The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas
Ewan A Gibb et al. Mol Cancer. 2011.
Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging as new players in the cancer paradigm demonstrating potential roles in both oncogenic and tumor suppressive pathways. These novel genes are frequently aberrantly expressed in a variety of human cancers, however the biological functions of the vast majority remain unknown. Recently, evidence has begun to accumulate describing the molecular mechanisms by which these RNA species function, providing insight into the functional roles they may play in tumorigenesis. In this review, we highlight the emerging functional role of lncRNAs in human cancer.
Figures
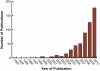
Figure 1
Publications describing cancer-associated ncRNAs. Entries are based on a National Library of Medicine Pubmed search using the terms "ncRNA" or "non-coding RNA" or "noncoding RNA" or non-protein-coding RNA" with cancer and annual (Jan.1-Dec.31) date limitations.
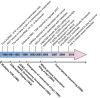
Figure 2
Timeline of cancer-associated ncRNA discoveries relative to transcriptome analysis technologies (not drawn to scale).
Figure 3
Proposed mechanism of HOTAIR mediated gene silencing of 40 kb of the HOXD locus, which is involved in developmental patterning. The HOTAIR lncRNA is transcribed from the HOXC locus and functions in the binding and recruitment and binding of the PRC2 and LSD1 complex to the HOXD locus. For clarity, only the PRC2 complex is indicated in the above figure. Through an undetermined mechanism, the _HOTAIR_-PRC2-LSD1 complex is redirected to the HOXD locus on chromosome 2 where genes involved in metastasis suppression are silenced through H3K27 methylation and H3K4 demethylation. This drives breast cancer cells to develop gene expression patterns that more closely resemble embryonic fibroblasts than epithelial cells.
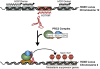
Figure 4
Expression and processing of MALAT1 transcripts. Full length 7.5 kb MALAT1 RNA is processed by RNaseP and RNaseZ to generate the small ncRNA mascRNA, which is then exported to the cytoplasm. The larger MALAT1 RNA is retained in the nuclear speckles where it is thought to have a role in regulating alternative splicing machinery.
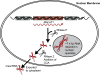
Figure 5
Proposed mechanism of HULC upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. (1) The kinase PRKACB functions as an activator of CREB. (2) Phosphorylated (activated) CREB forms part of the RNA pol II transcriptional machinery to activate HULC expression. (3) Abundant HULC RNA acts as a molecular sponge to sequester and inactivate the repressive function miR-372. (4) PRKACB levels increase, as transcripts are normally translationally repressed by high miR-372 levels.
Figure 6
Genomic locations of the five classes of T-UCRs. The exons of coding genes are indicated by boxes, while the locations of the T-UCR elements are marked by a double-T bar. The five possible positions are as indicated exonic, partly exonic, exon containing, intronic and intergenic.
Similar articles
- Noncoding RNAs in cancer and cancer stem cells.
Huang T, Alvarez A, Hu B, Cheng SY. Huang T, et al. Chin J Cancer. 2013 Nov;32(11):582-93. doi: 10.5732/cjc.013.10170. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24206916 Free PMC article. Review. - Involvement of Non-coding RNAs in the Signaling Pathways of Colorectal Cancer.
Yang Y, Du Y, Liu X, Cho WC. Yang Y, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;937:19-51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42059-2_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27573893 Review. - Non-coding RNAs in Precursor Lesions of Colorectal Cancer: Their Role in Cancer Initiation and Formation.
Mohammadpour S, Noukabadi FN, Esfahani AT, Kazemi F, Esmaeili S, Zafarjafarzadeh N, Sarpash S, Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E. Mohammadpour S, et al. Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(5):565-575. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230523155719. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37226783 Review. - Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer: Pathogenesis and clinical implications.
Xie SS, Jin J, Xu X, Zhuo W, Zhou TH. Xie SS, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 21;22(3):1213-23. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1213. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26811659 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNAs in ovarian carcinomas.
Dahiya N, Morin PJ. Dahiya N, et al. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010 Jan 29;17(1):F77-89. doi: 10.1677/ERC-09-0203. Print 2010 Mar. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19903743 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Long noncoding RNA DANCR confers cytarabine resistance in acute myeloid leukemia by activating autophagy via the miR-874-3P/ATG16L1 axis.
Zhang H, Liu L, Chen L, Liu H, Ren S, Tao Y. Zhang H, et al. Mol Oncol. 2021 Apr;15(4):1203-1216. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12661. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Mol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33638615 Free PMC article. - Long non-coding RNA: a new player in cancer.
Zhang H, Chen Z, Wang X, Huang Z, He Z, Chen Y. Zhang H, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2013 May 31;6:37. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-37. J Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23725405 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of apoptosis by long non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS1 in VSMCs: implications for TAA pathogenesis.
Zhao Y, Feng G, Wang Y, Yue Y, Zhao W. Zhao Y, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Oct 15;7(11):7643-52. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25550800 Free PMC article. - Up-Regulating ERIC by CRISPR-dCas9-VPR Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Invasion and Promotes Apoptosis in Human Bladder Cancer.
Yang J, Xia A, Zhang H, Liu Q, You H, Ding D, Yin Y, Wen B. Yang J, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Mar 29;8:654718. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.654718. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33855049 Free PMC article. - Genomic analysis of drug resistant pancreatic cancer cell line by combining long non-coding RNA and mRNA expression profling.
Zhou M, Ye Z, Gu Y, Tian B, Wu B, Li J. Zhou M, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jan 1;8(1):38-52. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25755691 Free PMC article.
References
- Birney E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigo R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH, Weng Z, Snyder M, Dermitzakis ET, Thurman RE. et al.Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 2007;447(7146):799–816. doi: 10.1038/nature05874. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5U01 CA84971-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MOP 13690/Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
- MOP 77903/Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
- MOP 86731/Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources