Agaricus blazei Murill as an efficient hepatoprotective and antioxidant agent against CCl4-induced liver injury in rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
Agaricus blazei Murill as an efficient hepatoprotective and antioxidant agent against CCl4-induced liver injury in rats
Abeer M Al-Dbass et al. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2012 Jul.
Abstract
Agaricus blazei Murill is one of the very popular edible medicinal mushrooms. The present study investigated the protective effect of this biologically active mushroom on the tissue peroxidative damage and abnormal antioxidant levels in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in male albino rats. Male albino rats of Sprague-Dawley strain weighting (120-150 g) were categorized into five groups. The first group served as the normal control, the second and the third groups were treated with Agaricus blazei Mushroom extract and carbon tetrachloride dose, respectively. Fourth group (protective group) was first treated with Agaricus blazei Mushroom extract followed by carbon tetrachloride treatment and fifth (therapeutic group) with carbon tetrachloride first followed by Agaricus blazei Mushroom treatment. The wet fruiting bodies of mushroom Agaricus blazei Murill, crushed and suspended in distilled water was administered orally to the treated groups of male albino rats. The activities of various enzymes (aspartate and alanine transaminase, lactate dehydrogenase, glutathione reductase), levels of non-enzymatic antioxidants (glutathione, vitamin C, vitamin E) and level of lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde) were determined in the serum of all the experimental animals. Decrease in all the enzymes and non-enzymatic antioxidant, along with an increase in the lipid peroxidative index (malondialdehyde) was found in all the carbon tetrachloride treated rats as compared with normal controls. Also increase level of non-enzymatic antioxidant along with the decrease level in malondialdehyde was found in all experimental animals which were treated with Agaricus blazei Mushroom extract as compared with normal controls. The findings indicate that the extract of Agaricus blazei Murill can protect the liver against carbon tetrachloride induced oxidative damage in rats and is an efficient hepatoprotective and antioxidant agent against carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury.
Keywords: ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase; AbM, Agaricus blazei Murill; Agaricus blazei Murill; Antioxidant; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; Carbon tetrachloride; GR, glutathione reductase; GSH, glutathione; Hepatoprotective; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; Liver; MDA, malondialdehyde; vit. C, vitamin C; vit. E, vitamin E.
Figures
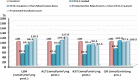
Figure 1
Percentage change of LDH, ALT, AST and GR in CCl4-treated, CCl4-treated + then Mushroom dose, Protected by Mushroom + then CCl4-treated and Protected by Mushroom groups compared to control.
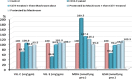
Figure 2
Percentage change of Vit. C, Vit. E, MDA and GSH in CCl4-treated, CCl4-treated + then Mushroom dose, Protected by Mushroom + then CCl4-treated and Protected by Mushroom groups compared to control.
Similar articles
- Agaricus blazei Murill extract abrogates CCl4-induced liver injury in rats.
Wu MF, Hsu YM, Tang MC, Chen HC, Chung JG, Lu HF, Lin JP, Tang NY, Yeh C, Yeh MY. Wu MF, et al. In Vivo. 2011 Jan-Feb;25(1):35-40. In Vivo. 2011. PMID: 21282732 - Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Fagonia schweinfurthii (Hadidi) Hadidi extract in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cell line and rats.
Pareek A, Godavarthi A, Issarani R, Nagori BP. Pareek A, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):973-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.048. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140589 - Investigation of the protective effects of horse mushroom (Agaricus arvensis Schaeff.) against carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress in rats.
Dogan A, Dalar A, Sadullahoglu C, Battal A, Uzun Y, Celik I, Demirel K. Dogan A, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Oct;45(5):787-797. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4218-4. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29931536 - Critical review on chemical compositions and health-promoting effects of mushroom Agaricus blazei Murill.
Huang K, El-Seedi HR, Xu B. Huang K, et al. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022 Nov 5;5:2190-2203. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.10.029. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36387602 Free PMC article. Review. - Polysaccharides and extracts from Agaricus brasiliensis Murill - A comprehensive review.
da Silva Campelo M, Neto JFC, Lima ABN, das Chagas Neto FC, da Costa Gonzaga ML, de Aguiar Soares S, Leal LKAM, Ribeiro MENP, Ricardo NMPS. da Silva Campelo M, et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jul 31;183:1697-1714. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.112. Epub 2021 May 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34022313 Review.
Cited by
- Sesamin ameliorates oxidative liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rat.
Lv D, Zhu CQ, Liu L. Lv D, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):5733-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191289 Free PMC article. - Synthesis and hepatoprotective properties of Acanthus ilicifolius alkaloid A and its derivatives.
Liu L, Fan H, Qi P, Mei Y, Zhou L, Cai L, Lin X, Lin J. Liu L, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2013 Sep;6(3):796-802. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1189. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 24137268 Free PMC article. - Edible mushrooms: improving human health and promoting quality life.
Valverde ME, Hernández-Pérez T, Paredes-López O. Valverde ME, et al. Int J Microbiol. 2015;2015:376387. doi: 10.1155/2015/376387. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Int J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25685150 Free PMC article. Review. - The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases.
Li S, Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang ZJ, Lao L, Wong CW, Feng Y. Li S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 2;16(11):26087-124. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125942. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26540040 Free PMC article. Review. - Differences in antioxidant activities of outdoor- and indoor-cultivated Agaricus brasiliensis, and protective effects against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic injury in mice.
Yamanaka D, Motoi M, Motoi A, Ohno N. Yamanaka D, et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Nov 24;14:454. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-454. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25418207 Free PMC article.
References
- Abou Gabal A.A., Essawy A.E., Abdel-Moneim A.M., Hamed S.S., Elzergy A.A. The protective effect of black seed (Nigella sativa) against carbon tetrachloride-induced chromosomal aberrations and ultrastructural changes of bone marrow cells. Arab J. Biotechnol. 2007;10(2):275–288.
- Abdulmajeed N.A. Influence of Agaricus blazei on rate liver toxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride. J. Egypt. Soc. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2007;9:63–79.
- Aldrige W.N. Mechanism of toxicity: new concept are required in toxicology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1981;2:228–231.
- Aletor V.A., Aladetimi O.O. Compositional studies on edible tropical species of mushrooms. Food Chem. 1995;54(3):265–268.
- Al-Ghamdi M.S. Protective effect of Nigella sativa seeds against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2003;31(5):721–728. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources