Cancer-stromal cell interactions mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors promote angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2013 Aug 29;32(35):4057-63.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.578. Epub 2012 Dec 10.
Affiliations
- PMID: 23222717
- PMCID: PMC4415159
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.578
Review
Cancer-stromal cell interactions mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors promote angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis
G L Semenza. Oncogene. 2013.
Abstract
Interactions between cancer cells and stromal cells, including blood vessel endothelial cells (BECs), lymphatic vessel endothelial cells (LECs), bone marrow-derived angiogenic cells (BMDACs) and other bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs) play important roles in cancer progression. Intratumoral hypoxia, which affects both cancer and stromal cells, is associated with a significantly increased risk of metastasis and mortality in many human cancers. Recent studies have begun to delineate the molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of intratumoral hypoxia on cancer progression. Reduced O2 availability induces the activity of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which activate the transcription of target genes encoding proteins that play important roles in many critical aspects of cancer biology. Included among these are secreted factors, including angiopoietin 2, angiopoietin-like 4, placental growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor B, stem cell factor (kit ligand), stromal-derived factor 1, and vascular endothelial growth factor. These factors are produced by hypoxic cancer cells and directly mediate functional interactions with BECs, LECs, BMDACs and other BMDCs that promote angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis. In addition, lysyl oxidase (LOX) and LOX-like proteins, which are secreted by hypoxic breast cancer cells, remodel extracellular matrix in the lungs, which leads to BMDC recruitment and metastatic niche formation.
Figures
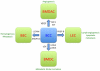
Figure 1
Functional interactions between breast cancer cells and stromal cells that are mediated by the HIF-dependent expression of secreted factors. In response to hypoxia, HIFs are induced and activate transcription of genes encoding angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4), L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM), lysyl oxidase (LOX), LOX-like 2 (LOXL2), LOXL4, platelet-derived growth factor B (PDGF-B), stem cell factor (SCF), stromal-derived factor 1 (SDF1), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). These factors promote functional interactions with blood endothelial cells (BECs), lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) bone marrow-derived angiogenic cells (BMDACs), and other bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs). These interactions promote angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, lymphatic metastasis, metastatic niche formation, and blood vessel (hematogenous) metastasis.
Figure 2
Deconvolution of steps involved in hematogenous metastasis of cancer cells. The process includes the invasion of a cancer cell into a blood vessel within the primary tumor (intravasation); survival of the cancer cell in the circulation; adherence of the cancer cell to the endothelium of a blood vessel in a distant tissue (margination); migration through the endothelium (extravasation); and cancer cell survival and proliferation at the distant site (colonization), which requires prior metastatic niche formation.
Similar articles
- Inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 block breast cancer metastatic niche formation and lung metastasis.
Wong CC, Zhang H, Gilkes DM, Chen J, Wei H, Chaturvedi P, Hubbi ME, Semenza GL. Wong CC, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012 Jul;90(7):803-15. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0855-y. Epub 2012 Jan 10. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22231744 Free PMC article. - Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a master regulator of breast cancer metastatic niche formation.
Wong CC, Gilkes DM, Zhang H, Chen J, Wei H, Chaturvedi P, Fraley SI, Wong CM, Khoo US, Ng IO, Wirtz D, Semenza GL. Wong CC, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Sep 27;108(39):16369-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113483108. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21911388 Free PMC article. - Molecular mechanisms mediating metastasis of hypoxic breast cancer cells.
Semenza GL. Semenza GL. Trends Mol Med. 2012 Sep;18(9):534-43. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.08.001. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Trends Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22921864 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of hypoxia-inducible factors in breast cancer metastasis.
Gilkes DM, Semenza GL. Gilkes DM, et al. Future Oncol. 2013 Nov;9(11):1623-36. doi: 10.2217/fon.13.92. Future Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24156323 Free PMC article. Review. - Sunitinib inhibits lymphatic endothelial cell functions and lymph node metastasis in a breast cancer model through inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3.
Kodera Y, Katanasaka Y, Kitamura Y, Tsuda H, Nishio K, Tamura T, Koizumi F. Kodera Y, et al. Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 21;13(3):R66. doi: 10.1186/bcr2903. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21693010 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR, a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α activated driver of malignancy, enhances hypoxic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer.
Zhou C, Ye L, Jiang C, Bai J, Chi Y, Zhang H. Zhou C, et al. Tumour Biol. 2015 Dec;36(12):9179-88. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3453-8. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 26088446 - Role of the Hypoxic-Secretome in Seed and Soil Metastatic Preparation.
Clemente-González C, Carnero A. Clemente-González C, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;14(23):5930. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235930. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497411 Free PMC article. Review. - 3D hydrogel breast cancer models for studying the effects of hypoxia on epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
Wang Y, Mirza S, Wu S, Zeng J, Shi W, Band H, Band V, Duan B. Wang Y, et al. Oncotarget. 2018 Aug 14;9(63):32191-32203. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25891. eCollection 2018 Aug 14. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30181809 Free PMC article. - Hypoxia-targeted drug delivery.
Sharma A , Arambula JF , Koo S , Kumar R , Singh H , Sessler JL , Kim JS . Sharma A , et al. Chem Soc Rev. 2019 Feb 4;48(3):771-813. doi: 10.1039/c8cs00304a. Chem Soc Rev. 2019. PMID: 30575832 Free PMC article. Review. - Endothelial hypoxic metabolism in carcinogenesis and dissemination: HIF-A isoforms are a NO metastatic phenomenon.
Branco-Price C, Evans CE, Johnson RS. Branco-Price C, et al. Oncotarget. 2013 Dec;4(12):2567-76. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1461. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 24318195 Free PMC article.
References
- Hanahan D, Coussens LM. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:309–322. - PubMed
- Höckel M, Schlenger K, Aral B, Mitze M, Schäfer U, Vaupel P. Association between tumor hypoxia and malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4509–4515. - PubMed
- Brizel DM, Scully SP, Harrelson JM, Layfield LJ, Bean JM, Prosnitz LR, et al. Tumor oxygenation predicts the likelihood of distant metastases in human soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer Res. 1996;56:941–943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical