Korean red ginseng extract alleviates advanced glycation end product-mediated renal injury - PubMed (original) (raw)
Korean red ginseng extract alleviates advanced glycation end product-mediated renal injury
Hai Yan Quan et al. J Ginseng Res. 2013 Apr.
Abstract
The effect of Korean red ginseng (KRG) on diabetic renal damage was investigated using streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. The diabetic rats showed loss of body weight gain, and increases in kidney weight and urine volume, whereas the oral administration of KRG at a dose of 100 or 250 mg/kg of body weight per day for 28 d prevented these diabetes-induced physiological abnormalities. Among the kidney function parameters, elevated plasma levels of urea nitrogen and creatinine in diabetic control rats tended to be lowered in KRG-treated rats. In addition, administration of KRG at a dose of 100 mg/kg body weight in the diabetic rats showed significant decreases in serum glucose and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), implying that KRG might prevent the pathogenesis of diabetic complications caused by impaired glucose metabolism and oxidative stress. KRG also significantly reduced advanced glycation end product (AGE) formation and secretion from kidney of diabetic rats. Furthermore, KRG decreased the levels of N-(carboxymethyl) lysine and expression of AGE receptor. KRG also reduced the overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the kidney via deactivation of nuclear factor-kappa B. We also found that KRG prevented STZ-induced destruction of glomerular structure and significantly suppressed high glucose-induced fibronectin production. Taken together, KRG ameliorates abnormalities associated with diabetic nephropathy through suppression of inflammatory pathways activated by TNF-α and AGEs. These findings indicate that KRG has a beneficial effect on pathological conditions associated with diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: Advanced glycation end products; Nuclear factor-kappa B; Panax ginseng; Streptozotocin; Tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures
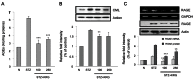
Fig. 1.. Effects of Korean red ginseng (KRG) extract on (A) advanced glycation end products (AGEs), (B) N-(carboxymethyl) lysine (CML), and (C) receptors for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) protein and gene expressions in kidney of SD rats. N, normal rats; STZ, streptozotocin, diabetic control rats; KRG, diabetic rats treated with KRG (100 or 250 mg/kg/d). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared with STZ.
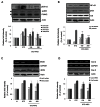
Fig. 2.. Effects of Korean red ginseng (KRG) extract on (A) mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), (B) nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), (C) inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and (D) cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein and gene expressions in kidney of SD rats. N, normal rats; STZ, streptozotocin, diabetic control rats; KRG, diabetic rats treated with KRG (100 or 250 mg/kg/d). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared with STZ. IκB, inhibitor of κB.
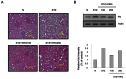
Fig. 3.. Glomerular injury in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic kidney. (A) Glomerular histopathology analysis by H&E staining. The pictures display representative glomeruli of H&E-stained sections in control (N), diabetic (STZ), and Korean red ginseng (KRG) groups at an original magnification of 100. (B) The protein expression levels of fibronectin (FN) in the rat kidneys were detected by Western blot analysis.
Similar articles
- Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) ameliorates type 1 diabetes and restores immune cell compartments.
Hong YJ, Kim N, Lee K, Hee Sonn C, Eun Lee J, Tae Kim S, Ho Baeg I, Lee KM. Hong YJ, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Nov 21;144(2):225-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.08.009. Epub 2012 Aug 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22925946 - Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on metabolic syndrome.
Yoon SJ, Kim SK, Lee NY, Choi YR, Kim HS, Gupta H, Youn GS, Sung H, Shin MJ, Suk KT. Yoon SJ, et al. J Ginseng Res. 2021 May;45(3):380-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34025131 Free PMC article. Review. - Korean red ginseng attenuates hyperglycemia-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis via accelerated autophagy and protects against diabetic kidney disease.
Karunasagara S, Hong GL, Park SR, Lee NH, Jung DY, Kim TW, Jung JY. Karunasagara S, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 23;254:112693. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112693. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32112899 - Protective effect of heat-processed American ginseng against diabetic renal damage in rats.
Kim HY, Kang KS, Yamabe N, Nagai R, Yokozawa T. Kim HY, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Oct 17;55(21):8491-7. doi: 10.1021/jf071770y. Epub 2007 Sep 26. J Agric Food Chem. 2007. PMID: 17894462 - The effects of Korean Red Ginseng on heme oxygenase-1 with a focus on mitochondrial function in pathophysiologic conditions.
Kim CH, Kim HY, Nah SY, Choi YK. Kim CH, et al. J Ginseng Res. 2023 Sep;47(5):615-621. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.04.001. Epub 2023 Apr 8. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 37720574 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Ginseng improves cognitive deficit via the RAGE/NF-κB pathway in advanced glycation end product-induced rats.
Tan X, Gu J, Zhao B, Wang S, Yuan J, Wang C, Chen J, Liu J, Feng L, Jia X. Tan X, et al. J Ginseng Res. 2015 Apr;39(2):116-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Nov 1. J Ginseng Res. 2015. PMID: 26045684 Free PMC article. - Pectin lyase-modified red ginseng extract exhibits potent anti-glycation effects in vitro and in vivo.
Kim CS, Jo K, Pyo MK, Kim JS, Kim J. Kim CS, et al. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2017 Jun 30;21(2):56-62. doi: 10.20463/jenb.2017.0011. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715887 Free PMC article. - Protective Effects of Traditional Polyherbs on Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Cell Model by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and MAPK Signaling Pathway.
Dachuri V, Song PH, Kim YW, Ku SK, Song CH. Dachuri V, et al. Molecules. 2020 Nov 30;25(23):5641. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235641. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33266089 Free PMC article. - Ginseng total saponin modulates the changes of α-actinin-4 in podocytes induced by diabetic conditions.
Ha TS, Choi JY, Park HY, Nam JA, Seong SB. Ha TS, et al. J Ginseng Res. 2014 Oct 15;38(4):233-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 28. J Ginseng Res. 2014. PMID: 25379001 Free PMC article.
References
- Karihaloo A. Anti-fibrosis therapy and diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12:414–422. - PubMed
- Yang CY, Wang J, Zhao Y, Shen L, Jiang X, Xie ZG, Liang N, Zhang L, Chen ZH. Anti-diabetic effects of Panax notoginseng saponins and its major anti-hyperglycemic components. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;130:231–236. - PubMed
- Yuan HD, Kim SJ, Chung SH. Beneficial effects of IH-901 on glucose and lipid metabolisms via activating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase pathways. Metabolism. 2011;60:43–51. - PubMed
- Lee HJ, Lee YH, Park SK, Kang ES, Kim HJ, Lee YC, Choi CS, Park SE, Ahn CW, Cha BS, et al. Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) improves insulin sensitivity and attenuates the development of diabetes in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats. Metabolism. 2009;58:1170–1177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials