Interleukin-27: balancing protective and pathological immunity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Interleukin-27: balancing protective and pathological immunity
Christopher A Hunter et al. Immunity. 2012.
Abstract
It has been more than 15 years since the identification of individual interleukin-27 (IL-27) and IL-27 receptor components. The last decade has seen the description of the signaling pathways engaged by IL-27, and an appreciation has emerged that this cytokine can modulate the intensity and duration of many classes of T cell responses. Here we provide an overview of the immunobiology of IL-27 and review advances in understanding the functions of individual IL-27 and IL-27 receptor subunits and the role of IL-27 in dictating the balance between protective and pathological immunity. Additionally, this cytokine has been proposed as a therapy to modify inflammatory conditions or to promote antitumor responses, and situations where experimental and clinical data sets implicate IL-27 in the outcome of disease are highlighted.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
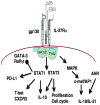
Figure 1
Impact of IL-27 on lymphocyte signaling pathways. Dimerization of gp130 and IL-27Ra engages JAK1, 2 and Tyk2 that engage the MAPK pathway and activation of multiple STATs, most notably STAT1 and STAT3. The activation of STAT1 is linked to inhibition of GATA-3 and RoRγt but upregulation of PD-L1, T-bet and IL-10. The ability to engage STAT3 is linked to increased proliferation as well as IL-10 while the MAPK pathway intersects with AHR to promote IL-10 and IL-21.
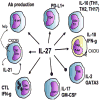
Figure 2
Key regulatory effects of IL-27 on T and B cells. The pro-inflammatory properties attributed to IL-27 include the development of CTL, the promotion of TFH as well as a direct ability to promote B cell production of antibodies. The regulatory activities of IL-27 includes the ability to promote expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-L1 and IL-10 production by multiple helper T cells. The ability to generate a CXCR3+ Treg population is specialized to operate at sites of TH1 inflammation while the ability to control Th2 and Th17 inflammation is due to direct inhibitory effects on GATA3 and RoRgt.
Similar articles
- Retinal cells suppress intraocular inflammation (uveitis) through production of interleukin-27 and interleukin-10.
Lee YS, Amadi-Obi A, Yu CR, Egwuagu CE. Lee YS, et al. Immunology. 2011 Apr;132(4):492-502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03379.x. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Immunology. 2011. PMID: 21294722 Free PMC article. - Targeting of interleukin (IL)-17A inhibits PDL1 expression in tumor cells and induces anticancer immunity in an estrogen receptor-negative murine model of breast cancer.
Ma YF, Chen C, Li D, Liu M, Lv ZW, Ji Y, Xu J. Ma YF, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7614-7624. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13819. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27935862 Free PMC article. - Regulation of immune responses by interleukin-27.
Yoshida H, Miyazaki Y. Yoshida H, et al. Immunol Rev. 2008 Dec;226:234-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00710.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 19161428 Review. - Interleukin-27: biological properties and clinical application.
Jankowski M, Kopiński P, Goc A. Jankowski M, et al. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2010 Dec;58(6):417-25. doi: 10.1007/s00005-010-0098-6. Epub 2010 Sep 26. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2010. PMID: 20872282 Review. - IL-27 in tumor immunity and immunotherapy.
Murugaiyan G, Saha B. Murugaiyan G, et al. Trends Mol Med. 2013 Feb;19(2):108-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23306374 Review.
Cited by
- Immunologic and inflammatory pathogenesis of chronic coronary syndromes: A review.
Chen T, Yang Y. Chen T, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e40354. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040354. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496055 Free PMC article. Review. - MR1 blockade drives differential impact on integrative signatures based on circuits of circulating immune cells and soluble mediators in visceral leishmaniasis.
Borges-Fernandes LO, de Lima Moreira M, Pereira VHS, Pascoal-Xavier MA, Lopes Ribeiro Á, da Costa-Rocha IA, Lopes LR, Moreira GTC, Araújo MSDS, Teixeira-Carvalho A, Brito-de-Sousa JP, de Carvalho AL, Mourão MVA, Campos FA, Borges M, Carneiro M, Tsuji M, Martins-Filho OA, Coelho-Dos-Reis JGA, Peruhype-Magalhães V. Borges-Fernandes LO, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 13;15:1373498. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1373498. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39192975 Free PMC article. - IL-27 Gene Therapy Ameliorates IPEX Syndrome Caused by Germline Mutation of Foxp3 Gene: A Major Role for Induction of IL-10.
Liu JQ, Jabbari A, Lin CH, Akkanapally V, Frankel WL, Basu S, He K, Zheng P, Liu Y, Bai XF. Liu JQ, et al. J Immunol. 2024 Sep 1;213(5):559-566. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2400056. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38975727 - IL-27 expression regulation and its effects on adaptive immunity against viruses.
Andres-Martin F, James C, Catalfamo M. Andres-Martin F, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1395921. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395921. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38966644 Free PMC article. Review. - Interplay of Cytokines and Chemokines in Aspergillosis.
Shankar J, Thakur R, Clemons KV, Stevens DA. Shankar J, et al. J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Mar 27;10(4):251. doi: 10.3390/jof10040251. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Amadi-Obi A, Yu CR, Liu X, Mahdi RM, Clarke GL, Nussenblatt RB, Gery I, Lee YS, Egwuagu CE. T(H)17 cells contribute to uveitis and scleritis and are expanded by IL-2 and inhibited by IL-27/STAT1. Nat Med. 2007;13:711–718. - PubMed
- Artis D, Johnson LM, Joyce K, Saris C, Villarino A, Hunter CA, Scott P. Cutting Edge: Early IL-4 production governs the requirement for IL-27-WSX-1 signaling in the development of protective Th1 cytokine responses following Leishmania major infection. J Immunol. 2004a;172:4672–4675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources