BF02, a recombinant TNFR2 fusion protein, alleviates adjuvant arthritis by regulating T lymphocytes in rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.171. Epub 2013 Feb 4.
Bei Huang, Qing-tong Wang, Yu-jing Wu, Jing-jing Fu, Yun-fang Zhang, Yan Chang, Jing-yu Chen, Hua-xun Wu, Di Wang, Ling-ling Zhang, Wei Wei
Affiliations
- PMID: 23377547
- PMCID: PMC4002494
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2012.171
BF02, a recombinant TNFR2 fusion protein, alleviates adjuvant arthritis by regulating T lymphocytes in rats
Shan-shan Song et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Mar.
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the therapeutic effects of BF02 on adjuvant arthritis (AA) in rats and the regulatory effects of BF02 on T lymphocyte function.
Methods: SD rats received a single intradermal injection of Freund's complete adjuvant emulsion into the right hind metatarsal footpad. After the onset of AA, the rats were injected BF02 (1, 3, or 9 mg/kg, sc) every 3 d for a total of 15 d. Intragastric administration of methotrexate (MTX, 0.5 mg/kg, every 3 d for a total of 15 d) was taken as the positive control drug. Arthritis index, swollen joint count, ankle joint histopathology, spleen histopathology and the paw radiography were used for evaluating the drug effects on AA rats. T lymphocyte function was assessed by measuring T lymphocyte cytokine levels, IL17 and TNF-α mRNA expression levels, and percentage of T lymphocyte subsets.
Results: In the AA rats, remarkable secondary inflammatory responses exhibited, accompanied by significantly higher levels of IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-17, LTα, RANKL, and MMP-13. The expression of IL17 and TNF-α mRNAs was also substantially higher than in normal rats. The percentages of CD3(+)CD4(+) and CD4(+)CD25(+) T lymphocytes were increased, whereas the percentages of CD4(+)CD62L(+) and CD4(+)CD25(+)FoxP3(+) T lymphocytes were decreased. Treatment of the AA rats with BF02 (9 mg/kg) or MTX significantly decreased the arthritis index, swollen joint count and arthritis global assessment. Moreover, both BF02 (9 mg/kg) and MTX significantly inhibited T lymphocyte proliferation, and blocked the above mentioned aberrance in T lymphocyte cytokine levels, IL17 and TNF-α mRNA expression, and percentages of T lymphocyte subsets.
Conclusion: BF02 exerts therapeutic effects on AA rats via the regulation of T lymphocytes.
Figures
Figure 1
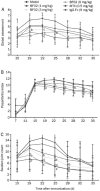
Effects of BF02 on arthritis global assessment, arthritis index and swollen joint count. The onset of secondary arthritis of the disease appeared on d 11 after immunization, with a peak onset on d 20 to d 28. (A) BF02 (9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) could diminish arthritis global assessment significantly in rats with AA from d 22 to d 25. (B) BF02 (9 mg/kg) could inhibit arthritis index obviously in AA rats from d 19 to d 35. (C) Swollen joint count (SJC) increased in every group compared with the normal group, and the BF02 treatment group had marked changes compared with the model group. On d 22 to d 25 after immunization, BF02 (9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) could diminish SJC obviously compared with the model group and IgG-Fc had no obvious effect on SJC. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 12 animals for each group. b_P_<0.05, c_P_<0.01 vs model group.
Figure 2
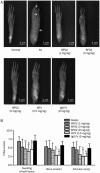
Effects of BF02 on radiological examination of paws. (A) Radiographs of AA model group showed swelling of soft tissue, bone erosion and narrow articular cavity compared with the normal group. (B) BF02 (9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) could significantly reduce the increased radiograph scores, and IgG-Fc had no obvious effect on radiograph scores. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 12 animals for each group. b_P_<0.05, c_P_<0.01 vs model group.
Figure 3
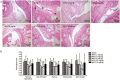
Effects of BF02 on ankle joint histopathology. (A) Compared to the normal group, the model group showed marked synovium hyperplasia, cellular infiltration, pannus formation, bone erosion and inflammation (HE staining, ×40). (B) BF02 (9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) showed only minimal inflammation and pathological changes: bone erosion and degradation were scarcely detected, inflammatory cell infiltration was also obviously reduced, and the increased scores of pannus were decreased. IgG-Fc had no obvious effect. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 12 animals for each group. b_P_<0.05, c_P_<0.01 vs model group.
Figure 4
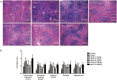
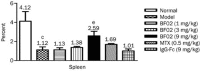
Effects of BF02 on spleen histopathology. (A) In AA rats, proliferated white pulp, emerged germinal centers, and red pulp hyperemia, infiltrated spleens with inflammatory cells (HE staining, ×40). BF02 (3 and 9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) significantly alleviated these abnormal changes. (B) BF02 (3 and 9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) diminished the scores of cell density lymphatic sheath, lymphoid follicular hyperplasia, marginal zone and red pulp. There were no significant changes in IgG-Fc group. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 12 animals for each group. c_P_<0.01 vs normal group. e_P_<0.05, f_P_<0.01 vs model group.
Figure 5
Effects of BF02 on T lymphocyte proliferations. Results showed that ConA-induced T lymphocyte proliferation in AA group was increased. BF02 (3 and 9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) could reduce T lymphocyte proliferations. IgG-Fc had no obvious effect on T lymphocyte proliferations. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 12 animals for each group. b_P_<0.05 vs normal group. e_P_<0.05, f_P_<0.01 vs model group.
Figure 6
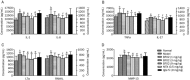
Effects of BF02 on the levels of TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, LTα, RANKL, and MMP-13 in serum of AA. Results showed that the level of (A) IL-1 and IL-6, (B) TNF-α and IL-17, (C) LTα and RANKL and (D) MMP-13 was increased in the model group compared to the normal group. The administration of BF02 (3 and 9mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) significantly decreased the production of IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, LTα, TNF-α, and MMP-13. BF02 (9 mg/kg) could reduce the level of RANKL. IgG-Fc had no obvious effect on the level of cytokines. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 12 animals for each group. b_P_<0.05, c_P_<0.01 vs normal group. e_P_<0.05, f_P_<0.01 vs model group.
Figure 7
Effects of BF02 on IL-17 and TNF-α mRNA expression in T lymphocytes. The mRNA levels of (A) IL-17 and (B) TNF-α were increased in T lymphocytes of AA. The expression mRNA levels of IL-17 and TNF-α were significantly reduced in BF02-treated rats. Data are expressed as mean±SEM. b_P_<0.05, c_P_<0.01 vs model group.
Figure 8
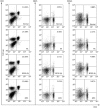
Effects of BF02 on the subsets of T lymphocytes in spleen. According to flow cytometry analysis, the model group had a higher percent of CD3+CD4+ and CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes in spleen than the normal group. CD4+CD62L+ T lymphocytes were reduced in model group. BF02 (1, 3, and 9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) could inhibit the percentage of CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes. Moreover, BF02 (3 and 9 mg/kg) and MTX (0.5 mg/kg) could restore the decreased percentage of CD4+CD62L+ T lymphocytes.
Figure 9
Effects of BF02 on the CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ T lymphocytes spleen in AA rats. Compared to the normal group, the percentage of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ T lymphocytes decreased obviously in the model group. BF02 (9 mg/kg) could restore the decreased percentage of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ T cells. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 12 animals for each group. c_P_<0.01 vs normal group. e_P_<0.05 vs model group.
Similar articles
- Ginsenoside metabolite compound k alleviates adjuvant-induced arthritis by suppressing T cell activation.
Chen J, Wu H, Wang Q, Chang Y, Liu K, Song S, Yuan P, Fu J, Sun W, Huang Q, Liu L, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zhou A, Wei W. Chen J, et al. Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1608-15. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9887-0. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24736881 - Combined use of etanercept and MTX restores CD4⁺/CD8⁺ ratio and Tregs in spleen and thymus in collagen-induced arthritis.
Huang B, Wang QT, Song SS, Wu YJ, Ma YK, Zhang LL, Chen JY, Wu HX, Jiang L, Wei W. Huang B, et al. Inflamm Res. 2012 Nov;61(11):1229-39. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0520-0. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Inflamm Res. 2012. PMID: 22802109 - Therapeutic effects of TACI-Ig on collagen-induced arthritis by regulating T and B lymphocytes function in DBA/1 mice.
Liu Y, Zhang L, Wu Y, Tong T, Zhao W, Li P, Huang M, Wang W, Fang J, Wei W. Liu Y, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Mar 11;654(3):304-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Jan 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21244850 - Influence of polysaccharide fractions isolated from Caltha palustris L. on the cellular immune response in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice. A comparison with methotrexate.
Suszko A, Obmińska-Mrukowicz B. Suszko A, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jan 9;145(1):109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.038. Epub 2012 Nov 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23123796 - Norisoboldine alleviates joint destruction in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis by reducing RANKL, IL-6, PGE(2), and MMP-13 expression.
Wei ZF, Jiao XL, Wang T, Lu Q, Xia YF, Wang ZT, Guo QL, Chou GX, Dai Y. Wei ZF, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Mar;34(3):403-13. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.187. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013. PMID: 23396374 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Suppression of arthritis-induced bone erosion by a CRAC channel antagonist.
Blair HC, Soboloff J, Robinson LJ, Tourkova IL, Larrouture QC, Witt MR, Holaskova I, Schafer R, Elliott M, Hirsch R, Barnett JB. Blair HC, et al. RMD Open. 2016 Jan 8;2(1):e000093. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2015-000093. eCollection 2016. RMD Open. 2016. PMID: 26819750 Free PMC article. - Ginsenoside metabolite compound k alleviates adjuvant-induced arthritis by suppressing T cell activation.
Chen J, Wu H, Wang Q, Chang Y, Liu K, Song S, Yuan P, Fu J, Sun W, Huang Q, Liu L, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zhou A, Wei W. Chen J, et al. Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1608-15. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9887-0. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24736881 - Catechin ameliorates cardiac dysfunction in rats with chronic heart failure by regulating the balance between Th17 and Treg cells.
Zhang Q, Hu LQ, Yin CS, Chen P, Li HQ, Sun X, Yan G. Zhang Q, et al. Inflamm Res. 2014 Aug;63(8):619-28. doi: 10.1007/s00011-014-0734-4. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Inflamm Res. 2014. PMID: 24760105 - Qingluoyin granules protect against adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via downregulating the CXCL12/CXCR4-NF-κB signalling pathway.
Si M, Ma Z, Zhang J, Li X, Li R, Wang C, Jia H, Luo S. Si M, et al. Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):1441-1451. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1991386. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34693865 Free PMC article. - Shikonin inhibits TNF-α production through suppressing PKC-NF-κB-dependent decrease of IL-10 in rheumatoid arthritis-like cell model.
Sun WX, Liu Y, Zhou W, Li HW, Yang J, Chen ZB. Sun WX, et al. J Nat Med. 2017 Apr;71(2):349-356. doi: 10.1007/s11418-016-1064-3. Epub 2016 Dec 9. J Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 27943122
References
- Jawaheer D, Lum RF, Gregersen PK, Criswell LA. Influence of male sex on disease phenotype in familial rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3087–94. - PubMed
- Yan Z, Ferucci ED, Geraghty DE, Yang Y, Lanier AP, Smith WP, et al. Resequencing of the human major histocompatibility complex in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy controls in Alaska Natives of Southeast Alaska. Tissue Antigens. 2007;70:487–94. - PubMed
- Nam J, Emery P. Aspects of TNF inhibitor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2010;20:325–30. - PubMed
- Bradley JR. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol. 2008;214:149–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials