Obesity susceptibility loci and dietary intake in the Look AHEAD Trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2012 Jun;95(6):1477-86.
doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.026955. Epub 2012 Apr 18.
Collaborators, Affiliations
- PMID: 22513296
- PMCID: PMC3349457
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.111.026955
Randomized Controlled Trial
Obesity susceptibility loci and dietary intake in the Look AHEAD Trial
Jeanne M McCaffery et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012 Jun.
Abstract
Background: Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified consistent associations with obesity. However, the mechanisms remain unclear.
Objective: The objective was to determine the association between obesity susceptibility loci and dietary intake.
Design: The association of GWAS-identified obesity risk alleles (FTO, MC4R, SH2B1, BDNF, INSIG2, TNNI3K, NISCH-STAB1, MTIF3, MAP2K5, QPCTL/GIPR, and PPARG) with dietary intake, measured through food-frequency questionnaires, was investigated in 2075 participants from the Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) clinical trial. We adjusted for age, sex, population stratification, and study site.
Results: Obesity risk alleles at FTO rs1421085 significantly predicted more eating episodes per day (P = 0.001)-an effect that persisted after adjustment for body weight (P = 0.004). Risk variants within BDNF were significantly associated with more servings from the dairy product and the meat, eggs, nuts, and beans food groups (P ≤ 0.004). The risk allele at SH2B1 rs4788099 was significantly associated with more servings of dairy products (P = 0.001), whereas the risk allele at TNNI3K rs1514176 was significantly associated with a lower percentage of energy from protein (P = 0.002).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that obesity risk loci may affect the pattern and content of food consumption among overweight or obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. The Look AHEAD Genetic Ancillary Study was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT01270763 and the Look AHEAD study as NCT00017953.
Figures
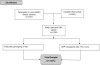
FIGURE 1.
Consort flow diagram. IBC, ITMAT-Broad-CARe array chip; Look AHEAD, Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) clinical trial; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.
Similar articles
- Replication of the Association of BDNF and MC4R Variants With Dietary Intake in the Diabetes Prevention Program.
McCaffery JM, Jablonski KA, Franks PW, Delahanty LM, Aroda V, Marrero D, Hamman RF, Horton ES, Dagogo-Jack S, Wylie-Rosett J, Barrett-Connor E, Kitabchi A, Knowler WC, Wing RR, Florez JC; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. McCaffery JM, et al. Psychosom Med. 2017 Feb/Mar;79(2):224-233. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000380. Psychosom Med. 2017. PMID: 27551991 Free PMC article. - Association of type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci with one-year weight loss in the look AHEAD clinical trial.
Peter I, McCaffery JM, Kelley-Hedgepeth A, Hakonarson H, Reis S, Wagenknecht LE, Kopin AS, Huggins GS; Genetics Subgroup of the Look AHEAD Study. Peter I, et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012 Aug;20(8):1675-82. doi: 10.1038/oby.2012.11. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012. PMID: 22307069 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Implication of genetic variants in overweight and obesity susceptibility among the young Arab population of the United Arab Emirates.
El Hajj Chehadeh S, Osman W, Nazar S, Jerman L, Alghafri A, Sajwani A, Alawlaqi M, AlObeidli M, Jelinek HF, AlAnouti F, Khalaf K, Alsafar H. El Hajj Chehadeh S, et al. Gene. 2020 May 20;739:144509. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144509. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32109558 - Interaction between genes involved in energy intake regulation and diet in obesity.
Crovesy L, Rosado EL. Crovesy L, et al. Nutrition. 2019 Nov-Dec;67-68:110547. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.06.027. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Nutrition. 2019. PMID: 31472367 Review. - What model organisms and interactomics can reveal about the genetics of human obesity.
Williams MJ, Almén MS, Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB. Williams MJ, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Nov;69(22):3819-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1022-5. Epub 2012 May 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22618246 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Genetic Variants in the Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Gene and Risk of Obesity/Overweight in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Eghbali M, Mottaghi A, Taghizadeh S, Cheraghi S. Eghbali M, et al. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024 Jul;7(4):e00510. doi: 10.1002/edm2.510. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38973101 Free PMC article. Review. - Interaction Effects of FTO and MC4R Polymorphisms on Total Body Weight Loss, Post-Surgery Weight, and Post-Body Mass Index after Bariatric Surgery.
Perez-Luque E, Daza-Hernandez ES, Figueroa-Vega N, Cardona-Alvarado MI, Muñoz-Montes N, Martinez-Cordero C. Perez-Luque E, et al. Genes (Basel). 2024 Mar 22;15(4):391. doi: 10.3390/genes15040391. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674326 Free PMC article. - Implication of DNA methylation during lifestyle mediated weight loss.
Aurich S, Müller L, Kovacs P, Keller M. Aurich S, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 8;14:1181002. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1181002. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37614712 Free PMC article. Review. - The rs1421085 variant within FTO promotes brown fat thermogenesis.
Zhang Z, Chen N, Yin N, Liu R, He Y, Li D, Tong M, Gao A, Lu P, Zhao Y, Li H, Zhang J, Zhang D, Gu W, Hong J, Wang W, Qi L, Ning G, Wang J. Zhang Z, et al. Nat Metab. 2023 Aug;5(8):1337-1351. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00847-2. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 37460841 - Impact of the FTO Gene Variation on Appetite and Fat Oxidation in Young Adults.
Ponce-Gonzalez JG, Martínez-Ávila Á, Velázquez-Díaz D, Perez-Bey A, Gómez-Gallego F, Marín-Galindo A, Corral-Pérez J, Casals C. Ponce-Gonzalez JG, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Apr 23;15(9):2037. doi: 10.3390/nu15092037. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432153 Free PMC article.
References
- Cannon CP. Obesity-related cardiometabolic complications. Clin Cornerstone 2008;9:11–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK57151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK056992-11S1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD006899/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK57008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000056 44/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK072497/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK48520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR0021140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK 046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR02719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous