The collagen family - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The collagen family
Sylvie Ricard-Blum. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011.
Abstract
Collagens are the most abundant proteins in mammals. The collagen family comprises 28 members that contain at least one triple-helical domain. Collagens are deposited in the extracellular matrix where most of them form supramolecular assemblies. Four collagens are type II membrane proteins that also exist in a soluble form released from the cell surface by shedding. Collagens play structural roles and contribute to mechanical properties, organization, and shape of tissues. They interact with cells via several receptor families and regulate their proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Some collagens have a restricted tissue distribution and hence specific biological functions.
Figures
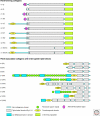
Figure 1.
Structural organization of collagens. Domain composition and supramolecular assemblies of collagens. COL, Collagenous, triple-helical, domains; NC, Non-collagenous, nontriple-helical, domains. They are numbered from the carboxy- to the amino-terminus, except for collagen VII. (Figure continued on following page.)
Figure 1.
Structural organization of collagens. Domain composition and supramolecular assemblies of collagens. COL, Collagenous, triple-helical, domains; NC, Non-collagenous, nontriple-helical, domains. They are numbered from the carboxy- to the amino-terminus, except for collagen VII. (Figure continued on following page.)
Figure 2.
Supramolecular assemblies formed by collagens.
Figure 3.
Collagen cross-links. Lysyl-mediated mature cross-links: argoline, deoxypyridinoline, pyridinoline, and histidinohydroxylysinonorleucine. Advanced glycation endproducts: glucosepane and pentosidine.
Similar articles
- The collagen family members as cell adhesion proteins.
Heino J. Heino J. Bioessays. 2007 Oct;29(10):1001-10. doi: 10.1002/bies.20636. Bioessays. 2007. PMID: 17876790 Review. - Transmembrane collagen receptors.
Leitinger B. Leitinger B. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:265-90. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154013. Epub 2011 May 13. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21568710 Review. - Mammalian collagen receptors.
Leitinger B, Hohenester E. Leitinger B, et al. Matrix Biol. 2007 Apr;26(3):146-55. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2006.10.007. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Matrix Biol. 2007. PMID: 17141492 Review. - [Collagens associated with basement membranes and their matricryptins].
Ricard-Blum S, Faye C. Ricard-Blum S, et al. J Soc Biol. 2005;199(4):321-8. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2005033. J Soc Biol. 2005. PMID: 16738526 Review. French. - Advances in Molecular Function and Recombinant Expression of Human Collagen.
Sun W, Shahrajabian MH, Ma K, Wang S. Sun W, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;18(3):430. doi: 10.3390/ph18030430. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143206 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The role of metabolic reprogramming and de novo amino acid synthesis in collagen protein production by myofibroblasts: implications for organ fibrosis and cancer.
Hamanaka RB, Mutlu GM. Hamanaka RB, et al. Amino Acids. 2021 Dec;53(12):1851-1862. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-02996-8. Epub 2021 May 8. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 33963932 Free PMC article. Review. - The contribution of adiponectin to diabetic retinopathy progression: Association with the AGEs-RAGE pathway.
Fu M, Zhengran L, Yingli L, Tong W, Liyang C, Xi G, Xiongyi Y, Mingzhe C, Guoguo Y. Fu M, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Aug 12;10(17):e36111. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36111. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296166 Free PMC article. - Updated Understanding of the Glial-Vascular Unit in Central Nervous System Disorders.
Yao D, Zhang R, Xie M, Ding F, Wang M, Wang W. Yao D, et al. Neurosci Bull. 2023 Mar;39(3):503-518. doi: 10.1007/s12264-022-00977-9. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Neurosci Bull. 2023. PMID: 36374471 Free PMC article. Review. - Type II Collagen from Cartilage of Acipenser baerii Promotes Wound Healing in Human Dermal Fibroblasts and in Mouse Skin.
Lai CS, Tu CW, Kuo HC, Sun PP, Tsai ML. Lai CS, et al. Mar Drugs. 2020 Oct 11;18(10):511. doi: 10.3390/md18100511. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33050593 Free PMC article. - Collagen at the maternal-fetal interface in human pregnancy.
Shi JW, Lai ZZ, Yang HL, Yang SL, Wang CJ, Ao D, Ruan LY, Shen HH, Zhou WJ, Mei J, Fu Q, Li MQ. Shi JW, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2020 May 25;16(12):2220-2234. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45586. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Amenta PS, Scivoletti NA, Newman MD, Sciancalepore JP, Li D, Myers JC 2005. Proteoglycan-collagen XV in human tissues is seen linking banded collagen fibers subjacent to the basement membrane. J Histochem Cytochem 53: 165–176 - PubMed
- Avery NC, Bailey AJ 2006. The effects of the Maillard reaction on the physical properties and cell interactions of collagen. Pathol Biol 54: 387–395 - PubMed
- Bader HL, Keene DR, Charvet B, Veit G, Driever W, Koch M, Ruggiero F 2009. Zebrafish collagen XII is present in embryonic connective tissue sheaths (fascia) and basement membranes. Matrix Biol 28: 32–43 - PubMed
- Banos CC, Thomas AH, Kuo CK 2008. Collagen fibrillogenesis in tendon development: Current models and regulation of fibril assembly. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 84: 228–244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources