A Phase-1b study of tivantinib (ARQ 197) in adult patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2013 Jan 15;108(1):21-4.
doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.556. Epub 2013 Jan 3.
M Simonelli, C Rodriguez-Lope, P Zucali, L H Camacho, A Granito, N Senzer, L Rimassa, G Abbadessa, B Schwartz, M Lamar, R E Savage, J Bruix
Affiliations
- PMID: 23287988
- PMCID: PMC3553536
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.556
Clinical Trial
A Phase-1b study of tivantinib (ARQ 197) in adult patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis
A Santoro et al. Br J Cancer. 2013.
Abstract
Background: The mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET) receptor is dysregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and tivantinib (ARQ 197) is an oral, selective, MET inhibitor.
Methods: This Phase-1b study assessed tivantinib safety as primary objective in patients with previously treated HCC and Child-Pugh A or B liver cirrhosis. Patients received oral tivantinib 360 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Results: Among 21 HCC patients, common drug-related adverse events (AEs) were neutropaenia, anaemia, asthenia, leucopaenia, anorexia, diarrhoea, and fatigue. No drug-related worsening of liver function or performance status occurred, but one Child-Pugh B patient experienced drug-related bilirubin increase. Four patients had drug-related serious AEs, including one neutropaenia-related death. Haematologic toxicities were more frequent than in previous tivantinib studies but were manageable with prompt therapy. Best response was stable disease (median, 5.3 months) in 9 of 16 evaluable patients (56%). Median time to progression was 3.3 months.
Conclusion: Tivantinib demonstrated a manageable safety profile and preliminary antitumour activity in patients with HCC and Child-Pugh A or B cirrhosis.
Conflict of interest statement
JB is a consultant for Abbott, AngioDynamics, ArQule, Bayer, BioAlliance, Biocompatibles, BMS, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, ImClone, Jennerex, Kowa, Lilly, MedImmune, Novartis, OSI, Pharmexa, Roche, Sanofi, Schering-Plough, and Sumitomo. AS is a consultant for ArQule and Bayer. GA, ML, BS, and RS are employees of ArQule. LR received travel grants from ArQule. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
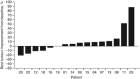
Figure 1
Maximum change from baseline in tumour burden in the evaluable efficacy population (_n_=16).
Similar articles
- Tivantinib for second-line treatment of MET-high, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (METIV-HCC): a final analysis of a phase 3, randomised, placebo-controlled study.
Rimassa L, Assenat E, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Pracht M, Zagonel V, Mathurin P, Rota Caremoli E, Porta C, Daniele B, Bolondi L, Mazzaferro V, Harris W, Damjanov N, Pastorelli D, Reig M, Knox J, Negri F, Trojan J, López López C, Personeni N, Decaens T, Dupuy M, Sieghart W, Abbadessa G, Schwartz B, Lamar M, Goldberg T, Shuster D, Santoro A, Bruix J. Rimassa L, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 May;19(5):682-693. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30146-3. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29625879 Clinical Trial. - Tivantinib for second-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study.
Santoro A, Rimassa L, Borbath I, Daniele B, Salvagni S, Van Laethem JL, Van Vlierberghe H, Trojan J, Kolligs FT, Weiss A, Miles S, Gasbarrini A, Lencioni M, Cicalese L, Sherman M, Gridelli C, Buggisch P, Gerken G, Schmid RM, Boni C, Personeni N, Hassoun Z, Abbadessa G, Schwartz B, Von Roemeling R, Lamar ME, Chen Y, Porta C. Santoro A, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jan;14(1):55-63. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70490-4. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Lancet Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23182627 Clinical Trial. - Selective Inhibitor of the c-Met Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: No Beneficial Effect With the Use of Tivantinib?
Zhao S, Wu W, Jiang H, Ma L, Pan C, Jin C, Mo J, Wang L, Wang K. Zhao S, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 2;12:731527. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731527. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34804015 Free PMC article. Review. - Tivantinib in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Trojan J, Zeuzem S. Trojan J, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013 Jan;22(1):141-7. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.741586. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23167786 Review. - Phase I study of tivantinib in Japanese patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Distinctive pharmacokinetic profiles from other solid tumors.
Okusaka T, Aramaki T, Inaba Y, Nakamura S, Morimoto M, Moriguchi M, Sato T, Ikawa Y, Ikeda M, Furuse J. Okusaka T, et al. Cancer Sci. 2015 May;106(5):611-7. doi: 10.1111/cas.12644. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25711511 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
- Precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma: driver mutations and targeted therapy.
Ding XX, Zhu QG, Zhang SM, Guan L, Li T, Zhang L, Wang SY, Ren WL, Chen XM, Zhao J, Lin S, Liu ZZ, Bai YX, He B, Zhang HQ. Ding XX, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 6;8(33):55715-55730. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18382. eCollection 2017 Aug 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28903454 Free PMC article. Review. - Progress in systemic therapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gong XL, Qin SK. Gong XL, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 7;22(29):6582-94. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6582. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27547002 Free PMC article. Review. - Hepatocellular carcinoma: Where there is unmet need.
Bupathi M, Kaseb A, Meric-Bernstam F, Naing A. Bupathi M, et al. Mol Oncol. 2015 Oct;9(8):1501-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26160430 Free PMC article. Review. - Underexpression of miR-34a in hepatocellular carcinoma and its contribution towards enhancement of proliferating inhibitory effects of agents targeting c-MET.
Dang Y, Luo D, Rong M, Chen G. Dang Y, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 10;8(4):e61054. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061054. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593387 Free PMC article. - A Phase I/II Multicenter Study of Single-Agent Foretinib as First-Line Therapy in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Yau TCC, Lencioni R, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, Chao Y, Yen CJ, Lausoontornsiri W, Chen PJ, Sanpajit T, Camp A, Cox DS, Gagnon RC, Liu Y, Raffensperger KE, Kulkarni DA, Kallender H, Ottesen LH, Poon RTP, Bottaro DP. Yau TCC, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 May 15;23(10):2405-2413. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1789. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27821605 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Bagai R, Fan W, Ma PC (2010) ARQ-197, an oral small molecule inhibitor of c-Met for the treatment of solid tumors. IDrugs 13(6): 404–414 - PubMed
- Bathala MS, Nakai D, Murai T, Pickersgill F, Zahir H, Tokui T (2012) Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of 14C-labeled tivantinib (ARQ 197) in healthy male subjects. 103rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research 31 Mar–4 Apr 2012; Chicago, IL. Abstract 747
- Boix L, Rosa JL, Ventura F, Castells A, Bruix J, Rodes J, Bartrons R (1994) c-met mRNA overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 19(1): 88–91 - PubMed
- Bruix J, Sherman M (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 42(5): 1208–1236 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous