Misfolded SOD1 associated with motor neuron mitochondria alters mitochondrial shape and distribution prior to clinical onset - PubMed (original) (raw)
Misfolded SOD1 associated with motor neuron mitochondria alters mitochondrial shape and distribution prior to clinical onset
Christine Vande Velde et al. PLoS One. 2011.
Abstract
Mutations in superoxide dismutase (SOD1) are causative for inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A proportion of SOD1 mutant protein is misfolded onto the cytoplasmic face of mitochondria in one or more spinal cord cell types. By construction of mice in which mitochondrially targeted enhanced green fluorescent protein is selectively expressed in motor neurons, we demonstrate that axonal mitochondria of motor neurons are primary in vivo targets for misfolded SOD1. Mutant SOD1 alters axonal mitochondrial morphology and distribution, with dismutase active SOD1 causing mitochondrial clustering at the proximal side of Schmidt-Lanterman incisures within motor axons and dismutase inactive SOD1 producing aberrantly elongated axonal mitochondria beginning pre-symptomatically and increasing in severity as disease progresses. Somal mitochondria are altered by mutant SOD1, with loss of the characteristic cylindrical, networked morphology and its replacement by a less elongated, more spherical shape. These data indicate that mutant SOD1 binding to mitochondria disrupts normal mitochondrial distribution and size homeostasis as early pathogenic features of SOD1 mutant-mediated ALS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
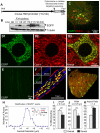
Figure 1. Generation of a novel transgenic mouse with mitochondria labeled uniquely in motor neurons.
(A) Schematic of Hb9-MitoEGFP transgene. (B) Immunoblot of spinal cord homogenates of Hb9-MitoEGFP founders (F34, F17, F36, F20) and F34 sublines probed for EGFP and tubulin (loading control). (C–G) MitoEGFP (green) expression in spinal cord motor neurons (C & D), sciatic nerve (E), and L5 motor axons (F & G) labeled with SMI32 (C, red), cytochrome c (D & F, red), and Fluoromyelin Red (F & G, blue/red). Note that mitochondria have typical tubular and punctate morphologies and MitoEGFP expression is excluded from Schwann cells. (G & H) 15% of large caliber (>4.5 µm) L5 motor axons express MitoEGFP in 12 months animal. The expected biphasic distribution of axonal caliber in adult C57Bl/6 mice is indicated in the upper right corner. Comparison of axonal and somal mitochondrial length (I), width (J) and aspect ratio (K) in Hb9-MitoEGFP mice. Scale bars, 10 µm.
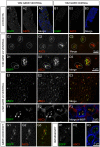
Figure 2. Misfolded SOD1 associates with motor neuron axonal mitochondria in vivo.
An antibody raised against misfolded SOD1 (A5C3, red) labels ventral (A) but not dorsal (B) axons of 10 month SOD1G85R mouse. Myelin Basic Protein (MBP, blue) is included as a counter-label. Misfolded SOD1 (A5C3, red) is often colocalized with mitochondria (EGFP, green) in motor axons of both SOD1G85R (C & D) and SOD1G37R animals (E & F) but not non-SOD1 MitoEGFP littermates (H). Regions of the spinal cord, consistent with axonal exit zones also demonstrate double-labeling (G). The boundaries of individual axons are indicated either by MBP labeling (blue) or dotted lines. Scale bars are as indicated.
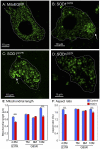
Figure 3. Motor neuron mitochondria are rounder in mutant SOD1 mice.
MitoEGFP (green) expression in spinal cord motor neurons in control MitoEGFP (A) and SOD1G37R early symptomatic animals (B–D). The control neuron has normal mitochondria of diverse shapes and sizes. In contrast, SOD1G37R motor neurons have rounded swollen mitochondria with uneven distribution. Arrows indicate possible axon hillocks. Motor neuron boundaries have been outlined with dotted line. Quantification of mitochondrial length (E) and aspect ratio (F) in motor neuron cell bodies of mutant SOD1 animals of various ages and age-matched MitoEGFP control animals. ***, p<0.0005. Scale bars, 10 µm.
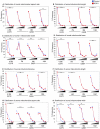
Figure 4. Distributions of mitochondrial morphology and distribution.
Distributions in various morphological parameters of somal (A–D) and axonal (E–H) mitochondria. Bins for area (A,E) are 0–0.25, 0.26–0.50, 0.51–0.75, 0.76–1.0, and >1.0 µm2. Bins for length (B,F) are 0–1, 1.01–2, 2.01–3, 3.01–4, and >4 µm. Bins for aspect ratio (C,G) are 1–2, 2.01–4, 4.01–6, 6.01–8, and >8. Bins for width (D,H) are 0–0.25, 0.26–0.50, 0.51–0.75, 0.76–1.0, and >1.0 µm. Statistics have been calculated using Chi-square with Yates' correction for continuity and significant differences in distributions are indicated: *, p<0.05; **, p<0.005; ***, p<0.0005.
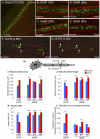
Figure 5. Mitochondria morphology is altered in mutant SOD1 axons.
MitoEGFP (green) expressed in the sciatic nerves in control (A), asymptomatic SOD1G85R 7 months (B and C), SOD1G85R 8 months (D and E), and SOD1G37R early symptomatic (F and G) labeled with Fluoromyelin red (red). Round and evenly distributed mitochondria are seen in both SOD1G85R (symptomatic stage) and SOD1G37R (early symptomatic stage). Mitochondria `pile-up or clusters are also seen in the proximal side of SLIs (arrows) in the SOD1G37R axons. Arrowheads indicate “strings” of mitochondria. Arrows indicate SLIs (H) Schematic indicating proximal and distal locations of SLIs. Mitochondrial area (I), length (J), aspect ratio (K), and density (L) were evaluated in motor axons of the sciatic nerves of and mutant SOD1 animals of various ages and age-matched MitoEGFP control animals, as described in detail in the Materials and Methods. Statistics are indicated: *, p<0.05; **, p<0.005; ***, p<0.0005.
or clusters are also seen in the proximal side of SLIs (arrows) in the SOD1G37R axons. Arrowheads indicate “strings” of mitochondria. Arrows indicate SLIs (H) Schematic indicating proximal and distal locations of SLIs. Mitochondrial area (I), length (J), aspect ratio (K), and density (L) were evaluated in motor axons of the sciatic nerves of and mutant SOD1 animals of various ages and age-matched MitoEGFP control animals, as described in detail in the Materials and Methods. Statistics are indicated: *, p<0.05; **, p<0.005; ***, p<0.0005.
Similar articles
- Enhancing mitochondrial calcium buffering capacity reduces aggregation of misfolded SOD1 and motor neuron cell death without extending survival in mouse models of inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Parone PA, Da Cruz S, Han JS, McAlonis-Downes M, Vetto AP, Lee SK, Tseng E, Cleveland DW. Parone PA, et al. J Neurosci. 2013 Mar 13;33(11):4657-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1119-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23486940 Free PMC article. - Selective association of misfolded ALS-linked mutant SOD1 with the cytoplasmic face of mitochondria.
Vande Velde C, Miller TM, Cashman NR, Cleveland DW. Vande Velde C, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 11;105(10):4022-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712209105. Epub 2008 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18296640 Free PMC article. - Misfolded SOD1 and ALS: zeroing in on mitochondria.
Pickles S, Vande Velde C. Pickles S, et al. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2012 Jun;13(4):333-40. doi: 10.3109/17482968.2012.648645. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2012. PMID: 22471903 Review. - Mitochondrial damage revealed by immunoselection for ALS-linked misfolded SOD1.
Pickles S, Destroismaisons L, Peyrard SL, Cadot S, Rouleau GA, Brown RH Jr, Julien JP, Arbour N, Vande Velde C. Pickles S, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Oct 1;22(19):3947-59. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt249. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23736301 Free PMC article. - Oxidized/misfolded superoxide dismutase-1: the cause of all amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?
Kabashi E, Valdmanis PN, Dion P, Rouleau GA. Kabashi E, et al. Ann Neurol. 2007 Dec;62(6):553-9. doi: 10.1002/ana.21319. Ann Neurol. 2007. PMID: 18074357 Review.
Cited by
- Copper toxicity and deficiency: the vicious cycle at the core of protein aggregation in ALS.
Min JH, Sarlus H, Harris RA. Min JH, et al. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jul 9;17:1408159. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1408159. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39050823 Free PMC article. Review. - A Cellular Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis to Study the Therapeutic Effects of Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Microglial Activation.
Dabrowska S, Turano E, Scambi I, Virla F, Nodari A, Pezzini F, Galiè M, Bonetti B, Mariotti R. Dabrowska S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 24;25(11):5707. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115707. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891895 Free PMC article. - Skeletal muscle dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a mitochondrial perspective and therapeutic approaches.
Kubat GB, Picone P. Kubat GB, et al. Neurol Sci. 2024 Sep;45(9):4121-4131. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07508-6. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38676818 Free PMC article. Review. - New Insights into Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Scarian E, Viola C, Dragoni F, Di Gerlando R, Rizzo B, Diamanti L, Gagliardi S, Bordoni M, Pansarasa O. Scarian E, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 26;25(5):2698. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052698. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473944 Free PMC article. Review. - Mitochondria: A Promising Convergent Target for the Treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.
Cunha-Oliveira T, Montezinho L, Simões RF, Carvalho M, Ferreiro E, Silva FSG. Cunha-Oliveira T, et al. Cells. 2024 Jan 29;13(3):248. doi: 10.3390/cells13030248. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Boillee S, Vande Velde C, Cleveland DW. ALS: A disease of motor neurons and their nonneuronal neighbors. Neuron. 2006;52:1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R01 NS027036/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 089701/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R37 NS027036/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS27036/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous