Doses of insulin and its analogues and cancer occurrence in insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Sep;33(9):1997-2003.
doi: 10.2337/dc10-0476. Epub 2010 Jun 14.
Matteo Monami, Daniela Balzi, Barbara Cresci, Laura Pala, Cecilia Melani, Caterina Lamanna, Ilaria Bracali, Michela Bigiarini, Alessandro Barchielli, Niccolo Marchionni, Carlo Maria Rotella
Affiliations
- PMID: 20551014
- PMCID: PMC2928350
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0476
Doses of insulin and its analogues and cancer occurrence in insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients
Edoardo Mannucci et al. Diabetes Care. 2010 Sep.
Abstract
Objective: Recent epidemiological studies suggested that some insulin analogues could be associated with increased risk of cancer. The present study is aimed at assessing the long-term association of different insulin analogues with cancer incidence.
Research design and methods: A nested case-control study dataset was generated from the cohort study dataset (n = 1,340 insulin-treated diabetic outpatients) by sampling control subjects from the risk sets. For each case subject, the control subjects (up to five) were chosen randomly from those members of the cohort who are at risk for the same follow-up time of the case subject. Five-year age classes, sex, and BMI classes (<18.5, 18.5-24.9, 25-29.9, and >or=30 kg/m(2)) were considered as additional categorical matching variables.
Results: During a median follow-up of 75.9 months (interquartile range 27.4-133.7), 112 case subjects of incident cancer were compared with 370 matched control subjects. A significantly higher mean daily dose of glargine was observed in case subjects than in control subjects (0.24 IU/kg/day [0.10-0.39] versus 0.16 IU/kg/day [0.12-0.24], P = 0.036). Incident cancer was associated with a dose of glargine >or=0.3 IU/kg/day even after adjusting for Charlson comorbidity score, other types of insulin administration, and metformin exposure (odds ratio 5.43 [95% CI 2.18-13.53], P < 0.001). No association between incident cancer and insulin doses was found for human insulin or other analogues.
Conclusions: The possibility of association between cancer and higher glargine doses suggests that dosages should always be considered when assessing the possible association of insulin and its analogues with cancer.
Figures
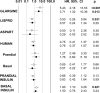
Figure 1
Risk of cancer associated with doses of each insulin type ≥0.3 IU/kg/day, adjusted for comorbidity, exposure to metformin, and doses of other types of insulin. ○, all case subjects; ●, after exclusion of case subjects with cancer occurring within the first 12 months of observation and of their matched control subjects.
Similar articles
- Metformin and cancer occurrence in insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients.
Monami M, Colombi C, Balzi D, Dicembrini I, Giannini S, Melani C, Vitale V, Romano D, Barchielli A, Marchionni N, Rotella CM, Mannucci E. Monami M, et al. Diabetes Care. 2011 Jan;34(1):129-31. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1287. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Diabetes Care. 2011. PMID: 20980415 Free PMC article. - Risk of malignancies in patients with diabetes treated with human insulin or insulin analogues: a cohort study.
Hemkens LG, Grouven U, Bender R, Günster C, Gutschmidt S, Selke GW, Sawicki PT. Hemkens LG, et al. Diabetologia. 2009 Sep;52(9):1732-44. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1418-4. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Diabetologia. 2009. PMID: 19565214 Free PMC article. - Risk of cancer in patients on insulin glargine and other insulin analogues in comparison with those on human insulin: results from a large population-based follow-up study.
Ruiter R, Visser LE, van Herk-Sukel MP, Coebergh JW, Haak HR, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Straus SM, Herings RM, Stricker BH. Ruiter R, et al. Diabetologia. 2012 Jan;55(1):51-62. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2312-4. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 21956710 Free PMC article. - Insulin glargine: a systematic review of a long-acting insulin analogue.
Wang F, Carabino JM, Vergara CM. Wang F, et al. Clin Ther. 2003 Jun;25(6):1541-77, discussion 1539-40. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(03)80156-x. Clin Ther. 2003. PMID: 12860485 Review. - Insulin Glargine: a review 8 years after its introduction.
Goykhman S, Drincic A, Desmangles JC, Rendell M. Goykhman S, et al. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009 Mar;10(4):705-18. doi: 10.1517/14656560902775677. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19284367 Review.
Cited by
- Impact of Insulin Therapies on Cancer Incidence in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Cohort Study in Reggio Emilia, Italy.
Vicentini M, Ballotari P, Venturelli F, Ottone M, Manicardi V, Gallo M, Greci M, Pinotti M, Pezzarossi A, Giorgi Rossi P. Vicentini M, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 31;14(11):2719. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112719. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681699 Free PMC article. - Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Metformin in Cervical Cancer.
Chen YH, Wang PH, Chen PN, Yang SF, Hsiao YH. Chen YH, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 22;13(11):2545. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112545. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067321 Free PMC article. Review. - Cancer Biology and Prevention in Diabetes.
Srivastava SP, Goodwin JE. Srivastava SP, et al. Cells. 2020 Jun 2;9(6):1380. doi: 10.3390/cells9061380. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32498358 Free PMC article. Review. - Human Insulin Therapy Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Lung Cancer: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study.
Tseng CH. Tseng CH. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jul 11;10:443. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00443. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31354621 Free PMC article. - Glucose-lowering medications and the risk of cancer: A methodological review of studies based on real-world data.
Bykov K, He M, Franklin JM, Garry EM, Seeger JD, Patorno E. Bykov K, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Sep;21(9):2029-2038. doi: 10.1111/dom.13766. Epub 2019 May 29. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 31062453 Free PMC article.
References
- Monami M, Marchionni N, Mannucci E: Long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH human insulin in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2008;81:184–189 - PubMed
- Jonasson JM, Ljung R, Talback M, Haglund B, Gudbjornsdottir S, Steineck G: Insulin glargine use and short-term incidence of malignancies—a population-based follow-up study in Sweden. Diabetologia 2009;52:1745–1754 - PubMed
- Currie CJ, Poole CD, Gale EA: The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009;52:1766–1777 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical