Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in an exploratory trial of intravenous minocycline for acute ischemic stroke - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in an exploratory trial of intravenous minocycline for acute ischemic stroke
Jeffrey A Switzer et al. Stroke. 2011 Sep.
Abstract
Background and purpose: Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 levels predict posttissue plasminogen activator (tPA) hemorrhage.
Methods: The authors investigated the effect of minocycline on plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 in acute ischemic stroke in the Minocycline to Improve Neurological Outcome in Stroke (MINOS) trial and a comparison group.
Results: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 level decreased at 72 hours compared with baseline in MINOS (tPA, P=0.0022; non-tPA, P=0.0066) and was lower than in the non-MINOS comparison group at 24 hours (tPA, P<0.0001; non-tPA, P=0.0019).
Conclusions: Lower plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 was seen among tPA-treated subjects in the MINOS trial. Combining minocycline with tPA may prevent the adverse consequences of thrombolytic therapy through suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity.
Figures
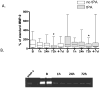
Figure 1
Levels of MMP-9 over time in MINOS. (A) MMP-9 levels in tPA-treated and tPA-untreated subjects at each timepoint in MINOS.Box = 25 to 75% interquartile range; horizontal line = median; vertical lines = range. *p < 0.0083. (B) A representative zymogram from a MINOS patient showing MMP-9 over time.
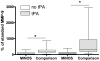
Figure 2
Levels of MMP-9 in MINOS and comparison subjects at 24 hours. MMP-9 in tPA-treated and tPA-untreated MINOS and comparison subjects at 24 hours. Box = 25 to 75% interquartile range; horizontal line = median; vertical lines = range. *p < 0.0125.
Comment in
- Letter by Lee regarding article, "Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in an exploratory trial of intravenous minocycline for acute stroke".
Lee R. Lee R. Stroke. 2011 Oct;42(10):e566; author reply e567. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.632869. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21903959 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Extension of the thrombolytic time window with minocycline in experimental stroke.
Murata Y, Rosell A, Scannevin RH, Rhodes KJ, Wang X, Lo EH. Murata Y, et al. Stroke. 2008 Dec;39(12):3372-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.514026. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Stroke. 2008. PMID: 18927459 Free PMC article. - Letter by Lee regarding article, "Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in an exploratory trial of intravenous minocycline for acute stroke".
Lee R. Lee R. Stroke. 2011 Oct;42(10):e566; author reply e567. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.632869. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21903959 No abstract available. - Effects of minocycline plus tissue plasminogen activator combination therapy after focal embolic stroke in type 1 diabetic rats.
Fan X, Lo EH, Wang X. Fan X, et al. Stroke. 2013 Mar;44(3):745-52. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000309. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23422086 Free PMC article. - Repurposing an old drug to improve the use and safety of tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: minocycline.
Hess DC, Fagan SC. Hess DC, et al. Pharmacotherapy. 2010 Jul;30(7 Pt 2):55S-61S. doi: 10.1592/phco.30.pt2.55S. Pharmacotherapy. 2010. PMID: 20575623 Free PMC article. Review. - Low- versus Standard-Dose Intravenous Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator for Acute Ischemic Stroke: An Updated Meta-Analysis.
Liu H, Zheng H, Cao Y, Pan Y, Wang D, Zhang R, You S, Zhang X, Li S, Tong X, Liu CF, Wang Y. Liu H, et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Apr;27(4):988-997. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29224744 Review.
Cited by
- Systems Biology of Immunomodulation for Post-Stroke Neuroplasticity: Multimodal Implications of Pharmacotherapy and Neurorehabilitation.
Alam MA, Subramanyam Rallabandi VP, Roy PK. Alam MA, et al. Front Neurol. 2016 Jun 28;7:94. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00094. eCollection 2016. Front Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27445961 Free PMC article. - Ischemic postconditioning decreases cerebral edema and brain blood barrier disruption caused by relief of carotid stenosis in a rat model of cerebral hypoperfusion.
Yang F, Zhang X, Sun Y, Wang B, Zhou C, Luo Y, Ge P. Yang F, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057869. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469092 Free PMC article. - Cerebral microvascular matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3) contributes to vascular injury after stroke in female diabetic rats.
Abdul Y, Jamil S, Li W, Ergul A. Abdul Y, et al. Neurochem Int. 2023 Jan;162:105462. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105462. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Neurochem Int. 2023. PMID: 36509234 Free PMC article. - Hemorrhagic Transformation after Tissue Plasminogen Activator Reperfusion Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms, Models, and Biomarkers.
Wang W, Li M, Chen Q, Wang J. Wang W, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;52(3):1572-1579. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8952-x. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25367883 Free PMC article. Review. - Gelatinase activity imaged by activatable cell-penetrating peptides in cell-based and in vivo models of stroke.
Chen S, Cui J, Jiang T, Olson ES, Cai QY, Yang M, Wu W, Guthrie JM, Robertson JD, Lipton SA, Ma L, Tsien RY, Gu Z. Chen S, et al. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017 Jan;37(1):188-200. doi: 10.1177/0271678X15621573. Epub 2015 Dec 17. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017. PMID: 26681768 Free PMC article.
References
- Ning M, Furie KL, Koroshetz WJ, Lee H, Barron M, Lederer M, Wang X, Zhu M, Sorensen AG, Lo EH, Kelly PJ. Association between tpa therapy and raised early matrix metalloproteinase-9 in acute stroke. Neurology. 2006;66:1550–1555. - PubMed
- Montaner J, Alvarez-Sabin J, Molina C, Angles A, Abilleira S, Arenillas J, Gonzalez MA, Monasterio J. Matrix metalloproteinase expression after human cardioembolic stroke: Temporal profile and relation to neurological impairment. Stroke. 2001;32:1759–1766. - PubMed
- Montaner J, Molina CA, Monasterio J, Abilleira S, Arenillas JF, Ribo M, Quintana M, Alvarez-Sabin J. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 pretreatment level predicts intracranial hemorrhagic complications after thrombolysis in human stroke. Circulation. 2003;107:598–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS055728/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS063965/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS063965/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS055728/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000347/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical