-8. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21107760 No abstract available. - Insulin resistance and oxidative stress: two therapeutic targets in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Voican CS, Perlemuter G. Voican CS, et al. J Hepatol. 2011 Feb;54(2):388-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.054. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21112115 No abstract available. - Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis treatment.
Luong M, Lau GK. Luong M, et al. Gastroenterology. 2011 Sep;141(3):1121-3; discussion 1123. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21791210 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, Darland C, Finch J, Hardies J, Balas B, Gastaldelli A, Tio F, Pulcini J, Berria R, Ma JZ, Dwivedi S, Havranek R, Fincke C, DeFronzo R, Bannayan GA, Schenker S, Cusi K. Belfort R, et al. N Engl J Med. 2006 Nov 30;355(22):2297-307. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa060326. N Engl J Med. 2006. PMID: 17135584 Clinical Trial. - Pioglitazone versus vitamin E versus placebo for the treatment of non-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: PIVENS trial design.
Chalasani NP, Sanyal AJ, Kowdley KV, Robuck PR, Hoofnagle J, Kleiner DE, Unalp A, Tonascia J; NASH CRN Research Group. Chalasani NP, et al. Contemp Clin Trials. 2009 Jan;30(1):88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2008.09.003. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Contemp Clin Trials. 2009. PMID: 18804555 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A pilot study of vitamin E versus vitamin E and pioglitazone for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Sanyal AJ, Mofrad PS, Contos MJ, Sargeant C, Luketic VA, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Shiffman ML, Clore J, Mills AS. Sanyal AJ, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004 Dec;2(12):1107-15. doi: 10.1016/s1542-3565(04)00457-4. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. PMID: 15625656 Clinical Trial. - Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials of Pharmacologic Agents in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis.
Said A, Akhter A. Said A, et al. Ann Hepatol. 2017 Jul-Aug;16(4):538-547. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.0284. Ann Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28611274 - Vitamin E and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Pacana T, Sanyal AJ. Pacana T, et al. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2012 Nov;15(6):641-8. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e328357f747. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2012. PMID: 23075940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Safety and Dosing Study of a Cholecystokinin Receptor Antagonist in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis.
Rabiee A, Gay MD, Shivapurkar N, Cao H, Nadella S, Smith CI, Lewis JH, Bansal S, Cheema A, Kwagyan J, Smith JP. Rabiee A, et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Dec;112(6):1271-1279. doi: 10.1002/cpt.2745. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36087237 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The latest idea in NAFLD/NASH pathogenesis.
Ono M, Okamoto N, Saibara T. Ono M, et al. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2010 Dec;3(6):263-70. doi: 10.1007/s12328-010-0182-9. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 26190482 - Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases: update on the challenge of diagnosis and treatment.
Oh H, Jun DW, Saeed WK, Nguyen MH. Oh H, et al. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016 Sep;22(3):327-335. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2016.0049. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27729634 Free PMC article. Review. - Obstructive sleep apnea and non-alcoholic Fatty liver disease: is the liver another target?
Mirrakhimov AE, Polotsky VY. Mirrakhimov AE, et al. Front Neurol. 2012 Oct 17;3:149. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2012.00149. eCollection 2012. Front Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23087670 Free PMC article. - Role of Insulin Resistance in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in People With Type 2 Diabetes: From Bench to Patient Care.
Nogueira JP, Cusi K. Nogueira JP, et al. Diabetes Spectr. 2024 Winter;37(1):20-28. doi: 10.2337/dsi23-0013. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Diabetes Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38385099 Free PMC article.
References
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
- Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB, Oh BJ. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55:434–438. - PubMed
- Adams LA, Sanderson S, Lindor KD, Angulo P. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J Hepatol. 2005;42:132–138. - PubMed
- Ekstedt M, Franzén LE, Mathiesen UL, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology. 2006;44:865–873. - PubMed
- Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2001;50:1844–1850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024128/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK002957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024128/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK61730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases