Combined antibacterial activity of stingless bee (Apis mellipodae) honey and garlic (Allium sativum) extracts against standard and clinical pathogenic bacteria - PubMed (original) (raw)
Combined antibacterial activity of stingless bee (Apis mellipodae) honey and garlic (Allium sativum) extracts against standard and clinical pathogenic bacteria
Berhanu Andualem. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013 Sep.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the synergic antibacterial activity of garlic and tazma honey against standard and clinical pathogenic bacteria.
Methods: Antimicrobial activity of tazma honey, garlic and mixture of them against pathogenic bacteria were determined. Chloramphenicol and water were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration of antimicrobial samples were determined using standard methods.
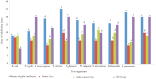
Results: Inhibition zone of mixture of garlic and tazma honey against all tested pathogens was significantly (P≤0.05) greater than garlic and tazma honey alone. The diameter zone of inhibition ranged from (18±1) to (35±1) mm for mixture of garlic and tazma honey, (12±1) to (20±1) mm for tazma honey and (14±1) to (22±1) mm for garlic as compared with (10±1) to (30±1) mm for chloramphenicol. The combination of garlic and tazma honey (30-35 mm) was more significantly (P≤0.05) effective against Salmonella (NCTC 8385), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923), Lyesria moncytogenes (ATCC 19116) and Streptococcus pneumonia (ATCC 63). Results also showed considerable antimicrobial activity of garlic and tazma honey. MIC of mixture of garlic and tazma honey at 6.25% against total test bacteria was 88.9%. MIC of mixture of garlic and tazma honey at 6.25% against Gram positive and negative were 100% and 83.33%, respectively. The bactericidal activities of garlic, tazma honey, and mixture of garlic and tazma honey against all pathogenic bacteria at 6.25% concentration were 66.6%, 55.6% and 55.6%, respectively.
Conclusions: This finding strongly supports the claim of the local community to use the combination of tazma honey and garlic for the treatment of different pathogenic bacterial infections. Therefore, garlic in combination with tazma honey can serve as an alternative natural antimicrobial drug for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. Further in vivo study is recommended to come up with a comprehensive conclusion.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity; Bactericidal activity; Garlic; Honey; Inhibition zone; Minimum bactericidal concentration; Minimum inhibitory concentration.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: I declare that I have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1.. Antibacterial activity of different concentrations of garlic, hone and mixture of garlic and honey (v/v) by agar well diffusion method.
Chl: Chloramphenicol. Values are means of triplicate determinations. Values of the same colour bars followed by different letters are significantly different (P<0.05).
Similar articles
- Antimicrobial Effect of Garlic (Allium sativum) and Thyme (Zataria multiflora Boiss) Extracts on Some Food Borne Pathogens and Their Effect on Virulence Gene Expression.
El-Azzouny MM, El-Demerdash AS, Seadawy HG, Abou-Khadra SH. El-Azzouny MM, et al. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018 Jul 30;64(10):79-86. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018. PMID: 30084799 - Onion and Garlic Extracts Potentiate the Efficacy of Conventional Antibiotics against Standard and Clinical Bacterial Isolates.
Mahomoodally F, Ramcharun S, Zengin G. Mahomoodally F, et al. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18(9):787-796. doi: 10.2174/1568026618666180604083313. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29866009 - Antibacterial effect of Allium sativum cloves and Zingiber officinale rhizomes against multiple-drug resistant clinical pathogens.
Karuppiah P, Rajaram S. Karuppiah P, et al. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012 Aug;2(8):597-601. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60104-X. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012. PMID: 23569978 Free PMC article. - Honey microbiota, methods for determining the microbiological composition and the antimicrobial effect of honey - A review.
Luca L, Pauliuc D, Oroian M. Luca L, et al. Food Chem X. 2024 Jun 4;23:101524. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101524. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38947342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- In Vitro Antimicrobial Effectiveness Tests Using Garlic (Allium sativum) against Salmonella enterica Subspecies enterica Serovar Enteritidis.
Circella E, Casalino G, D'Amico F, Pugliese N, Dimuccio MM, Camarda A, Bozzo G. Circella E, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;11(11):1481. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111481. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358136 Free PMC article. - Synergetic antimicrobial effects of mixtures of ethiopian honeys and ginger powder extracts on standard and resistant clinical bacteria isolates.
Ewnetu Y, Lemma W, Birhane N. Ewnetu Y, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:562804. doi: 10.1155/2014/562804. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24772182 Free PMC article. - The role of spices and lactic acid bacteria as antimicrobial agent to extend the shelf life of metata ayib (traditional Ethiopian spiced fermented cottage cheese).
Geremew T, Kebede A, Andualem B. Geremew T, et al. J Food Sci Technol. 2015 Sep;52(9):5661-70. doi: 10.1007/s13197-014-1694-y. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Food Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26344979 Free PMC article. - Comparative analysis of two kinds of garlic seedings: qualities and transcriptional landscape.
Ai P, Xue J, Zhu Y, Tan W, Wu Y, Wang Y, Li Z, Shi Z, Kang D, Zhang H, Jiang L, Wang Z. Ai P, et al. BMC Genomics. 2023 Feb 24;24(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09183-x. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36829121 Free PMC article. - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Phyto-L, Thiosulfonate from Allium spp. Containing Supplement, against Escherichia Coli Strains from Rabbits.
D'Amico F, Casalino G, Dinardo FR, Schiavitto M, Camarda A, Romito D, Bove A, Circella E. D'Amico F, et al. Vet Sci. 2023 Jun 23;10(7):411. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10070411. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37505817 Free PMC article.
References
- Namita P, Mukesh R. Medicinal plants used as antimicrobial agents: A review. Int Res J Pharm. 2012;3(1):31–40.
- Patel RV, Thaker VT, Patel VK, Shukla P, Bhatnagar P, Patel A. In vitro study of changing antibiotic sensitivity and resistance by honey on gingival inflammation during orthodontic treatment-a preliminary report. Orthodontic Cyber J. 2010 [Online] Available from: http://orthocj.com/2010/06/in-vitro-study-antibiotic-sensitivity-resista.... [Assessed on 2 April, 2013].
- Efem SEE, Udoh KT, Iwara CI. The antimicrobial spectrum of honey and its clinical significance. Infect. 1992;20(4):227–229. - PubMed
- Taghizadeh M, Saffari M, Pourbabaei M, Mahboubi M. Antimicrobial activity of different honey samples against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro. Biharean Biol. 2011;5(2):113–115.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical