DAMBE5: a comprehensive software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution - PubMed (original) (raw)
DAMBE5: a comprehensive software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution
Xuhua Xia. Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Jul.
Abstract
Since its first release in 2001 as mainly a software package for phylogenetic analysis, data analysis for molecular biology and evolution (DAMBE) has gained many new functions that may be classified into six categories: 1) sequence retrieval, editing, manipulation, and conversion among more than 20 standard sequence formats including MEGA, NEXUS, PHYLIP, GenBank, and the new NeXML format for interoperability, 2) motif characterization and discovery functions such as position weight matrix and Gibbs sampler, 3) descriptive genomic analysis tools with improved versions of codon adaptation index, effective number of codons, protein isoelectric point profiling, RNA and protein secondary structure prediction and calculation of minimum folding energy, and genomic skew plots with optimized window size, 4) molecular phylogenetics including sequence alignment, testing substitution saturation, distance-based, maximum parsimony, and maximum-likelihood methods for tree reconstructions, testing the molecular clock hypothesis with either a phylogeny or with relative-rate tests, dating gene duplication and speciation events, choosing the best-fit substitution models, and estimating rate heterogeneity over sites, 5) phylogeny-based comparative methods for continuous and discrete variables, and 6) graphic functions including secondary structure display, optimized skew plot, hydrophobicity plot, and many other plots of amino acid properties along a protein sequence, tree display and drawing by dragging nodes to each other, and visual searching of the maximum parsimony tree. DAMBE features a graphic, user-friendly, and intuitive interface and is freely available from http://dambe.bio.uottawa.ca (last accessed April 16, 2013).
Keywords: Gibbs sampler; bioinformatics; codon usage; dating; genomic analysis; hidden Markov model; motif discovery; phylogenetics; secondary structure.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Gibbs sampler in action. The yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) intron sequences in the top panel represent the input to the Gibbs sampler. The bottom panel represents part of the output showing the identified motif (i.e., TAATAAC, bolded) shared among the sequences. Output from DAMBE5 also includes the PWM, the significance tests associated with PWM, and the PWM scores for individual motifs as a measure of motif strength, which is correlated with slicing efficiency. The input intron sequence file (YeastAllIntron.fas) is in DAMBE installation directory in FASTA format. Modified from Xia (2012b).
Fig. 2.
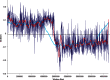
Skew plots of the Bacillus subtilis genome at three different window sizes, with the skew curve colored in red having the optimal window size. The horizontal line is the global GC skew computed from the entire genome.
Fig. 3.
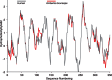
Hydrophobicity plot for human (NP_000530.1) and avian (Emberiza bruniceps: AFK10338) rhodopsin with seven transmembrane domains (peaks). The weak 7th peak is due to a relatively short α-helix. Output from DAMBE. A sliding window of 12 AAs is used.
Fig. 4.
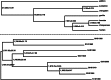
Regular dating with internal node calibration (top panel) and tip dating with sampling times (specified in OTU name following “@”) for calibration, based on the LS method in DAMBE.
Similar articles
- DAMBE6: New Tools for Microbial Genomics, Phylogenetics, and Molecular Evolution.
Xia X. Xia X. J Hered. 2017 Jun 1;108(4):431-437. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esx033. J Hered. 2017. PMID: 28379490 Free PMC article. - DAMBE7: New and Improved Tools for Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Xia X. Xia X. Mol Biol Evol. 2018 Jun 1;35(6):1550-1552. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy073. Mol Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29669107 Free PMC article. - MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods.
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. Tamura K, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2011 Oct;28(10):2731-9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121. Epub 2011 May 4. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 21546353 Free PMC article. - [A bird's eye view of the algorithms and software packages for reconstructing phylogenetic trees].
Zhang LN, Rong CH, He Y, Guan Q, He B, Zhu XW, Liu JN, Chen HJ. Zhang LN, et al. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2013 Dec;34(6):640-50. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2013. PMID: 24415699 Review. Chinese. - Computational advances in maximum likelihood methods for molecular phylogeny.
Schadt EE, Sinsheimer JS, Lange K. Schadt EE, et al. Genome Res. 1998 Mar;8(3):222-33. doi: 10.1101/gr.8.3.222. Genome Res. 1998. PMID: 9521926 Review.
Cited by
- Records of three mammal tick species parasitizing an atypical host, the multi-ocellated racerunner lizard, in arid regions of Xinjiang, China.
Zhou Q, Li J, Guo X, Liu J, Song Q, Gong X, Chen H, Zhang J, He J, Zheng Z, Chen D, Chen J. Zhou Q, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2021 Mar 4;14(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04639-z. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33663591 Free PMC article. - Seven new species of Urocleidoides (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from Brazilian fishes supported by morphological and molecular data.
Zago AC, Yamada FH, de Oliveira Fadel Yamada P, Franceschini L, Bongiovani MF, da Silva RJ. Zago AC, et al. Parasitol Res. 2020 Oct;119(10):3255-3283. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06831-z. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32856113 - Molecular analysis of polymorphic species of the genus Marshallagia (Nematoda: Ostertagiinae).
Kuchboev A, Sobirova K, Karimova R, Amirov O, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Krücken J. Kuchboev A, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2020 Aug 12;13(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04265-1. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32787940 Free PMC article. - The population history of Garra orientalis (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) using mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite data with approximate Bayesian computation.
Yang JQ, Hsu KC, Liu ZZ, Su LW, Kuo PH, Tang WQ, Zhou ZC, Liu D, Bao BL, Lin HD. Yang JQ, et al. BMC Evol Biol. 2016 Apr 11;16:73. doi: 10.1186/s12862-016-0645-9. BMC Evol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27068356 Free PMC article. - Mitochondrial genomes of stick insects (Phasmatodea) and phylogenetic considerations.
Song N, Li X, Na R. Song N, et al. PLoS One. 2020 Oct 6;15(10):e0240186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240186. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33021991 Free PMC article.
References
- Baron D, Cocquet J, Xia X, Fellous M, Guiguen Y, Veitia RA. An evolutionary and functional analysis of FoxL2 in rainbow trout gonad differentiation. J Mol Endocrinol. 2004;33:705–715. - PubMed
- Bisconti R, Canestrelli D, Colangelo P, Nascetti G. Multiple lines of evidence for demographic and range expansion of a temperate species (Hyla sarda) during the last glaciation. Mol Ecol. 2011;20:5313–5327. - PubMed
- Bisconti R, Canestrelli D, Salvi D, Nascetti G. A geographic mosaic of evolutionary lineages within the insular endemic newt Euproctus montanus. Mol Ecol. 2013;22:143–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous