A chemical tool box defines mitotic and interphase roles for Mps1 kinase - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
A chemical tool box defines mitotic and interphase roles for Mps1 kinase
Weijie Lan et al. J Cell Biol. 2010.
Abstract
In this issue, three groups (Hewitt et al. 2010. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201002133; Maciejowski et al. 2010. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201001050; Santaguida et al. 2010. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201001036) use chemical inhibitors to analyze the function of the mitotic checkpoint kinase Mps1. These studies demonstrate that Mps1 kinase activity ensures accurate chromosome segregation through its recruitment to kinetochores of mitotic checkpoint proteins, formation of interphase and mitotic inhibitors of Cdc20, and correction of faulty microtubule attachments.
Figures
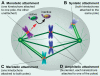
Figure 1.
Microtubule–kinetochore attachments. Four types of kinetochore–microtubule attachments are highlighted. (A) Monotelic attachment with only one kinetochore attached. Unattached kinetochores produce the mitotic checkpoint inhibitor that delays advance to anaphase by inactivating Cdc20, an activator of the ubiquitin ligase APC/C. (B) Syntelic attachment with both kinetochores attached to microtubules from the same pole. (C) Merotelic attachment with one kinetochore attached to microtubules from both poles. (D) Bioriented attachment (also known as amphitelic) with the two kinetochores of each chromatid pair attached to opposite spindle poles.
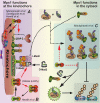
Figure 2.
Mps1 functions at multiple steps to inhibit Cdc20–APC/C. (A) All three groups (Hewitt et al., 2010; Maciejowski et al., 2010; Santaguida et al., 2010) demonstrate that at unattached kinetochores, Mps1 kinase activity is required to recruit other mitotic checkpoint components, including Mad1, Mad2, Bub1, BubR1, Bub3, and the Rod–Zw10–Zwilch complex. Discrepancies exist on exactly which components depend on Mps1 activity (see Table I for details). (B) Hewitt et al. (2010) show that Mps1 kinase activity maintains the recruitment at unattached kinetochores of O-Mad2 to the stably bound Mad1–C-Mad2 template. The molecular mechanism is yet to be elucidated. Mps1 may dimerize and be activated by self phosphorylation at kinetochores followed by quick release into the cytosol. (C) Maciejowski et al. (2010) demonstrate that Mps1 kinase activity in the cytosol promotes the assembly and/or prevents the disassembly of Cdc20–APC/C inhibitory complexes. Although the relative abundance and contribution of specific Cdc20–APC/C inhibitory complexes are unclear, all inhibit Cdc20 to prevent polyubiquitination of the key mitotic regulators cyclin B and securin by APC/C, an event which targets them for degradation as an irreversible trigger for anaphase entry.
Similar articles
- Mps1 directs the assembly of Cdc20 inhibitory complexes during interphase and mitosis to control M phase timing and spindle checkpoint signaling.
Maciejowski J, George KA, Terret ME, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Jallepalli PV. Maciejowski J, et al. J Cell Biol. 2010 Jul 12;190(1):89-100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201001050. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20624902 Free PMC article. - Chemical genetic inhibition of Mps1 in stable human cell lines reveals novel aspects of Mps1 function in mitosis.
Sliedrecht T, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Kops GJ. Sliedrecht T, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Apr 22;5(4):e10251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010251. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20422024 Free PMC article. - A Biosensor for the Mitotic Kinase MPS1 Reveals Spatiotemporal Activity Dynamics and Regulation.
Kuijt TEF, Lambers MLA, Weterings S, Ponsioen B, Bolhaqueiro ACF, Staijen DHM, Kops GJPL. Kuijt TEF, et al. Curr Biol. 2020 Oct 5;30(19):3862-3870.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.07.062. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32888483 - Dividing the goods: co-ordination of chromosome biorientation and mitotic checkpoint signalling by mitotic kinases.
Kops GJ. Kops GJ. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Oct;37(Pt 5):971-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0370971. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19754434 Review.
Cited by
- RZZ and Mad1 dynamics in Drosophila mitosis.
Défachelles L, Raich N, Terracol R, Baudin X, Williams B, Goldberg M, Karess RE. Défachelles L, et al. Chromosome Res. 2015 Jun;23(2):333-42. doi: 10.1007/s10577-015-9472-x. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Chromosome Res. 2015. PMID: 25772408 Free PMC article. - Mps1 and Ipl1/Aurora B act sequentially to correctly orient chromosomes on the meiotic spindle of budding yeast.
Meyer RE, Kim S, Obeso D, Straight PD, Winey M, Dawson DS. Meyer RE, et al. Science. 2013 Mar 1;339(6123):1071-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1232518. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Science. 2013. PMID: 23371552 Free PMC article. - Bub1 and BubR1: at the interface between chromosome attachment and the spindle checkpoint.
Elowe S. Elowe S. Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;31(15):3085-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05326-11. Epub 2011 May 31. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21628528 Free PMC article. Review. - ARHGEF17 is an essential spindle assembly checkpoint factor that targets Mps1 to kinetochores.
Isokane M, Walter T, Mahen R, Nijmeijer B, Hériché JK, Miura K, Maffini S, Ivanov MP, Kitajima TS, Peters JM, Ellenberg J. Isokane M, et al. J Cell Biol. 2016 Mar 14;212(6):647-59. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201408089. Epub 2016 Mar 7. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26953350 Free PMC article. - Phosphoregulation of Spc105 by Mps1 and PP1 regulates Bub1 localization to kinetochores.
London N, Ceto S, Ranish JA, Biggins S. London N, et al. Curr Biol. 2012 May 22;22(10):900-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.052. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22521787 Free PMC article.
References
- D’Alise A.M., Amabile G., Iovino M., Di Giorgio F.P., Bartiromo M., Sessa F., Villa F., Musacchio A., Cortese R. 2008. Reversine, a novel Aurora kinases inhibitor, inhibits colony formation of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 7:1140–1149 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2051 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources