Physiological and behavioral adaptation to relocation stress in differentially reared rhesus monkeys: hair cortisol as a biomarker for anxiety-related responses - PubMed (original) (raw)
Physiological and behavioral adaptation to relocation stress in differentially reared rhesus monkeys: hair cortisol as a biomarker for anxiety-related responses
Amanda M Dettmer et al. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012 Feb.
Abstract
Increased hair cortisol concentrations have been associated with stress exposure in both human and nonhuman primates, and hair cortisol is now gaining attention as a biomarker for stress-related health problems. The present study examined the behavioral and physiological reactions of rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) infants reared in three different rearing environments to the major stressor of relocation. Infant monkeys (n=61) were studied from birth through 2 years of age. For the first 8 months of life, infants were either with their mothers and peers (MPR, n=21) or reared in a nursery using either peer-rearing (PR, n=20) or surrogate-peer-rearing (SPR, n=20). At approximately 8 months of age, infants were removed from their rearing group, simultaneously placed into a large social environment consisting of infants from all three rearing conditions, and observed for the next 16 months. Behavior was recorded twice per week from 1 to 24 months, and composite anxiety scores were calculated for each monkey. Monkeys were initially shaved at the nape of the neck on day 14 to remove any prenatal effects on hair cortisol deposition. Hair samples were then collected by re-shaving at 6, 12, 18 and 24 months and analyzed for cortisol content. MPR monkeys were the least affected by the stressor, showing smaller increases in anxious behavior than the other groups and more rapid physiological adaptation as assessed using hair cortisol. PR monkeys showed heightened and prolonged anxious behavior, had the highest cortisol levels prior to relocation, and their cortisol levels did not decline until more than a year later. SPR monkeys exhibited more rapid behavioral adaptation than PR monkeys, showing heightened but not prolonged anxious behavior. However, the SPR group showed a marked increase in cortisol in response to the relocation, and like the PR group, their physiological adaptation was slower than that of the MPR group as indicated by elevated cortisol levels at 18 months. By 24 months of age (16 months after relocation), all rearing groups were indistinguishable from one another physiologically and behaviorally. Spearman rank correlation revealed that hair cortisol taken at month 6 was not correlated with composite anxiety scores from months 6 to 8 (just before the relocation), but was positively correlated with composite anxiety scores between months 8 and 12 (immediately after relocation) for PR infants only (r(s)=0.75, p<0.001). Month 6-hair cortisol tended to positively correlate with composite anxiety scores for the following 6 months (months 12-18) for PR monkeys only (r(s)=0.47, p=0.037), which exhibited more anxious behavior than MPR and SPR infants during this period (ANOVA: F((2,60))=14.761, p<0.001) This is the first study to show that elevated hair cortisol early in life is a biomarker for the later development of anxious behavior in response to a major life stressor, particularly for infant monkeys exposed to early life adversity in the form of peer-rearing.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
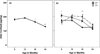
Figure 1
(a) Hair cortisol concentrations declined across the first two years of life. *month 18 < month 12 (_p_<0.05); **month 24 < months 6, 12, and 18 (_p_<0.01). (b) Rearing differences in hair cortisol across the first 2 years of life. *PR > MPR=SPR (p<0.05); ** PR=SPR > MPR (p<0.01). Data shown as mean ± SEM.
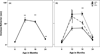
Figure 2
(a) Anxious behavior rose and remained elevated after the major life stressor at month 8, then returned to pre-move levels. **differs from every other time point (p<0.001). (b) Rearing differences in anxious behavior across the first 2 years of life. **PR > MPR=SPR (_p_≤0.01). Data shown as mean ± SEM.
Similar articles
- Associations between early life experience, chronic HPA axis activity, and adult social rank in rhesus monkeys.
Dettmer AM, Wooddell LJ, Rosenberg KL, Kaburu SS, Novak MA, Meyer JS, Suomi SJ. Dettmer AM, et al. Soc Neurosci. 2017 Feb;12(1):92-101. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2016.1176952. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Soc Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27063359 Free PMC article. - Social stability influences the association between adrenal responsiveness and hair cortisol concentrations in rhesus macaques.
Vandeleest JJ, Capitanio JP, Hamel A, Meyer J, Novak M, Mendoza SP, McCowan B. Vandeleest JJ, et al. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019 Feb;100:164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30342315 Free PMC article. - Hair cortisol predicts object permanence performance in infant rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta).
Dettmer AM, Novak MF, Novak MA, Meyer JS, Suomi SJ. Dettmer AM, et al. Dev Psychobiol. 2009 Dec;51(8):706-13. doi: 10.1002/dev.20405. Dev Psychobiol. 2009. PMID: 19771550 Free PMC article. - Population density-dependent hair cortisol concentrations in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta).
Dettmer AM, Novak MA, Meyer JS, Suomi SJ. Dettmer AM, et al. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014 Apr;42:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24636502 Free PMC article. - Stress-linked cortisol concentrations in hair: what we know and what we need to know.
Sharpley CF, McFarlane JR, Slominski A. Sharpley CF, et al. Rev Neurosci. 2011 Dec 8;23(1):111-21. doi: 10.1515/RNS.2011.058. Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22150070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Atypical experiences of captive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) are associated with higher hair cortisol concentrations as adults.
Jacobson SL, Freeman HD, Santymire RM, Ross SR. Jacobson SL, et al. R Soc Open Sci. 2017 Dec 13;4(12):170932. doi: 10.1098/rsos.170932. eCollection 2017 Dec. R Soc Open Sci. 2017. PMID: 29308234 Free PMC article. - Early life temperamental anxiety is associated with excessive alcohol intake in adolescence: A rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) model.
Wood EK, Kruger R, Cash E, Lindell SG, Schwandt ML, Barr CS, Suomi SJ, Higley JD. Wood EK, et al. Addict Biol. 2020 Nov;25(6):e12825. doi: 10.1111/adb.12825. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Addict Biol. 2020. PMID: 31670432 Free PMC article. - Are hair cortisol levels dependent on hair growth rate? A pilot study in rhesus macaques.
Dettmer AM, Novak MA, Meyer JS. Dettmer AM, et al. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2023 Sep 1;340:114308. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2023.114308. Epub 2023 May 25. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37244411 Free PMC article. - Longitudinal Baboon (Papio anubis) Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), and Correlations with Monthly Sedation Rate and Within-Group Sedation Order.
Neal SJ, Schapiro SJ, Magden ER. Neal SJ, et al. Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 11;11(9):423. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11090423. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39330802 Free PMC article. - Womb to womb: Maternal litter size and birth weight but not adult characteristics predict early neonatal death of offspring in the common marmoset monkey.
Rutherford JN, Ross CN, Ziegler T, Burke LA, Steffen AD, Sills A, Layne Colon D, deMartelly VA, Narapareddy LR, Tardif SD. Rutherford JN, et al. PLoS One. 2021 Jun 9;16(6):e0252093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252093. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34106943 Free PMC article.
References
- Blumstein DT, Daniel JC, Evans CS. JWatcher (Version 1.0) [Software] 2006 Available from http://www.jwatcher.ucla.edu.
- Capitanio JP, Mendoza SP, Mason WA, Maninger N. Rearing environment and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal regulations in young rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) Dev. Psychobiol. 2005;46:318–330. - PubMed
- Clarke AS. Social rearing effects on HPA axis activity over early development and in response to stress in rhesus monkeys. Dev. Psychobiol. 1993;26:433–446. - PubMed
- Coplan JD, Andrews MW, Rosenblum LA, Owens MJ, Friedman S, Gorman JM, Nemeroff CB. Persistent elevations of cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of corticotrophin releasing hormone in adult nonhuman primates exposed to early life stressors: implications for the pathophysiology of mood and anxiety disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996;93:1619–1623. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous