Activation and evasion of antiviral innate immunity by hepatitis C virus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Activation and evasion of antiviral innate immunity by hepatitis C virus
Stacy M Horner. J Mol Biol. 2014.
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) chronically infects 130-170 million people worldwide and is a major public health burden. HCV is an RNA virus that infects hepatocytes within liver, and this infection is sensed as non-self by the intracellular innate immune response to program antiviral immunity to HCV. HCV encodes several strategies to evade this antiviral response, and this evasion of innate immunity plays a key role in determining viral persistence. This review discusses the molecular mechanisms of how the intracellular innate immune system detects HCV infection, including how HCV pathogen-associated molecular patterns are generated during infection and where they are recognized as foreign by the innate immune system. Further, this review highlights the key innate immune evasion strategies used by HCV to establish persistent infection within the liver, as well as how host genotype influences the outcome of HCV infection. Understanding these HCV-host interactions is key in understanding how to target HCV during infection and for the design of more effective HCV therapies at the immunological level.
Keywords: HCV; MAM; MAVS; RIG-I; interferon.
© 2013.
Figures
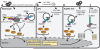
Figure 1. Innate immune sensing of HCV
Hallmarks of HCV infection can be sensed by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in a number of cell types within the liver to activate innate immunity. (A) HCV infection in hepatocytes is sensed by RIG-I, which detects the poly U/UC tract present in the 3’end of HCV RNA, and by TLR3, which detects dsRNA replication intermediates or HCV RNA that has been endocytosed from dying cells. These PRRs signal downstream to activate the innate immune response program, including the production of IFNβ, IFNλ, and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which act in an autocrine and paracrine manner to establish the full innate immune response. The red “X” indicates points of regulation of these signaling pathways by the HCV NS3/4A protease. (B) HCV is sensed in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) by TLR7-mediated recognition of HCV RNA in the endosome. While pDCs themselves are not productively infected with HCV, the viral RNA is taken up by the pDC following exosomal transfer of viral RNA from productively infected hepatocytes. C) HCV can also be sensed in Kupffer cells, the liver resident macrophages, by the inflammasome signaling complex. Kupffer cells phagocytose HCV RNA (Signal 1) for TLR7-dependent signaling that activates the transcription of the pro-forms of IL-1β and IL-18, while potassium efflux (Signal 2) sensed by NLRP3 drives caspase 1 processing of IL-1β and IL-18 into the mature form for secretion and full activation of the inflammasome.
Similar articles
- Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern Recognition of Hepatitis C Virus Transmitted/Founder Variants by RIG-I Is Dependent on U-Core Length.
Kell A, Stoddard M, Li H, Marcotrigiano J, Shaw GM, Gale M Jr. Kell A, et al. J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(21):11056-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01964-15. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26311867 Free PMC article. - Insights into antiviral innate immunity revealed by studying hepatitis C virus.
Horner SM. Horner SM. Cytokine. 2015 Aug;74(2):190-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25819428 Free PMC article. Review. - Innate detection of hepatitis B and C virus and viral inhibition of the response.
Yi Z, Chen J, Kozlowski M, Yuan Z. Yi Z, et al. Cell Microbiol. 2015 Sep;17(9):1295-303. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12489. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Cell Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26243406 Review. - Innate immune responses in hepatitis C virus infection.
Li K, Lemon SM. Li K, et al. Semin Immunopathol. 2013 Jan;35(1):53-72. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0332-x. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Semin Immunopathol. 2013. PMID: 22868377 Free PMC article. Review. - Hepatitis A and hepatitis C viruses: divergent infection outcomes marked by similarities in induction and evasion of interferon responses.
Qu L, Lemon SM. Qu L, et al. Semin Liver Dis. 2010 Nov;30(4):319-32. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1267534. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Semin Liver Dis. 2010. PMID: 20960373 Review.
Cited by
- Proteomic analysis of mitochondrial-associated ER membranes (MAM) during RNA virus infection reveals dynamic changes in protein and organelle trafficking.
Horner SM, Wilkins C, Badil S, Iskarpatyoti J, Gale M Jr. Horner SM, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 3;10(3):e0117963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117963. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25734423 Free PMC article. - Message in a bottle: lessons learned from antagonism of STING signalling during RNA virus infection.
Maringer K, Fernandez-Sesma A. Maringer K, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Dec;25(6):669-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25212897 Free PMC article. Review. - Elevated on-treatment levels of serum IFN-gamma is associated with treatment failure of peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C.
Lu MY, Huang CI, Dai CY, Wang SC, Hsieh MY, Hsieh MH, Liang PC, Lin YH, Hou NJ, Yeh ML, Huang CF, Lin ZY, Chen SC, Huang JF, Chuang WL, Yu ML. Lu MY, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 11;6:22995. doi: 10.1038/srep22995. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26965318 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome analysis of PK-15 cells in innate immune response to porcine deltacoronavirus infection.
Jiang S, Li F, Li X, Wang L, Zhang L, Lu C, Zheng L, Yan M. Jiang S, et al. PLoS One. 2019 Oct 1;14(10):e0223177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223177. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31574122 Free PMC article. - RIG-I in RNA virus recognition.
Kell AM, Gale M Jr. Kell AM, et al. Virology. 2015 May;479-480:110-21. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25749629 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lavanchy D. The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2009;29(Suppl 1):74–81. - PubMed
- Soriano V, Peters MG, Zeuzem S. New therapies for hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:313–20. - PubMed
- Hofmann WP, Zeuzem S. A new standard of care for the treatment of chronic HCV infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:257–64. - PubMed
- Sarrazin C, Hezode C, Zeuzem S, Pawlotsky JM. Antiviral strategies in hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2012;56(Suppl):S88–S100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous