The mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis (MSCIMS) trial protocol and baseline cohort characteristics: an open-label pre-test: post-test study with blinded outcome assessments - PubMed (original) (raw)
Controlled Clinical Trial
doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-62.
Madhan Kolappan, Rickie Patani, Michael A Scott, Charles Crawley, Xiao-Ling He, Karen Richardson, Kelly Barber, Daniel J Webber, Claudia A M Wheeler-Kingshott, Daniel J Tozer, Rebecca S Samson, David L Thomas, Ming-Qing Du, Shi L Luan, Andrew W Michell, Daniel R Altmann, Alan J Thompson, David H Miller, Alastair Compston, Siddharthan Chandran
Affiliations
- PMID: 21366911
- PMCID: PMC3059276
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-62
Controlled Clinical Trial
The mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis (MSCIMS) trial protocol and baseline cohort characteristics: an open-label pre-test: post-test study with blinded outcome assessments
Peter Connick et al. Trials. 2011.
Abstract
Background: No treatments are currently available that slow, stop, or reverse disease progression in established multiple sclerosis (MS). The Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Multiple Sclerosis (MSCIMS) trial tests the safety and feasibility of treatment with a candidate cell-based therapy, and will inform the wider challenge of designing early phase clinical trials to evaluate putative neuroprotective therapies in progressive MS. Illustrated by the MSCIMS trial protocol, we describe a novel methodology based on detailed assessment of the anterior visual pathway as a model of wider disease processes--the "sentinel lesion approach".
Methods/design: MSCIMS is a phase IIA study of autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in secondary progressive MS. A pre-test : post-test design is used with healthy controls providing normative data for inter-session variability. Complementary eligibility criteria and outcomes are used to select participants with disease affecting the anterior visual pathway.
Results: Ten participants with MS and eight healthy controls were recruited between October 2008 and March 2009. Mesenchymal stem cells were successfully isolated, expanded and characterised in vitro for all participants in the treatment arm.
Conclusions: In addition to determining the safety and feasibility of the intervention and informing design of future studies to address efficacy, MSCIMS adopts a novel strategy for testing neuroprotective agents in MS--the sentinel lesion approach--serving as proof of principle for its future wider applicability.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00395200).
Figures
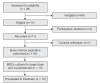
Figure 1
Recruitment and retention to treatment cohort.
Similar articles
- MEsenchymal StEm cells for Multiple Sclerosis (MESEMS): a randomized, double blind, cross-over phase I/II clinical trial with autologous mesenchymal stem cells for the therapy of multiple sclerosis.
Uccelli A, Laroni A, Brundin L, Clanet M, Fernandez O, Nabavi SM, Muraro PA, Oliveri RS, Radue EW, Sellner J, Soelberg Sorensen P, Sormani MP, Wuerfel JT, Battaglia MA, Freedman MS; MESEMS study group. Uccelli A, et al. Trials. 2019 May 9;20(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3346-z. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31072380 Free PMC article. - Autologous mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: an open-label phase 2a proof-of-concept study.
Connick P, Kolappan M, Crawley C, Webber DJ, Patani R, Michell AW, Du MQ, Luan SL, Altmann DR, Thompson AJ, Compston A, Scott MA, Miller DH, Chandran S. Connick P, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2012 Feb;11(2):150-6. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70305-2. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Lancet Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22236384 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Assessment of bone marrow-derived Cellular Therapy in progressive Multiple Sclerosis (ACTiMuS): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.
Rice CM, Marks DI, Ben-Shlomo Y, Evangelou N, Morgan PS, Metcalfe C, Walsh P, Kane NM, Guttridge MG, Miflin G, Blackmore S, Sarkar P, Redondo J, Owen D, Cottrell DA, Wilkins A, Scolding NJ. Rice CM, et al. Trials. 2015 Oct 14;16:463. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0953-1. Trials. 2015. PMID: 26467901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Amiloride, fluoxetine or riluzole to reduce brain volume loss in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: the MS-SMART four-arm RCT.
De Angelis F, Connick P, Parker RA, Plantone D, Doshi A, John N, Stutters J, MacManus D, Prados F, Marshall I, Solanky B, Samson RS, Barkhof F, Ourselin S, Braisher M, Ross M, Cranswick G, Pavitt SH, Gnanapavan S, Giovannoni G, Wheeler-Kingshott CAMG, Hawkins C, Sharrack B, Bastow R, Weir CJ, Stallard N, Chandran S, Chataway J. De Angelis F, et al. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2020 May. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2020 May. PMID: 32453521 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.
Reston JT, Uhl S, Treadwell JR, Nash RA, Schoelles K. Reston JT, et al. Mult Scler. 2011 Feb;17(2):204-13. doi: 10.1177/1352458510383609. Epub 2010 Oct 4. Mult Scler. 2011. PMID: 20921236 Review.
Cited by
- Translational research in Huntington's disease: opening up for disease modifying treatment.
Burgunder JM. Burgunder JM. Transl Neurodegener. 2013 Jan 25;2(1):2. doi: 10.1186/2047-9158-2-2. Transl Neurodegener. 2013. PMID: 23347646 Free PMC article. - Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Detection and Therapy.
Mehta KJ. Mehta KJ. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Oct;18(7):2234-2261. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10343-x. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35103937 Free PMC article. Review. - Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Hold Lower Heterogeneity and Great Promise in Biological Research and Clinical Applications.
Zhang J, Chen M, Liao J, Chang C, Liu Y, Padhiar AA, Zhou Y, Zhou G. Zhang J, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 30;9:716907. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.716907. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34660579 Free PMC article. - The development of hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cell transplantation as an effective treatment for multiple sclerosis.
Holloman JP, Ho CC, Hukki A, Huntley JL, Gallicano GI. Holloman JP, et al. Am J Stem Cells. 2013 Jun 30;2(2):95-107. Print 2013. Am J Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23862098 Free PMC article. - MEsenchymal StEm cells for Multiple Sclerosis (MESEMS): a randomized, double blind, cross-over phase I/II clinical trial with autologous mesenchymal stem cells for the therapy of multiple sclerosis.
Uccelli A, Laroni A, Brundin L, Clanet M, Fernandez O, Nabavi SM, Muraro PA, Oliveri RS, Radue EW, Sellner J, Soelberg Sorensen P, Sormani MP, Wuerfel JT, Battaglia MA, Freedman MS; MESEMS study group. Uccelli A, et al. Trials. 2019 May 9;20(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3346-z. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31072380 Free PMC article.
References
- Kappos L, Freedman MS, Polman CH, Edan G, Hartung HP, Miller DH, Montalbán X, Barkhof F, Radü EW, Bauer L, Dahms S, Lanius V, Pohl C, Sandbrink R. BENEFIT Study Group. Effect of early versus delayed interferon beta-1b treatment on disability after a first clinical event suggestive of multiple sclerosis: a 3-year follow-up analysis of the BENEFIT study. Lancet. 2007;370:389–97. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61194-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 926/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
- G0502107/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RG44871/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources