Identification and characterization of a loss-of-function human MPYS variant - PubMed (original) (raw)
Identification and characterization of a loss-of-function human MPYS variant
L Jin et al. Genes Immun. 2011 Jun.
Abstract
MPYS, also known as STING and MITA, is an interferon (IFN)β stimulator essential for host defense against RNA, DNA viruses and intracellular bacteria. MPYS also facilitates the adjuvant activity of DNA vaccines. Here, we report identification of a distinct human MPYS haplotype that contains three non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), R71H-G230A-R293Q (thus, named the HAQ haplotype). We estimate, in two cohorts (1,074 individuals), that ∼3% of Americans are homozygous for this HAQ haplotype. HAQ MPYS exhibits a > 90% loss in the ability to stimulate IFNβ production. Furthermore, fibroblasts and macrophage cells expressing HAQ are defective in Listeria monocytogenes infection-induced IFNβ production. Lastly, we find that the loss of IFNβ activity is due primarily to the R71H and R293Q SNPs in HAQ. We hypothesize that individuals carrying HAQ may exhibit heightened susceptibility to viral infection and respond poorly to DNA vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
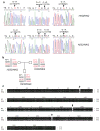
Figure 1. Identification of a R71H (rs11554776)-G230A (rs78233829)-R293Q (rs7380824) MPYS SNPs haplotype (HAQ) in human population
a. PCR sequencing of mpys exons from human samples that are homozygous (HAQ/HAQ) (upper three panels) and heterozygous (H232/HAQ) (lower three panels) for the HAQ haplotype. Red letters indicate the altered amino acids by SNPs. b. A family consists of homozygous (HAQ/HAQ) and heterozygous (H232/HAQ) of HAQ MPYS. c. Alignment of HAQ with WT MPYS. Altered amino acids due to SNPs are indicated by arrows.
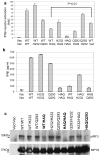
Figure 2. HAQ of MPYS is severely defective in IFNβ stimulation
a. 293MT cells (~1×105) were transfected with indicated plasmid (100ng) along with IFNβ-luciferase reporters. After 24 hrs, the luciferase activity was measured as described in Methods. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. P value was calculated by student T-test (one-tailed). b. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. The blot was probed with anti-MPYS or p-IRF3 Ab (4D4G). c. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids as before. The supernatant was collected and IFNβ proteins were measured as described in Methods. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. ND: not detected.
Figure 3. The WT/HAQ genotype is also defective in induction of IFNβ
a. 293MT cells were transfected with 100ng of each indicated plasmid (e.g 100ng each of WT and HAQ for the WT/HAQ) along with IFNβ-luciferase reporters. After 24 hrs, the luciferase activity was measured as before. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. b. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids as before. The supernatant was collected and IFNβ proteins were measured as described in Methods. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. ND: not detected. c. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. The blot was probed as before. Highlighted are the genotypes that are defective in IFNβ stimulation.
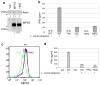
Figure 4. Listeria monocytogenes induction of IFNβ production is impaired in cells expressing HAQ
a. 293MT cells stably expressing Vec, WT or HAQ MPYS, were lysed in RIPA buffer. MPYS was detected as before. b. 293MT cells stably expressing Vec, WT or HAQ MPYS, were infected with Listeria monocytogenes as described in Methods. The IFNβ protein was measured as before. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. ND: not detected. c. BMM cells reconstituted with MPYS, HAQ or Vec control were fixed, permeabilized and stained with α-MPYS rabbit Ab followed by anti-rabbit-Alexa647 as in Methods. d. BMM cells were infected with Listeria monocytogenes as describe in Methods. IFNβ production was measured after 20 hrs by ELISA.
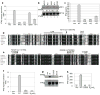
Figure 5. R293Q and R71H SNPs are responsible for the IFNβ stimulation defect in HAQ of MPYS
a. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmid (100ng) along with IFNβ-luciferase reporters. Luciferase activity was measured after 24 hrs as before. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. b. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. Phosphorylated IRF3 was probed as before. c. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids as before. The supernatant was collected and IFNβ proteins were measured as before. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. ND: not detected. d&e. Alignment of MPYS sequence from 7 different species. The locations of motifs and SNPs were indicated. f. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmid (100ng) along with IFNβ-luciferase reporters. Luciferase activity was measured after 24 hrs as before. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. g. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. Phosphorylated IRF3 was probed as before. h. 293MT cells were transfected with indicated plasmids as before. The supernatant was collected and IFNβ proteins were measured as before. Error bars represent SD of a duplicate. ND: not detected.
Similar articles
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms of human STING can affect innate immune response to cyclic dinucleotides.
Yi G, Brendel VP, Shu C, Li P, Palanathan S, Cheng Kao C. Yi G, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 21;8(10):e77846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077846. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24204993 Free PMC article. - The Common R71H-G230A-R293Q Human TMEM173 Is a Null Allele.
Patel S, Blaauboer SM, Tucker HR, Mansouri S, Ruiz-Moreno JS, Hamann L, Schumann RR, Opitz B, Jin L. Patel S, et al. J Immunol. 2017 Jan 15;198(2):776-787. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601585. Epub 2016 Dec 7. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27927967 Free PMC article. - Multiple Homozygous Variants in the STING-Encoding TMEM173 Gene in HIV Long-Term Nonprogressors.
Nissen SK, Pedersen JG, Helleberg M, Kjær K, Thavachelvam K, Obel N, Tolstrup M, Jakobsen MR, Mogensen TH. Nissen SK, et al. J Immunol. 2018 May 15;200(10):3372-3382. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701284. Epub 2018 Apr 9. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29632140 - TMEM173 variants and potential importance to human biology and disease.
Patel S, Jin L. Patel S, et al. Genes Immun. 2019 Jan;20(1):82-89. doi: 10.1038/s41435-018-0029-9. Epub 2018 May 1. Genes Immun. 2019. PMID: 29728611 Free PMC article. Review. - The use of host cell machinery in the pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes.
Cossart P, Bierne H. Cossart P, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001 Feb;13(1):96-103. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(00)00188-6. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11154924 Review.
Cited by
- Structural analysis of the STING adaptor protein reveals a hydrophobic dimer interface and mode of cyclic di-GMP binding.
Ouyang S, Song X, Wang Y, Ru H, Shaw N, Jiang Y, Niu F, Zhu Y, Qiu W, Parvatiyar K, Li Y, Zhang R, Cheng G, Liu ZJ. Ouyang S, et al. Immunity. 2012 Jun 29;36(6):1073-86. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.019. Epub 2012 May 10. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22579474 Free PMC article. - At the Crossroads of the cGAS-cGAMP-STING Pathway and the DNA Damage Response: Implications for Cancer Progression and Treatment.
Korneenko TV, Pestov NB, Nevzorov IA, Daks AA, Trachuk KN, Solopova ON, Barlev NA. Korneenko TV, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 1;16(12):1675. doi: 10.3390/ph16121675. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139802 Free PMC article. Review. - STING and the innate immune response to nucleic acids in the cytosol.
Burdette DL, Vance RE. Burdette DL, et al. Nat Immunol. 2013 Jan;14(1):19-26. doi: 10.1038/ni.2491. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23238760 Review. - G-quadruplex binders as cytostatic modulators of innate immune genes in cancer cells.
Miglietta G, Russo M, Duardo RC, Capranico G. Miglietta G, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jul 9;49(12):6673-6686. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab500. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34139015 Free PMC article. - The common TMEM173 HAQ, AQ alleles rescue CD4 T cellpenia, restore T-regs, and prevent SAVI (N153S) inflammatory disease in mice.
Aybar-Torres A, Saldarriaga LA, Pham AT, Emtiazjoo AM, Sharma AK, Bryant AJ, Jin L. Aybar-Torres A, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 17:2023.10.05.561109. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.05.561109. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 37886547 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
- Cook DN, Pisetsky DS, Schwartz DA. Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of human disease. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:975–9. - PubMed
- Arbour NC, et al. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet. 2000;25:187–91. - PubMed
- Lorenz E, Mira JP, Frees KL, Schwartz DA. Relevance of mutations in the TLR4 receptor in patients with gram-negative septic shock. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:1028–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19 ES011375/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062739-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 ES11375/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01AI062739-05S209/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062739/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089807/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062739-05S2/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL089807-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AI062739-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials