Transcription of the Hsp30, Hsp70, and Hsp90 heat shock protein genes is modulated by the PalA protein in response to acid pH-sensing in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans - PubMed (original) (raw)
Transcription of the Hsp30, Hsp70, and Hsp90 heat shock protein genes is modulated by the PalA protein in response to acid pH-sensing in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans
Janaína S Freitas et al. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011 Sep.
Abstract
Heat shock proteins are molecular chaperones linked to a myriad of physiological functions in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In this study, we show that the Aspergillus nidulans hsp30 (ANID_03555.1), hsp70 (ANID_05129.1), and hsp90 (ANID_08269.1) genes are preferentially expressed in an acidic milieu, whose expression is dependent on the palA (+) background under optimal temperature for fungal growth. Heat shock induction of these three hsp genes showed different patterns in response to extracellular pH changes in the palA(+) background. However, their accumulation upon heating for 2 h was almost unaffected by ambient pH changes in the palA (-) background. The PalA protein is a member of a conserved signaling cascade that is involved in the pH-mediated regulation of gene expression. Moreover, we identified several genes whose expression at pH 5.0 is also dependent on the palA (+) background. These results reveal novel aspects of the heat- and pH-sensing networks of A. nidulans.
Figures
Fig. 1
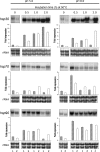
Northern blot analysis of hsp transcripts using total RNA from the control and palA1 strains of A. nidulans. The conidia from the control (lane 1) and palA1 (lane 2) strains were grown for 7 h at 37°C in low-Pi medium buffered at pH 5.0 or pH 8.0. The mycelia were incubated at 50°C for the time indicated. The ethidium bromide-stained rRNA band is shown as the loading control. The bars indicate the relative fold expression determined from the densitometric analyses. The data represent the average values ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent blot exposures
Fig. 2
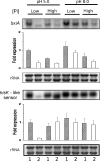
Northern blot analysis of bxiA and sensor histidine kinase (_hisK_-like sensor) transcripts using total RNA from the control and palA1 strains of A. nidulans. The conidia from the control (lane 1) and palA1 (lane 2) strains were grown for 7 h at 37°C in low- or high-Pi liquid medium buffered at pH 5.0 or pH 8.0. The ethidium bromide-stained rRNA band is shown as the loading control. The bars indicate the relative fold expression determined from the densitometric analyses. The data represent the average values ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent blot exposures
Fig. 3
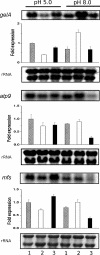
Northern blot analysis of the gelA, atp9, and mfs transcripts using total RNA from the control, palA1, and palC4 strains of A. nidulans. The conidia from the control (lane 1), palA1 (lane 2), and palC4 (lane 3) strains were grown for 7 h at 37°C in a low-Pi liquid medium buffered at pH 5.0 or pH 8.0. The ethidium bromide-stained rRNA band is shown as the loading control. The bars indicate the relative fold expression determined from the densitometric analyses. The data represent the average values ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent blot exposures
Similar articles
- Transcription of the Neurospora crassa 70-kDa class heat shock protein genes is modulated in response to extracellular pH changes.
Squina FM, Leal J, Cipriano VT, Martinez-Rossi NM, Rossi A. Squina FM, et al. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010 Mar;15(2):225-31. doi: 10.1007/s12192-009-0131-z. Epub 2009 Jul 18. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010. PMID: 19618296 Free PMC article. - Characterization of the pH signal transduction pathway gene palA of Aspergillus nidulans and identification of possible homologs.
Negrete-Urtasun S, Denison SH, Arst HN Jr. Negrete-Urtasun S, et al. J Bacteriol. 1997 Mar;179(5):1832-5. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.5.1832-1835.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9045850 Free PMC article. - Identification of genes differentially expressed in a strain of the mold Aspergillus nidulans carrying a loss-of-function mutation in the palA gene.
Silva EM, Freitas JS, Gras DE, Squina FM, Leal J, Silveira HC, Martinez-Rossi NM, Rossi A. Silva EM, et al. Can J Microbiol. 2008 Oct;54(10):803-11. doi: 10.1139/w08-072. Can J Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18923548 - pH regulation of gene expression in fungi.
Denison SH. Denison SH. Fungal Genet Biol. 2000 Mar;29(2):61-71. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.2000.1188. Fungal Genet Biol. 2000. PMID: 10919375 Review. - The expression and function of hsp30-like small heat shock protein genes in amphibians, birds, fish, and reptiles.
Heikkila JJ. Heikkila JJ. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2017 Jan;203:179-192. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27649598 Review.
Cited by
- Aspergillus niger Environmental Isolates and Their Specific Diversity Through Metabolite Profiling.
Šimonovičová A, Vojtková H, Nosalj S, Piecková E, Švehláková H, Kraková L, Drahovská H, Stalmachová B, Kučová K, Pangallo D. Šimonovičová A, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 23;12:658010. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.658010. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34248871 Free PMC article. - Fungal heat shock proteins: molecular phylogenetic insights into the host takeover.
Sagini JPN, Ligabue-Braun R. Sagini JPN, et al. Naturwissenschaften. 2024 Mar 14;111(2):16. doi: 10.1007/s00114-024-01903-x. Naturwissenschaften. 2024. PMID: 38483597 - Tracking fungal species-level responses in soil environments exposed to long-term warming and associated drying.
Romero-Olivares AL, Frey SD, Treseder KK. Romero-Olivares AL, et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023 Jan 17;370:fnad128. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnad128. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38059856 Free PMC article. - Ecology of aspergillosis: insights into the pathogenic potency of Aspergillus fumigatus and some other Aspergillus species.
Paulussen C, Hallsworth JE, Álvarez-Pérez S, Nierman WC, Hamill PG, Blain D, Rediers H, Lievens B. Paulussen C, et al. Microb Biotechnol. 2017 Mar;10(2):296-322. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12367. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Microb Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27273822 Free PMC article. Review. - Insights and Perspectives on the Role of Proteostasis and Heat Shock Proteins in Fungal Infections.
Neves-da-Rocha J, Santos-Saboya MJ, Lopes MER, Rossi A, Martinez-Rossi NM. Neves-da-Rocha J, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 25;11(8):1878. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11081878. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources