Plasma specific miRNAs as predictive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of glioma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Plasma specific miRNAs as predictive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of glioma
Qiong Wang et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012.
Abstract
Objective: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly malignant brain tumor with a poor prognosis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNAs, approximately 21-25 nucleotides in length. Recently, some researchers have demonstrated that plasma miRNAs are sensitive and specific biomarkers of various cancers. The primary aim of the study is to investigate whether miRNAs present in the plasma of GBM patients can be used as diagnostic biomarkers and are associated with glioma classification and clinical treatment.
Materials and methods: Plasma samples were attained by venipuncture from 50 patients and 10 healthy donors. Plasma levels of miRNAs were determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Results: The plasma levels of miR-21, miR-128 and miR-342-3p were significantly altered in GBM patients compared to normal controls and could discriminate glioma from healthy controls with high specificity and sensitivity. However, these three miRNAs were not significantly changed in patients with other brain tumors such as meningioma or pituitary adenoma. Furthermore, the plasma levels of these three miRNAs in GBM patients treated by operation and chemo-radiation almost revived to normal levels. Finally, we also demonstrated that miR-128 and miR-342-3p were positively correlated with histopathological grades of glioma.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that plasma specific miRNAs have potential use as novel biomarkers of glioma and may be useful in clinical management for glioma patients.
Figures
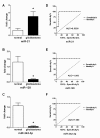
Figure 1
Relative expression levels of miR-21, miR-128 and miR-342-3p in plasma from healthy controls and GBM patients, ROC curve analysis based on expression of each miRNA in plasma. (A, B, C) Expression levels of the miR-21, miR-128 and miR-342-3p are normalized to mmu-miR-295 and analyzed using 2-△△Ct method. Statistically significant differences were determined using the Mann–Whitney U test. Plasma levels of miR-21 are significantly higher in GBM samples than in control samples (P < 0.001), and levels of miR-128 and miR-342-3p are significantly lower in GBM samples than in control samples (P < 0.001). (B) The AUC for miR-21 was 0.9300 (95% CI: 0.7940-1.066) with 90.0% sensitivity and 100% specificity. (D,F) The AUC for miR-128 or miR-342-3p was 1.000 (95% CI: 1.000 – 1.000) with 90.0% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
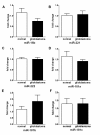
Figure 2
Expression levels miR-15b, miR-221/222, miR-181a/d/c levels in plasma of healthy controls and GBM patients. All these miRNAs are normalized to mmu-miR-295 and analyzed using 2-△△Ct method. Statistically significant differences were determined using the Mann–Whitney U test. There was no significant difference between controls and GBM patients (P > 0.05).
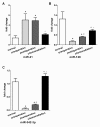
Figure 3
The relationship between the plasma levels of miR-21, miR-128 and miR-342-3p and classification of glioma. (A) Levels of miR-21 were up-regulated in grade II in comparison with control cohorts and much higher in grade III cohorts than in grade II cohorts, however there were no significant difference between glioblastoma patients (grade IV) and grade III cohorts or grade II cohorts. (B) Levels of miR-128 were significantly lower in grade II cohorts than in normal cohorts, much lower in grade III cohorts and in glioblastoma patients than in grade II cohorts (P < 0.001), there were no significant difference between glioblastoma patients and grade III cohorts. (C) Levels of miR-342-3p were significant difference among all formation. *P<0.008 in comparison with normal, #P < 0.008 in comparison with glioma II, △P < 0.008 in comparison with glioma III.
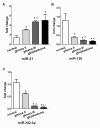
Figure 4
The miR-21, miR-128 and miR-342-3p expression in normal control (n = 10), preoperation (n =10), postoperation (n = 10) and chemo-radiation (n = 10) plasma samples. (A) Plasma levels of miR-21 are not significantly different between preoperative and postoperative patients, but levels of miR-21 are significantly lower in chemo-radiation cohorts. (B) and (C) Levels of miR-128 and miR-342-3p showed significant difference between cohorts of preoperation and postoperation and chemo-radiation. *P < 0.008 in comparison with normal, #P < 0.008 in comparison with preoperation, △P < 0.008 in comparison with postoperation.
Figure 5
Plasma levels of miR-21, miR-128 and miR-342-3p in normal cohorts, meningioma cohorts, pituitary adenoma cohorts and glioma cohorts. (A) Plasma levels of miR-21 are significantly increased in glioma samples compared to control samples, (B) and (C) levels of miR-128 and miR-342-3p are markedly reduced in glioma samples compared to control samples. But there was no significant difference between controls and meningioma patients or pituitary adenoma patients (P > 0.05). *P < 0.008 in comparison with normal, #P < 0.008 in comparison with meningioma, △P < 0.008 in comparison with pituitary adenoma.
Similar articles
- Profiling of novel circulating microRNAs as a non-invasive biomarker in diagnosis and follow-up of high and low-grade gliomas.
Tabibkhooei A, Izadpanahi M, Arab A, Zare-Mirzaei A, Minaeian S, Rostami A, Mohsenian A. Tabibkhooei A, et al. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Mar;190:105652. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105652. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31896490 - Plasma miR-185 as a predictive biomarker for prognosis of malignant glioma.
Tang H, Liu Q, Liu X, Ye F, Xie X, Xie X, Wu M. Tang H, et al. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015 Jul-Sep;11(3):630-4. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.146121. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26458593 - Low serum level of miR-485-3p predicts poor survival in patients with glioblastoma.
Wang ZQ, Zhang MY, Deng ML, Weng NQ, Wang HY, Wu SX. Wang ZQ, et al. PLoS One. 2017 Sep 20;12(9):e0184969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184969. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28931080 Free PMC article. - Serum microRNAs as potential noninvasive biomarkers for glioma.
Yu X, Li Z. Yu X, et al. Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):1407-10. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4515-7. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26628296 Review. - MicroRNAs in glioblastoma pathogenesis and therapy: A comprehensive review.
Ahir BK, Ozer H, Engelhard HH, Lakka SS. Ahir BK, et al. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017 Dec;120:22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 7. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017. PMID: 29198335 Review.
Cited by
- Exploring the role of Nrf2 signaling in glioblastoma multiforme.
Awuah WA, Toufik AR, Yarlagadda R, Mikhailova T, Mehta A, Huang H, Kundu M, Lopes L, Benson S, Mykola L, Vladyslav S, Alexiou A, Alghamdi BS, Hashem AM, Md Ashraf G. Awuah WA, et al. Discov Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;13(1):94. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00556-4. Discov Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36169772 Free PMC article. Review. - Liquid Biopsy in Glioblastoma.
Ronvaux L, Riva M, Coosemans A, Herzog M, Rommelaere G, Donis N, D'Hondt L, Douxfils J. Ronvaux L, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 13;14(14):3394. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143394. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884454 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Zhou Q, Liu J, Quan J, Liu W, Tan H, Li W. Zhou Q, et al. Cancer Sci. 2018 Sep;109(9):2651-2659. doi: 10.1111/cas.13714. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29949235 Free PMC article. Review. - Emerging biomarkers in glioblastoma.
McNamara MG, Sahebjam S, Mason WP. McNamara MG, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2013 Aug 22;5(3):1103-19. doi: 10.3390/cancers5031103. Cancers (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24202336 Free PMC article. - Circulating Noncoding RNAs in Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors-Two Sides of the Same Coin.
Butz H. Butz H. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 4;23(9):5122. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095122. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563510 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical