IL-27 and IL-21 are associated with T cell IL-10 responses in human visceral leishmaniasis - PubMed (original) (raw)
IL-27 and IL-21 are associated with T cell IL-10 responses in human visceral leishmaniasis
Nasim Akhtar Ansari et al. J Immunol. 2011.
Abstract
IL-10 is believed to underlie many of the immunologic defects in human visceral leishmaniasis (VL). We have identified CD4(+)CD25(-)Foxp3(-) T cells as the major source of IL-10 in the VL spleen. IL-27, a member of the IL-6/IL-12 cytokine family, has been shown to promote development of IL-10-producing T cells, in part by upregulating their production of autocrine IL-21. We investigated whether IL-27 and IL-21 are associated with human VL. IL-27 was elevated in VL plasma, and at pretreatment, spleen cells showed significantly elevated mRNA levels of both IL-27 subunits, IL-27p28 and EBI-3, as well as IL-21, compared with posttreatment biopsies. CD14(+) spleen cells were the main source of IL-27 mRNA, whereas CD3(+) T cells were the main source of IL-21. IL-27 mRNA could be strongly upregulated in normal donor macrophages with IFN-γ and IL-1β, conditions consistent with those in the VL spleen. Last, a whole-blood assay revealed that most VL patients could produce Ag-specific IFN-γ and IL-10 and that the IL-10 could be augmented with recombinant human IL-21. Thus, proinflammatory cytokines acting on macrophages in the VL spleen have the potential to upregulate IL-27, which in turn can induce IL-21 to expand IL-10-producing T cells as a mechanism of feedback control.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
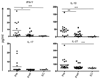
FIGURE 1
Cytokines in plasma from VL patients. IFN-γ, IL-10 and IL-17 were measured by multiplex analysis of plasma obtained from paired VL patients at pre- and post -treatment (n = 16) and from ECs (n = 10). Dual antibody sandwich ELISA was used to measure plasma IL-27 levels in paired VL patients (n = 21) and ECs (n = 10). Significant differences are indicated with *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001.
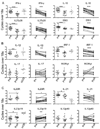
FIGURE 2
Cytokine mRNA expression in VL spleen. (A–C) Ex-vivo analysis of relative mRNA levels for indicated genes in splenic aspirates from VL patients before (n = 28) or 21–30 d after treatment (n = 18) and in HOD spleen samples (n = 10). Paired pre- and post- treatment samples(n = 18) are also shown separately. Significant differences are indicated with *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
FIGURE 3
Ex-vivo analysis of cytokine mRNA levels in splenic lymphocytes subsets. (A) Relative expression of IL-10, IL-21, IL-27p28 and EBI-3 mRNA levels in sequential, positively selected CD19+, CD3+(CD25-) and in the remaining depleted (Innate cells: NK, Macrophages, DCs) splenic cell population before treatment (n = 8). (B) Relative expression of cell specific markers (CD19/B cell, CD14/ Monocytes/ Macrophages and CD1c/DCs on sequential, positively selected CD19+, CD3+, CD14+, CD1c+, CD56+ and in the remaining ‘depleted’ splenic cell population. (C) Relative expression of mRNA levels for IL-10, IL-21, IL-27p28, and EBI-3 in positively selected splenic cell fractions from VL patients prior to treatment (n = 8). Significant differences are indicated with *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, ns, not significant.
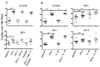
FIGURE 4
IFN-γ and IL-1β induces IL-27 mRNA in human monocyte derived macrophages. (A) Monocyte derived macrophages from normal donors (n = 7) were stimulated with rhIFN-γ or rhTNF-α or their combination or medium alone for 8 h prior to infection with L. donovani amastigotes. Macrophages were cultured for another 16 h before cells were lysed for mRNA expression analysis. (B) Monocyte derived macrophages from normal donors (n = 11) were stimulated with rhIFN-γ or rhIL-1β or their combination or medium alone for 24 h before cells were lysed for mRNA expression analysis. Significant differences are indicated with *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
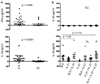
FIGURE 5
IL-21 upregulates antigen specific IL-10 production in whole blood cell cultures from active VL cases. (A) IFN-γ and IL-10 production by peripheral blood cells from pre-treatment VL patients (n = 27) and EC (n = 13 or 19) in response to SLA. (B) IL-10 production by peripheral blood cells from pre-treatment VL patients (n = 18) and ECs (n = 7) in response to SLA, rhIL-27 or rhIL-21 alone or in combination. (C) IL-21 production by peripheral blood cells from pre-treatment VL patients (n = 13). Whole blood cells were cultured in the absence or presence of 10µg/ml L. donovani soluble antigen and/or exogenous rhL-27(100ng/ml) and/or rhIL-21 (25ng/ml). Twenty four hours later supernatant was collected for cytokine analysis. Cytokine concentrations shown are the values in the stimulated cultures minus the medium control. Significant differences are indicated with p values.
Similar articles
- Splenic accumulation of IL-10 mRNA in T cells distinct from CD4+CD25+ (Foxp3) regulatory T cells in human visceral leishmaniasis.
Nylén S, Maurya R, Eidsmo L, Manandhar KD, Sundar S, Sacks D. Nylén S, et al. J Exp Med. 2007 Apr 16;204(4):805-17. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061141. Epub 2007 Mar 26. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17389235 Free PMC article. - PD-1 function in apoptosis of T lymphocytes in canine visceral leishmaniasis.
Chiku VM, Silva KL, de Almeida BF, Venturin GL, Leal AA, de Martini CC, de Rezende Eugênio F, Dos Santos PS, de Lima VM. Chiku VM, et al. Immunobiology. 2016 Aug;221(8):879-88. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.03.007. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Immunobiology. 2016. PMID: 27016050 - Cellular profile of cytokine production in a patient with visceral leishmaniasis: gammadelta+ T cells express both type 1 cytokines and interleukin-10.
Lagler H, Willheim M, Traunmüller F, Wahl K, Winkler H, Ramharter M, Graninger W, Winkler S. Lagler H, et al. Scand J Immunol. 2003 Mar;57(3):291-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2003.01223.x. Scand J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12641659 - Interleukin-10 and the pathogenesis of human visceral leishmaniasis.
Nylén S, Sacks D. Nylén S, et al. Trends Immunol. 2007 Sep;28(9):378-84. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Aug 6. Trends Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17689290 Review. - T-cell response in human leishmaniasis.
Kharazmi A, Kemp K, Ismail A, Gasim S, Gaafar A, Kurtzhals JA, El Hassan AM, Theander TG, Kemp M. Kharazmi A, et al. Immunol Lett. 1999 Jan;65(1-2):105-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(98)00132-1. Immunol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10065635 Review.
Cited by
- Regulatory actions of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 in Leishmania donovani infection in the liver.
Murray HW, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Raman VS, Reed SG, Ma X. Murray HW, et al. Infect Immun. 2013 Jul;81(7):2318-26. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01468-12. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23589575 Free PMC article. - Systematic review of biomarkers to monitor therapeutic response in leishmaniasis.
Kip AE, Balasegaram M, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH, de Vries PJ, Dorlo TP. Kip AE, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jan;59(1):1-14. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04298-14. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25367913 Free PMC article. Review. - Splenic CD4+ T Cells in Progressive Visceral Leishmaniasis Show a Mixed Effector-Regulatory Phenotype and Impair Macrophage Effector Function through Inhibitory Receptor Expression.
Medina-Colorado AA, Osorio EY, Saldarriaga OA, Travi BL, Kong F, Spratt H, Soong L, Melby PC. Medina-Colorado AA, et al. PLoS One. 2017 Jan 19;12(1):e0169496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169496. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28103263 Free PMC article. - Tr-1-like CD4+CD25-CD127-/lowFOXP3- cells are the main source of interleukin 10 in patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis.
Costa DL, Cardoso TM, Queiroz A, Milanezi CM, Bacellar O, Carvalho EM, Silva JS. Costa DL, et al. J Infect Dis. 2015 Mar 1;211(5):708-18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu406. Epub 2014 Aug 19. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25139022 Free PMC article. - Chemokines Signature and T Cell Dynamics in Leishmaniasis: Molecular insight and therapeutic application.
Upadhyay S, Kumar S, Singh VK, Tiwari R, Kumar A, Sundar S, Kumar R. Upadhyay S, et al. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Nov 26;27:1-55. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.36. Online ahead of print. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39587036 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Guerin PJ, Olliaro P, Sundar S, Boelaert M, Croft SL, Desjeux P, Wasunna MK, Bryceson AD. Visceral leishmaniasis: current status of control, diagnosis, and treatment, and a proposed research and development agenda. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2:494–501. - PubMed
- Sundar S, Rai M. Advances in the treatment of leishmaniasis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2002;15:593–598. - PubMed
- Ansari NA, Saluja S, Salotra P. Elevated levels of interferon-gamma, interleukin-10, and interleukin-6 during active disease in Indian kala azar. Clin Immunol. 2006;119:339–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials