IGFBP-2 is a negative predictor of cold-induced brown fat and bone mineral density in young non-obese women - PubMed (original) (raw)
IGFBP-2 is a negative predictor of cold-induced brown fat and bone mineral density in young non-obese women
Miriam A Bredella et al. Bone. 2013 Apr.
Abstract
Recent studies have shown a positive correlation between brown adipose tissue (BAT) and bone mineral density (BMD). However, mechanisms underlying this relationship are unknown. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is an important regulator of stem cell differentiation promoting bone formation. IGF binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) binds IGF-1 in the circulation and has been reported to inhibit bone formation in humans. IGF-1 is also a crucial regulator of brown adipocyte differentiation. We hypothesized that IGFBP-2 is a negative and IGF-1 a positive regulator of BAT-mediated osteoblastogenesis. We therefore investigated a cohort of 15 women (mean age 27.7±5.7years): 5 with anorexia nervosa (AN) in whom IGF-1 levels were low due to starvation, 5 recovered AN (AN-R), and 5 women of normal weight. All subjects underwent assessment of cold-activated BAT by PET/CT, BMD of the spine, hip, femoral neck, and total body by DXA, thigh muscle area by MRI, IGF-1 and IGFBP-2. There was a positive correlation between BAT and BMD and an inverse association between IGFBP-2 and both BAT and BMD. There was no association between IGF-1 and BAT. We show for the first time that IGFBP-2 is a negative predictor of cold-induced BAT and BMD in young non-obese women, suggesting that IGFBP-2 may serve as a regulator of BAT-mediated osteoblastogenesis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
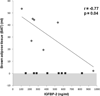
Figure 1
Regression analysis of brown adipose tissue (BAT) on IGFBP-2. There was an inverse association between BAT and IGFBP-2 in subjects with detectable BAT. Grey diamonds: subjects with BAT, black squares: subjects without BAT. Shaded area represents undetectable range.
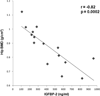
Figure 2
Regression analysis of hip bone mineral density (BMD) on IGFBP-2. There was an inverse association between hip BMD and IGFBP-2.
Similar articles
- Young women with cold-activated brown adipose tissue have higher bone mineral density and lower Pref-1 than women without brown adipose tissue: a study in women with anorexia nervosa, women recovered from anorexia nervosa, and normal-weight women.
Bredella MA, Fazeli PK, Freedman LM, Calder G, Lee H, Rosen CJ, Klibanski A. Bredella MA, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Apr;97(4):E584-90. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2246. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22259053 Free PMC article. - Cold-activated brown adipose tissue is an independent predictor of higher bone mineral density in women.
Lee P, Brychta RJ, Collins MT, Linderman J, Smith S, Herscovitch P, Millo C, Chen KY, Celi FS. Lee P, et al. Osteoporos Int. 2013 Apr;24(4):1513-8. doi: 10.1007/s00198-012-2110-y. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Osteoporos Int. 2013. PMID: 22890364 Free PMC article. - A potentially deleterious role of IGFBP-2 on bone density in aging men and women.
Amin S, Riggs BL, Atkinson EJ, Oberg AL, Melton LJ 3rd, Khosla S. Amin S, et al. J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Jul;19(7):1075-83. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040301. Epub 2004 Mar 22. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15176989 - Association between brown adipose tissue and bone mineral density in humans.
Sanchez-Delgado G, Martinez-Tellez B, Garcia-Rivero Y, Acosta FM, Alcantara JMA, Amaro-Gahete FJ, Llamas-Elvira JM, Gracia-Marco L, Ruiz JR. Sanchez-Delgado G, et al. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019 Aug;43(8):1516-1525. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0261-4. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30518823 - Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-2, and IGFBP-3 in osteoporotic patients with and without spinal fractures.
Sugimoto T, Nishiyama K, Kuribayashi F, Chihara K. Sugimoto T, et al. J Bone Miner Res. 1997 Aug;12(8):1272-9. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1997.12.8.1272. J Bone Miner Res. 1997. PMID: 9258758
Cited by
- Sexual Dimorphism and the Origins of Human Spinal Health.
Gilsanz V, Wren TAL, Ponrartana S, Mora S, Rosen CJ. Gilsanz V, et al. Endocr Rev. 2018 Apr 1;39(2):221-239. doi: 10.1210/er.2017-00147. Endocr Rev. 2018. PMID: 29385433 Free PMC article. Review. - Igfbp2 Deletion in Ovariectomized Mice Enhances Energy Expenditure but Accelerates Bone Loss.
DeMambro VE, Le PT, Guntur AR, Maridas DE, Canalis E, Nagano K, Baron R, Clemmons DR, Rosen CJ. DeMambro VE, et al. Endocrinology. 2015 Nov;156(11):4129-40. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1452. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 26230658 Free PMC article. - Anorexia nervosa, obesity and bone metabolism.
Misra M, Klibanski A. Misra M, et al. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2013 Sep;11(1):21-33. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24079076 Free PMC article. Review. - Muscle-bone and fat-bone interactions in regulating bone mass: do PTH and PTHrP play any role?
Datta NS. Datta NS. Endocrine. 2014 Nov;47(2):389-400. doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0273-3. Epub 2014 May 7. Endocrine. 2014. PMID: 24802058 Review. - 'Browning' the cardiac and peri-vascular adipose tissues to modulate cardiovascular risk.
Aldiss P, Davies G, Woods R, Budge H, Sacks HS, Symonds ME. Aldiss P, et al. Int J Cardiol. 2017 Feb 1;228:265-274. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.074. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27865196 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bredella MA, Fazeli PK, Freedman LM, Calder G, Lee H, Rosen CJ, Klibanski A. Young women with cold-activated brown adipose tissue have higher bone mineral density and lower Pref-1 than women without brown adipose tissue: a study in women with anorexia nervosa, women recovered from anorexia nervosa, and normal-weight women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:E584–E590. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R24 DK084970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR061164/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK092759/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous