An overview of population genetic data simulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
An overview of population genetic data simulation
Xiguo Yuan et al. J Comput Biol. 2012 Jan.
Abstract
Simulation studies in population genetics play an important role in helping to better understand the impact of various evolutionary and demographic scenarios on sequence variation and sequence patterns, and they also permit investigators to better assess and design analytical methods in the study of disease-associated genetic factors. To facilitate these studies, it is imperative to develop simulators with the capability to accurately generate complex genomic data under various genetic models. Currently, a number of efficient simulation software packages for large-scale genomic data are available, and new simulation programs with more sophisticated capabilities and features continue to emerge. In this article, we review the three basic simulation frameworks--coalescent, forward, and resampling--and some of the existing simulators that fall under these frameworks, comparing them with respect to their evolutionary and demographic scenarios, their computational complexity, and their specific applications. Additionally, we address some limitations in current simulation algorithms and discuss future challenges in the development of more powerful simulation tools.
Figures
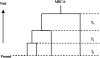
FIG. 1.
Kingman's n-coalescent process.
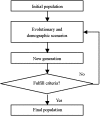
FIG. 2.
The general architecture of forward-time simulation.
Similar articles
- GENOMEPOP: a program to simulate genomes in populations.
Carvajal-Rodríguez A. Carvajal-Rodríguez A. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Apr 30;9:223. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-223. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18447924 Free PMC article. - Critical assessment of coalescent simulators in modeling recombination hotspots in genomic sequences.
Yang T, Deng HW, Niu T. Yang T, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Jan 3;15:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24387001 Free PMC article. - SLiM 2: Flexible, Interactive Forward Genetic Simulations.
Haller BC, Messer PW. Haller BC, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2017 Jan;34(1):230-240. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw211. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Mol Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 27702775 - Computer simulations: tools for population and evolutionary genetics.
Hoban S, Bertorelle G, Gaggiotti OE. Hoban S, et al. Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Jan 10;13(2):110-22. doi: 10.1038/nrg3130. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22230817 Review. - Genome simulation approaches for synthesizing in silico datasets for human genomics.
Ritchie MD, Bush WS. Ritchie MD, et al. Adv Genet. 2010;72:1-24. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380862-2.00001-1. Adv Genet. 2010. PMID: 21029846 Review.
Cited by
- A Density Peak-Based Method to Detect Copy Number Variations From Next-Generation Sequencing Data.
Xie K, Tian Y, Yuan X. Xie K, et al. Front Genet. 2021 Jan 13;11:632311. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.632311. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33519925 Free PMC article. - Efficient Coalescent Simulation and Genealogical Analysis for Large Sample Sizes.
Kelleher J, Etheridge AM, McVean G. Kelleher J, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 May 4;12(5):e1004842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004842. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27145223 Free PMC article. - Boosting forward-time population genetic simulators through genotype compression.
Ruths T, Nakhleh L. Ruths T, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Jun 14;14:192. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-192. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23763838 Free PMC article. - Demes: a standard format for demographic models.
Gower G, Ragsdale AP, Bisschop G, Gutenkunst RN, Hartfield M, Noskova E, Schiffels S, Struck TJ, Kelleher J, Thornton KR. Gower G, et al. Genetics. 2022 Nov 1;222(3):iyac131. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac131. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 36173327 Free PMC article. - Mate selection: A useful approach to maximize genetic gain and control inbreeding in genomic and conventional oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) hybrid breeding.
Tchounke B, Sanchez L, Bell JM, Cros D. Tchounke B, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Sep 11;19(9):e1010290. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010290. eCollection 2023 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37695766 Free PMC article.
References
- Calafell F. Grigorenko E.L. Chikanian A.A., et al. Haplotype evolution and linkage disequilibrium: a simulation study. Hum. Hered. 2001;51:85–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources