Hepatoprotective and in vitro antioxidant effect of Carthamus tinctorious L, var Annigeri-2-, an oil-yielding crop, against CCl(4) -induced liver injury in rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
Hepatoprotective and in vitro antioxidant effect of Carthamus tinctorious L, var Annigeri-2-, an oil-yielding crop, against CCl(4) -induced liver injury in rats
Mahadevappa Paramesha et al. Pharmacogn Mag. 2011 Oct.
Abstract
Background: The present investigation evaluates the hepatoprotective and in vitro antioxidant effect of methanolic extract and its isolated constituent, dehydroabietylamine, in Carthamus tinctorious L, var Annigeri-2-, an oil yielding crop.
Materials and methods: The hepatoprotective effects were estimated for the parameters viz, total bilirubin, total protein, serum alanine amino transaminase (ALT) and serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and along with the pathological findings of hepatotoxicity. The in vitro antioxidant activity was evaluated by using free radical scavenging assays: DPPH, nitric oxide radical scavenging, hydroxyl radical, reducing power, ferrous ion chelating ability and total antioxidant capacity.
Results: Both the methanolic extract (at 150 and 300 mg/kg bw) and dehydroabietylamine (at 50 mg/kg bw) showed significant liver protection against CCl(4) -induced liver damage that was comparable with the standard drug, silymarin (100 mg/kg bw), in reducing the elevated serum enzyme markers. The liver sections of the animals treated with dehydroabietylamine elicit a significant liver protection compared with the methanolic extract against CCl(4) -induced liver damage. Further, both the methanolic extract and dehydroabietylamine exhibited a considerable and dose-dependent scavenging activity of DPPH, nitric oxide and hydroxyl radical. Similarly, in the reducing power assay, the results were very persuasive. In addition, the Fe(2+) chelating activity and the total antioxidant assay established the antioxidant property of the methanolic extract and its isolated constituent. Among the two experimental samples, dehydroabietylamine proved to be more effective for the said parameters.
Conclusion: The potent antioxidant and its correlative hepatoprotective activity of the methanolic extract and isolated constituent dehydroabietylamine is therefore attributed to its antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Carthamus tinctorious L; carbon tetrachloride; dehydroabietylamine; hepatoprotection; var Annigeri-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures
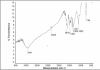
Figure 1a
IR Spectra (3441 Cm-1 for NH2 and 1610 Cm-1 for C=C)
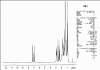
Figure 1b
1H NMR Spectra (singlet at 6.8 δ, a doublet appeared at 7 δ and another doublet at 7.2 δ)
Figure 1c
Mass Spectra, m/z: (m+1): 286
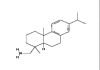
Figure 1d
Structure of Dehydroabietylamine
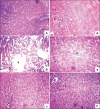
Figure 2
(a) Liver tissue of the control animal showing normal histology (b) Treated with CCl4 showing necrosis, central vein (V) and fatty vacuole (F) (c) Silymarin treated showing normal hepatocytes (arrow mark) with central vein (d) With methanolic extract @150 mg showing absence of necrosis with few fatty vacuoles with normal arrangement of hepatocytes (e) With methanolic extract @ 300 mg showing absence of necrosis with few fatty vacuoles with normal arrangement of hepatocytes (f) With dehydroabietylamine showing normal arrangement of hepatocytes, absence of necrosis and fatty vacuoles
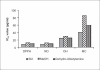
Figure 3
The IC50 values of in vitro antioxidant ability of Methanolic extract and Dehydroabietylamine (DPPH: DPPH radical scavenging activity, NO: Nitric oxide scavenging activity, OH: Hydroxyl ion scavenging activity, MC: Metal chelating activity)
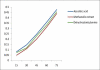
Figure 4
Absorbance of methanolic extract and dehydroabietylamine isolated from C. tinctorious in reducing power assay
Similar articles
- Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of methanolic extract of flowers of Nerium oleander against CCl4-induced liver injury in rats.
Singhal KG, Gupta GD. Singhal KG, et al. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012 Sep;5(9):677-85. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(12)60106-0. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012. PMID: 22805717 - Hautriwaic acid as one of the hepatoprotective constituent of Dodonaea viscosa.
Ali H, Kabir N, Muhammad A, Shah MR, Musharraf SG, Iqbal N, Nadeem S. Ali H, et al. Phytomedicine. 2014 Jan 15;21(2):131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.08.019. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Phytomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24075215 - Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of the methanolic extract from Halenia elliptica.
Huang B, Ban X, He J, Zeng H, Zhang P, Wang Y. Huang B, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Sep 15;131(2):276-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.06.029. Epub 2010 Jun 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20600758 - Exploring the antioxidant and protective effects of Marsdenia thyrsiflora Hook.f. leaf extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in rat models.
Saha S, Alshammari A, Albekairi NA, Zulfiquar TN, Shakil MS, Mondal KR, Kundu MK, Mondal M, Mubarak MS. Saha S, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1463922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1463922. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39502533 Free PMC article. - Hepatoprotective Activity of Some Medicinal Plants in Sudan.
Ali SA, Sharief NH, Mohamed YS. Ali SA, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Dec 18;2019:2196315. doi: 10.1155/2019/2196315. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31929810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Phytochemistry, pharmacology and medicinal properties of Carthamus tinctorius L.
Asgarpanah J, Kazemivash N. Asgarpanah J, et al. Chin J Integr Med. 2013 Feb;19(2):153-9. doi: 10.1007/s11655-013-1354-5. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Chin J Integr Med. 2013. PMID: 23371463 Review. - Cinnamomi Cortex (Cinnamomum verum) Suppresses Testosterone-induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating 5α-reductase.
Choi HM, Jung Y, Park J, Kim HL, Youn DH, Kang J, Jeong MY, Lee JH, Yang WM, Lee SG, Ahn KS, Um JY. Choi HM, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 23;6:31906. doi: 10.1038/srep31906. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27549514 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of diosgenin content from eleven different Indian varieties of fenugreek and fenugreek leaf powder fortified bread.
Paramesha M, Priyanka N, Crassina K, Shetty NP. Paramesha M, et al. J Food Sci Technol. 2021 Dec;58(12):4746-4754. doi: 10.1007/s13197-021-04967-z. Epub 2021 Jan 24. J Food Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34629539 Free PMC article. - The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases.
Li S, Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang ZJ, Lao L, Wong CW, Feng Y. Li S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 2;16(11):26087-124. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125942. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26540040 Free PMC article. Review. - A novel approach for the efficient extraction of silybin from milk thistle fruits.
Tan C, Xu X, Shang Y, Fu X, Xia G, Yang H. Tan C, et al. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Oct;10(40):536-40. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.141799. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014. PMID: 25422558 Free PMC article.
References
- Anthea M, Hopkins J, William C, McLaughlin, Johnson S, Warner MQ, et al. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall; 1993. Human Biology and Health.
- Sinha RK, Sinha S. Jaipur: Surabhi Publishers; 2001. Ethnobiology; Role of Indigenous and Ethnic Societies in Biodiversit conservation, Human Health Protection and Sustainable Development; p. 181.
- Koul IB, Kapil A. Evaluation of the liver protective potential of piperine: An active principle of black and long peppers. Planta Med. 1999;59:413–7. - PubMed
- Varier PS. Vol. 1. New Delhi: Orient Longman Private Ltd; 2007. Indian Medicinal Plants-a compendium of 500 species; pp. 390–3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources