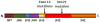JAK2 inhibitors: what's the true therapeutic potential? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
JAK2 inhibitors: what's the true therapeutic potential?
Fabio P S Santos et al. Blood Rev. 2011 Mar.
Abstract
Physicians treating patients with the classic Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (Ph-negative MPNs) (polycythemia vera [PV], essential thrombocythemia [ET] and primary myelofibrosis [PMF]) traditionally had few therapeutic drugs available. Spurred by the discovery of activating mutation of the JAK2 tyrosine kinase (JAK2 V617F mutation) in patients with Ph-negative MPNs several years ago, several JAK2 inhibitors were synthesized and are currently undergoing clinical trials in patients with PMF, PV and ET. Initial results from these studies have shown that these drugs can markedly reduce spleen size and alleviate constitutional symptoms, increase weight and improve exercise capacity in MF patients, thus improve quality of their life, which is significant clinical benefit. In ET and PV JAK2 inhibitor therapy may efficiently control blood cell count, as well as improve splenomegaly and control disease related symptoms. JAK2 inhibitors are a novel class of agents with promising results for treating patients with MF, PV and ET. In this article we will review the current evidence regarding the role of JAK2 mutations in the pathogenesis of Ph-negative MPNs and summarize results from the most recent clinical trials with JAK2 inhibitors in these disorders. JAK2 inhibitors are a novel class of agents with promising results for treating patients with MF, PV and ET.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None
Figures
Figure 1. JAK2 structure and mutation sites
The V617F mutation locates in the pseudokinase domain (JH2 domain) which regulates activity of the TK domain (JH1 domain). Exon 12 mutations of JAK2 (described in patients with JAK2 V617F negative polycythemia vera) cluster in residues F537-E543 and locate between the pseudokinase and SH2-like domain
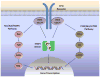
Figure 2. Signalling pathways activated by JAK2
Binding of the putative ligand to cytokine receptors leads to receptor dimerization and approximation of two JAK2 molecules, which trans-phosphorylate and activate each other. Activated JAK2 molecules initiate several distinct signalling pathways. Phosphorylation of STATs (STAT5 depicted in the figure) leads to STAT dimerization, nuclear translocation, binding to DNA and activation of expression of target genes. Other pathways that may be activated by JAKs include the Ras/Raf/MAPKinases and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.
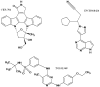
Figure 3
Biochemical structures of selected JAK2 inhibitors in clinical trials.
Similar articles
- Spleen deflation and beyond: the pros and cons of Janus kinase 2 inhibitor therapy for patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Quintás-Cardama A, Verstovsek S. Quintás-Cardama A, et al. Cancer. 2012 Feb 15;118(4):870-7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26359. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21766300 - Classical Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms: focus on mutations and JAK2 inhibitors.
Helbig G. Helbig G. Med Oncol. 2018 Aug 3;35(9):119. doi: 10.1007/s12032-018-1187-3. Med Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30074114 Free PMC article. Review. - Therapeutic potential of JAK2 inhibitors.
Verstovsek S. Verstovsek S. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009:636-42. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2009.1.636. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009. PMID: 20008249 Free PMC article. Review. - New JAK2 inhibitors for myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Quintás-Cardama A, Verstovsek S. Quintás-Cardama A, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011 Jul;20(7):961-72. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2011.579560. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21521147 Review.
Cited by
- The tyrphostin agent AG490 prevents and reverses type 1 diabetes in NOD mice.
Davoodi-Semiromi A, Wasserfall CH, Xia CQ, Cooper-DeHoff RM, Wabitsch M, Clare-Salzler M, Atkinson M. Davoodi-Semiromi A, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036079. Epub 2012 May 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615750 Free PMC article. - Up-regulation of Kv1.3 channels by janus kinase 2.
Hosseinzadeh Z, Warsi J, Elvira B, Almilaji A, Shumilina E, Lang F. Hosseinzadeh Z, et al. J Membr Biol. 2015 Apr;248(2):309-17. doi: 10.1007/s00232-015-9772-2. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Membr Biol. 2015. PMID: 25644777 - Downregulation of KCNQ4 by Janus kinase 2.
Hosseinzadeh Z, Sopjani M, Pakladok T, Bhavsar SK, Lang F. Hosseinzadeh Z, et al. J Membr Biol. 2013 Apr;246(4):335-41. doi: 10.1007/s00232-013-9537-8. Epub 2013 Mar 30. J Membr Biol. 2013. PMID: 23543186 - Downregulation of the creatine transporter SLC6A8 by JAK2.
Shojaiefard M, Hosseinzadeh Z, Bhavsar SK, Lang F. Shojaiefard M, et al. J Membr Biol. 2012 Mar;245(3):157-63. doi: 10.1007/s00232-012-9424-8. Epub 2012 Mar 11. J Membr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22407360 - Therapeutic targeting of IL-7Rα signaling pathways in ALL treatment.
Cramer SD, Aplan PD, Durum SK. Cramer SD, et al. Blood. 2016 Jul 28;128(4):473-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-679209. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27268088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Tefferi A, Gilliland G. Classification of chronic myeloid disorders: from Dameshek towards a semi-molecular system. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2006;19(3):365–85. - PubMed
- Tefferi A. Myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. N Engl J Med. 2000 Apr 27;342(17):1255–65. - PubMed
- Mesa RA, Silverstein MN, Jacobsen SJ, Wollan PC, Tefferi A. Population-based incidence and survival figures in essential thrombocythemia and agnogenic myeloid metaplasia: an Olmsted County Study, 1976–1995. Am J Hematol. 1999 May;61(1):10–5. - PubMed
- Finazzi G, Barbui T. Evidence and expertise in the management of polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Leukemia. 2008 Aug;22(8):1494–502. - PubMed
- Finazzi G, Caruso V, Marchioli R, Capnist G, Chisesi T, Finelli C, et al. Acute leukemia in polycythemia vera: an analysis of 1638 patients enrolled in a prospective observational study. Blood. 2005 Apr 1;105(7):2664–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous