The link between periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis: an updated review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The link between periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis: an updated review
Joanna Koziel et al. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014 Mar.
Abstract
Porphyromonas gingivalis is a leading pathogen in chronic periodontitis, a disease process involving progressive destruction of the tissues that support the teeth. Recently, the organism has been reported to produce a unique bacterial enzyme, P. gingivalis peptidyl-arginine deiminase (PPAD), which has the ability to convert arginine residues in proteins to citrulline. Protein citrullination alters protein structure and function; hence, PPAD may be involved in deregulation of the host's signalling network and immune evasion. Further, accumulating evidence suggests a role for autoimmunity against citrullinated proteins in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). As inflammatory conditions in the lungs of cigarette smokers contribute to the breakdown of immune tolerance to citrullinated epitopes, chronic exposure to citrullinated proteins at periodontitis sites may also predispose susceptible individuals to the development of autoantibodies and the initiation of RA. In this review, we discuss evidence that PPAD may represent a mechanistic link between periodontitis and RA, diseases that are known to be significantly associated at the epidemiological level.
Conflict of interest statement
Joanna Koziel, Piotr Mydel, and Jan Potempa declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
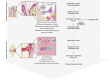
Fig. 1
A model of periodontitis-initiated pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) initiated by PPAD/PAD-catalysed modification of proteins in the inflamed periodontal tissue and driven by autoimmunity against citrullinated epitopes joints. Figure was created using Servier Medical Art
Similar articles
- Heightened immune response to autocitrullinated Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase: a potential mechanism for breaching immunologic tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis.
Quirke AM, Lugli EB, Wegner N, Hamilton BC, Charles P, Chowdhury M, Ytterberg AJ, Zubarev RA, Potempa J, Culshaw S, Guo Y, Fisher BA, Thiele G, Mikuls TR, Venables PJ. Quirke AM, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Jan;73(1):263-9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202726. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 23463691 Free PMC article. - Defining the role of Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase (PPAD) in rheumatoid arthritis through the study of PPAD biology.
Konig MF, Paracha AS, Moni M, Bingham CO 3rd, Andrade F. Konig MF, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Nov;74(11):2054-61. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205385. Epub 2014 May 26. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24864075 Free PMC article. - Crystal structure of Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase: implications for autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis.
Montgomery AB, Kopec J, Shrestha L, Thezenas ML, Burgess-Brown NA, Fischer R, Yue WW, Venables PJ. Montgomery AB, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Jun;75(6):1255-61. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207656. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26209657 Free PMC article. - Periodontal sources of citrullinated antigens and TLR agonists related to RA.
Vitkov L, Hannig M, Minnich B, Herrmann M. Vitkov L, et al. Autoimmunity. 2018 Sep;51(6):304-309. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2018.1527907. Epub 2018 Nov 10. Autoimmunity. 2018. PMID: 30417696 Review. - The association between rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis.
Leech MT, Bartold PM. Leech MT, et al. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Apr;29(2):189-201. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 May 1. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26362738 Review.
Cited by
- Higher odds of periodontitis in systemic lupus erythematosus compared to controls and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review, meta-analysis and network meta-analysis.
Tan PR, Lee AJL, Zhao JJ, Chan YH, Fu JH, Ma M, Tay SH. Tan PR, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1356714. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1356714. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38629069 Free PMC article. - Hemophore-like proteins of the HmuY family in the oral and gut microbiome: unraveling the mystery of their evolution.
Olczak T, Śmiga M, Antonyuk SV, Smalley JW. Olczak T, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Mar 27;88(1):e0013123. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00131-23. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38305743 Review. - The Effects of Periodontal Treatment on Rheumatoid Arthritis and of Anti-Rheumatic Drugs on Periodontitis: A Systematic Review.
Inchingolo F, Inchingolo AM, Avantario P, Settanni V, Fatone MC, Piras F, Di Venere D, Inchingolo AD, Palermo A, Dipalma G. Inchingolo F, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 7;24(24):17228. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417228. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139057 Free PMC article. Review. - Occurrence of radiopaque and mixed lesions at periapical region in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: a retrospective study.
Yilmaz M, Tunc F. Yilmaz M, et al. BMC Oral Health. 2023 Oct 24;23(1):781. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03493-y. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37875827 Free PMC article.
References
- Marotte H, Farge P, Gaudin P, Alexandre C, Mougin B, Miossec P. The association between periodontal disease and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis extends the link between the HLA-DR shared epitope and severity of bone destruction. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:905–909. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.036913. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Bonfil JJ, Dillier FL, Mercier P, Reviron D, Foti B, Sambuc R, et al. A "case control" study on the role of HLA DR4 in severe periodontitis and rapidly progressive periodontitis. Identification of types and subtypes using molecular biology (PCR.SSO) J Clin Periodontol. 1999;26:77–84. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.1999.260203.x. - DOI - PubMed
- de Pablo P, Dietrich T, McAlindon TE. Association of periodontal disease and tooth loss with rheumatoid arthritis in the US population. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:70–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials