Targeting the insulin growth factor receptor 1 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Targeting the insulin growth factor receptor 1
Fernanda I Arnaldez et al. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2012 Jun.
Abstract
The IGF axis is a tightly controlled endocrine system that regulates cell growth and development, known to have an important function in cancer biology. IGF1 and IGF2 can promote cancer growth in a GH-independent manner both through paracrine and autocrine secretion and can also confer resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Many alterations of this system have been found in neoplasias, including increased expression of ligands and receptors, loss of heterozygosity of the IGF2 locus and increased IGF1R gene copy number. The IGF1 network is an attractive candidate for targeted therapy, including receptor blockade with monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors of receptor downstream signaling. This article reviews the role of the IGF axis in the initiation and progression of cancer, and describes the recent advances in IGF inhibition as a therapeutic tool.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
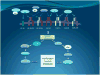
Figure 1. Components of the IGF axis
The IGF axis is composed by two IGF ligands, IGF-I and IGF-II. They bind one of the different IGF binding proteins, (BPs). The majority of circulating IGF is bound to IGFBP-3 and a molecule called acid labile subunit. The different combinations of receptors in the axis bind to IGF-I, IGF-II and insulin with different affinities, as represented by the large or small size of the ligand.
Similar articles
- Targeting insulin-like growth factor signaling: rational combination strategies.
Olmos D, Basu B, de Bono JS. Olmos D, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Sep;9(9):2447-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0719. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20807783 No abstract available. - IGF1R blockade with ganitumab results in systemic effects on the GH-IGF axis in mice.
Moody G, Beltran PJ, Mitchell P, Cajulis E, Chung YA, Hwang D, Kendall R, Radinsky R, Cohen P, Calzone FJ. Moody G, et al. J Endocrinol. 2014 Mar 17;221(1):145-55. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0306. Print 2014 Apr. J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24492468 Free PMC article. - Advances in insulin-like growth factor biology and -directed cancer therapeutics.
Fettig LM, Yee D. Fettig LM, et al. Adv Cancer Res. 2020;147:229-257. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Adv Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32593402 Free PMC article. Review. - Combination of two insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibitory antibodies targeting distinct epitopes leads to an enhanced antitumor response.
Dong J, Demarest SJ, Sereno A, Tamraz S, Langley E, Doern A, Snipas T, Perron K, Joseph I, Glaser SM, Ho SN, Reff ME, Hariharan K. Dong J, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Sep;9(9):2593-604. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-1018. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20716637 - Molecular Pathways: Clinical Applications and Future Direction of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Pathway Blockade.
Iams WT, Lovly CM. Iams WT, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 1;21(19):4270-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2518. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26429980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Clinical next generation sequencing of pediatric-type malignancies in adult patients identifies novel somatic aberrations.
Silva JG, Corrales-Medina FF, Maher OM, Tannir N, Huh WW, Rytting ME, Subbiah V. Silva JG, et al. Oncoscience. 2015 Feb 20;2(2):187-92. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.131. eCollection 2015. Oncoscience. 2015. PMID: 25859559 Free PMC article. - Selecting Targets for Tumor Imaging: An Overview of Cancer-Associated Membrane Proteins.
Boonstra MC, de Geus SW, Prevoo HA, Hawinkels LJ, van de Velde CJ, Kuppen PJ, Vahrmeijer AL, Sier CF. Boonstra MC, et al. Biomark Cancer. 2016 Sep 27;8:119-133. doi: 10.4137/BIC.S38542. eCollection 2016. Biomark Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27721658 Free PMC article. Review. - Adrenocortical carcinoma.
Else T, Kim AC, Sabolch A, Raymond VM, Kandathil A, Caoili EM, Jolly S, Miller BS, Giordano TJ, Hammer GD. Else T, et al. Endocr Rev. 2014 Apr;35(2):282-326. doi: 10.1210/er.2013-1029. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Endocr Rev. 2014. PMID: 24423978 Free PMC article. Review. - Lessons Learned from Targeting IGF-I Receptor in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy.
Janssen JAMJL, Smith TJ. Janssen JAMJL, et al. Cells. 2021 Feb 12;10(2):383. doi: 10.3390/cells10020383. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33673340 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNA and signal transduction pathways in tumor radiation response.
Zhao L, Lu X, Cao Y. Zhao L, et al. Cell Signal. 2013 Jul;25(7):1625-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23602933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Daughaday WH, Hall K, Raben MS, Salmon WD, Jr, van den Brande JL, et al. Somatomedin: proposed designation for sulphation factor. Nature. 1972;235:107. - PubMed
- Pollak M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:915–928. - PubMed
- Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D. Minireview: IGF, Insulin, and Cancer. Endocrinology. 2011;152:2546–2551. - PubMed
- Riedemann J, Macaulay VM. IGF1R signalling and its inhibition. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13(Suppl 1):S33–43. - PubMed
- Pollak M. Insulin-like growth factor-related signaling and cancer development. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007;174:49–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous