Gene set enrichment analysis: performance evaluation and usage guidelines - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Gene set enrichment analysis: performance evaluation and usage guidelines
Jui-Hung Hung et al. Brief Bioinform. 2012 May.
Abstract
A central goal of biology is understanding and describing the molecular basis of plasticity: the sets of genes that are combinatorially selected by exogenous and endogenous environmental changes, and the relations among the genes. The most viable current approach to this problem consists of determining whether sets of genes are connected by some common theme, e.g. genes from the same pathway are overrepresented among those whose differential expression in response to a perturbation is most pronounced. There are many approaches to this problem, and the results they produce show a fair amount of dispersion, but they all fall within a common framework consisting of a few basic components. We critically review these components, suggest best practices for carrying out each step, and propose a voting method for meeting the challenge of assessing different methods on a large number of experimental data sets in the absence of a gold standard.
Figures
Figure 1:
Key components of performing gene set enrichment analysis.
Figure 2:
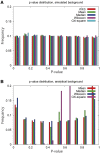
_P_-value distribution of null by (A) simulated background and (B) analytical background. It is clear that analytical backgrounds give biased _P_-value distributions. WKS (i.e. GSEA) is not shown in (B), because WKS does not follow an analytical background.
Figure 3:
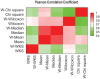
The Pearson correlation coefficient between all 10 gene-set statistics. The ‘W’- prefix indicates a TIF weighted statistic.
Similar articles
- Gene expression analysis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using gene set enrichment analysis for biostatistical management.
Maruschke M, Reuter D, Koczan D, Hakenberg OW, Thiesen HJ. Maruschke M, et al. BJU Int. 2011 Jul;108(2 Pt 2):E29-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09794.x. Epub 2011 Mar 16. BJU Int. 2011. PMID: 21435154 - Comparative study of gene set enrichment methods.
Abatangelo L, Maglietta R, Distaso A, D'Addabbo A, Creanza TM, Mukherjee S, Ancona N. Abatangelo L, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Sep 2;10:275. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-275. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19725948 Free PMC article. - Gene set enrichment; a problem of pathways.
Davies MN, Meaburn EL, Schalkwyk LC. Davies MN, et al. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010 Dec;9(5-6):385-90. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elq021. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20861160 Free PMC article. - Translational Metabolomics of Head Injury: Exploring Dysfunctional Cerebral Metabolism with Ex Vivo NMR Spectroscopy-Based Metabolite Quantification.
Wolahan SM, Hirt D, Glenn TC. Wolahan SM, et al. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. PMID: 26269925 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Comparing algorithms for clustering of expression data: how to assess gene clusters.
Yona G, Dirks W, Rahman S. Yona G, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:479-509. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381534 Review.
Cited by
- Consensus comparative analysis of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
Zhang S, Poon E, Xie D, Boheler KR, Li RA, Wong HS. Zhang S, et al. PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0125442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125442. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938587 Free PMC article. - A new microphysiological system shows hypoxia primes human ISCs for interleukin-dependent rescue of stem cell activity.
Rivera KR, Bliton RJ, Burclaff J, Czerwinski MJ, Liu J, Trueblood JM, Hinesley CM, Breau KA, Joshi S, Pozdin VA, Yao M, Ziegler AL, Blikslager AT, Daniele MA, Magness ST. Rivera KR, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 1:2023.01.31.524747. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.31.524747. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 36778265 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - Survival Prognosis, Tumor Immune Landscape, and Immune Responses of PPP1R18 in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma and Its Potentially Double Mechanisms.
Wang Y, Liu S, Chen Y, Zhu B, Xing Q. Wang Y, et al. World J Oncol. 2022 Feb;13(1):27-37. doi: 10.14740/wjon1446. Epub 2022 Feb 28. World J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35317332 Free PMC article. - Incorporating Pathway Information into Feature Selection towards Better Performed Gene Signatures.
Tian S, Wang C, Wang B. Tian S, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 3;2019:2497509. doi: 10.1155/2019/2497509. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31073522 Free PMC article. Review. - A novel microRNA signature predicts survival in stomach adenocarcinoma.
Ding B, Gao X, Li H, Liu L, Hao X. Ding B, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 25;8(17):28144-28153. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15961. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423653 Free PMC article.
References
- Molecular Signatures Database v3.0. Available from: http://www.broadinstitute.org/gsea/msigdb/index.jsp (9 September 2010, date last accessed)
- Gilchrist A, Au CE, Hiding J, et al. Quantitative proteomics analysis of the secretory pathway. Cell. 2006;127(6):1265–81. - PubMed