Magnetite nanoparticles for functionalized textile dressing to prevent fungal biofilms development - PubMed (original) (raw)
Magnetite nanoparticles for functionalized textile dressing to prevent fungal biofilms development
Ion Anghel et al. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012.
Abstract
The purpose of this work was to investigate the potential of functionalized magnetite nanoparticles to improve the antibiofilm properties of textile dressing, tested in vitro against monospecific Candida albicans biofilms. Functionalized magnetite (Fe3O4/C18), with an average size not exceeding 20 nm, has been synthesized by precipitation of ferric and ferrous salts in aqueous solution of oleic acid (C18) and NaOH. Transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, and differential thermal analysis coupled with thermo gravimetric analysis were used as characterization methods for the synthesized Fe3O4/C18. Scanning electron microscopy was used to study the architecture of the fungal biofilm developed on the functionalized textile dressing samples and culture-based methods for the quantitative assay of the biofilm-embedded yeast cells. The optimized textile dressing samples proved to be more resistant to C. albicans colonization, as compared to the uncoated ones; these functionalized surfaces-based approaches are very useful in the prevention of wound microbial contamination and subsequent biofilm development on viable tissues or implanted devices.
Figures
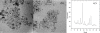
Figure 1
TEM images and XRD pattern of Fe 3 O 4 /C 18 nanofluid.
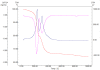
Figure 2
DTA-TG analysis of Fe 3 O 4 /C 18 .
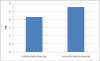
Figure 3
The logarithmic values of viable cell counts of fungal cells. The logarithmic values of viable cell counts of fungal cells which adhered and embedded in biofilms and formed on the textile dressing surface (uncoated versus coated textile dressing).
Figure 4
SEM micrographs of coated (a) and uncoated (b) textile dressing.
Similar articles
- Magnetite-Based Nanostructured Coatings Functionalized with Nigella sativa and Dicloxacillin for Improved Wound Dressings.
Dorcioman G, Hudiță A, Gălățeanu B, Craciun D, Mercioniu I, Oprea OC, Neguț I, Grumezescu V, Grumezescu AM, Dițu LM, Holban AM. Dorcioman G, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;12(1):59. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010059. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671260 Free PMC article. - Biohybrid nanostructured iron oxide nanoparticles and Satureja hortensis to prevent fungal biofilm development.
Anghel I, Grumezescu AM, Holban AM, Ficai A, Anghel AG, Chifiriuc MC. Anghel I, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Sep 4;14(9):18110-23. doi: 10.3390/ijms140918110. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24009022 Free PMC article. - Modified wound dressing with phyto-nanostructured coating to prevent staphylococcal and pseudomonal biofilm development.
Anghel I, Holban AM, Grumezescu AM, Andronescu E, Ficai A, Anghel AG, Maganu M, Laz R V, Chifiriuc MC. Anghel I, et al. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012 Dec 31;7(1):690. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-7-690. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012. PMID: 23272823 Free PMC article. - Hybrid magnetite nanoparticles/Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil nanobiosystem with antibiofilm activity.
Chifiriuc C, Grumezescu V, Grumezescu AM, Saviuc C, Lazăr V, Andronescu E. Chifiriuc C, et al. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012 Apr 10;7(1):209. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-7-209. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012. PMID: 22490675 Free PMC article. - PEG-Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles for Modulation of Microbial Biofilms on Voice Prosthesis.
Caciandone M, Niculescu AG, Roșu AR, Grumezescu V, Negut I, Holban AM, Oprea O, Vasile BȘ, Bîrcă AC, Grumezescu AM, Stan MS, Anghel AG, Anghel I. Caciandone M, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;11(1):39. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010039. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052915 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Impact of Biohybrid Magnetite Nanoparticles and Moroccan Propolis on Adherence of Methicillin Resistant Strains of Staphylococcus aureus.
El-Guendouz S, Aazza S, Lyoussi B, Bankova V, Lourenço JP, Costa AM, Mariano JF, Miguel MG, Faleiro ML. El-Guendouz S, et al. Molecules. 2016 Sep 9;21(9):1208. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091208. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27618006 Free PMC article. - Nanoparticles: Alternatives Against Drug-Resistant Pathogenic Microbes.
Rudramurthy GR, Swamy MK, Sinniah UR, Ghasemzadeh A. Rudramurthy GR, et al. Molecules. 2016 Jun 27;21(7):836. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070836. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27355939 Free PMC article. Review. - MAPLE Coatings Embedded with Essential Oil-Conjugated Magnetite for Anti-Biofilm Applications.
Gherasim O, Popescu RC, Grumezescu V, Mogoșanu GD, Mogoantă L, Iordache F, Holban AM, Vasile BȘ, Bîrcă AC, Oprea OC, Grumezescu AM, Andronescu E. Gherasim O, et al. Materials (Basel). 2021 Mar 25;14(7):1612. doi: 10.3390/ma14071612. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806228 Free PMC article. - Hybrid nanostructured coating for increased resistance of prosthetic devices to staphylococcal colonization.
Anghel I, Grumezescu AM. Anghel I, et al. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013 Jan 2;8(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-8-6. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013. PMID: 23281840 Free PMC article. - Magnetite-Based Nanostructured Coatings Functionalized with Nigella sativa and Dicloxacillin for Improved Wound Dressings.
Dorcioman G, Hudiță A, Gălățeanu B, Craciun D, Mercioniu I, Oprea OC, Neguț I, Grumezescu V, Grumezescu AM, Dițu LM, Holban AM. Dorcioman G, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;12(1):59. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010059. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671260 Free PMC article.
References
- Stewart PS, Mukherjee PK, Ghannoum MA. In: Microbial Biofilms. Ghannoum M, O’Toole GA, editor. Washington: ASM Press; 2004. Biofilm antimicrobial resistance; pp. 250–268.
- Bubulica MV, Anghel I, Grumezescu AM, Saviuc C, Anghel GA, Chifiriuc MC, Gheorghe I, Lazar V, Popescu A. In vitro evaluation of bactericidal and antibiofilm activity of Lonicera tatarica and Viburnum opulus plant extracts on Staphylococcus strains. Farmacia. 2012;60:80.
- Mermel LA, Farr BM, Sherertz RJ, Raad II, O’Grady N, Harris JS, Craven DE. Infectious Diseases Society of America American College of Critical Care Medicine Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Guidelines for the management of intravascular catheter related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1249. doi: 10.1086/320001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources