In vitro and in vivo anti-cancer activities of Kuding tea (Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng) against oral cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
In vitro and in vivo anti-cancer activities of Kuding tea (Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng) against oral cancer
Kai Zhu et al. Exp Ther Med. 2014 Mar.
Abstract
Kuding tea (Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng) is drunk widely in China. The in vitro anticancer effects of Kuding tea were evaluated in TCA8113 human tongue carcinoma cells using a 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. At a concentration of 200 μg/ml, Kuding tea exhibited an inhibitory effect of 75% in TCA8113 cells, which was higher than that observed at concentrations of 100 and 50 μg/ml (41 and 10% inhibition, respectively). Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot analyses of the apoptosis, inflammation and metastasis genes and proteins in Kuding tea-treated cancer cells were performed. Kuding tea significantly induced apoptosis in TCA8113 cancer cells (P<0.05) by upregulating Bax, caspase-3 and caspase-9 expression, and downregulating Bcl-2 expression. Expression of the NF-κB, iNOS and COX-2 genes that are associated with inflammation was significantly downregulated by Kuding tea, which demonstrated its anti-inflammatory properties. Kuding tea also exerted an anti-metastatic effect on cancer cells. This was demonstrated by the decreased expression of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) and the increased expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), and confirmed by the inhibition of the metastasis of U14 squamous cell carcinoma cells in imprinting control region (ICR) mice. The ICR mouse buccal mucosa cancer model was established by injecting the mice with U14 cells. Following injection, the wound at the injection site was topically treated with Kuding tea. It was observed that the tumor volumes for the group treated with Kuding tea were smaller than those from the control mice. Analysis of the sections of buccal mucosa cancer tissue demonstrated that the buccal mucosa cancer degrees of the Kuding tea-treated mice were weaker than that in the control mice. Similar results were observed in the lesion sections of the cervical lymph nodes. Based on these results, Kuding tea exhibited successful in vitro anticancer effects in TCA8113 cells and in vivo buccal mucosa cancer preventive activity.
Keywords: Kuding tea; U14 squamous cell carcinoma cells; buccal mucosa cancer; human tongue carcinoma TCA8113 cells; metastasis.
Figures
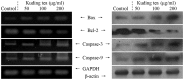
Figure 1
Effects of various concentrations of Kuding tea on the mRNA (left) and protein (right) expression levels of Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-3 and caspase-9 in human tongue carcinoma TCA8113 cells.
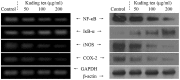
Figure 2
Effects of various concentrations of Kuding tea on the mRNA (left) and protein (right) expression levels of NF-κB, IκB-α, iNOS and COX-2 in human tongue carcinoma TCA8113 cells.
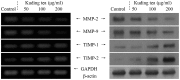
Figure 3
Effects of various concentrations of Kuding tea on the mRNA (left) and protein (right) expression levels of MMPs and TIMPs in human tongue carcinoma TCA8113 cells.
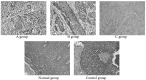
Figure 4
Histology of buccal mucosa tissues induced by injecting U14 squamous cell carcinoma cells into mice (H&E staining; magnification, ×100). Group A, mice were administered 400 mg/kg by gavage and topically treated with 100 mg/ml Kunming tea; Group B, mice were administered 800 mg/kg by gavage and topically treated with 200 mg/ml Kunming tea; Group C, mice were administered 1,600 mg/kg by gavage and topically treated with 400 mg/ml Kunming tea.
Similar articles
- Chemical Composition, Bioactivity and Safety Aspects of Kuding Tea-From Beverage to Herbal Extract.
Wüpper S, Lüersen K, Rimbach G. Wüpper S, et al. Nutrients. 2020 Sep 12;12(9):2796. doi: 10.3390/nu12092796. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32932672 Free PMC article. Review. - Pu-erh tea has in vitro anticancer activity in TCA8113 cells and preventive effects on buccal mucosa cancer in U14 cells injected mice in vivo.
Zhao X, Qian Y, Zhou YL, Wang R, Wang Q, Li GJ. Zhao X, et al. Nutr Cancer. 2014;66(6):1059-69. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2014.916317. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Nutr Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24945996 - Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng (Kudingcha) has in vitro anticancer activities in MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cells and exerts anti-metastatic effects in vivo.
Zhao X, Wang Q, Qian Y, Song JL. Zhao X, et al. Oncol Lett. 2013 May;5(5):1744-1748. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1253. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23760150 Free PMC article. - Purple bamboo salt has anticancer activity in TCA8113 cells in vitro and preventive effects on buccal mucosa cancer in mice in vivo.
Zhao X, Deng X, Park KY, Qiu L, Pang L. Zhao X, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2013 Feb;5(2):549-554. doi: 10.3892/etm.2012.848. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 23403521 Free PMC article. - The large-leaved Kudingcha (Ilex latifolia Thunb and Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng): a traditional Chinese tea with plentiful secondary metabolites and potential biological activities.
Li L, Xu LJ, Ma GZ, Dong YM, Peng Y, Xiao PG. Li L, et al. J Nat Med. 2013 Jul;67(3):425-37. doi: 10.1007/s11418-013-0758-z. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23529541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Ursolic acid-enriched kudingcha extract enhances the antitumor activity of bacteria-mediated cancer immunotherapy.
Xu H, Piao L, Liu X, Jiang SN. Xu H, et al. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 May 4;22(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03612-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35509047 Free PMC article. - Chemical Composition, Bioactivity and Safety Aspects of Kuding Tea-From Beverage to Herbal Extract.
Wüpper S, Lüersen K, Rimbach G. Wüpper S, et al. Nutrients. 2020 Sep 12;12(9):2796. doi: 10.3390/nu12092796. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32932672 Free PMC article. Review. - Health Benefits of Bioactive Compounds from the Genus Ilex, a Source of Traditional Caffeinated Beverages.
Gan RY, Zhang D, Wang M, Corke H. Gan RY, et al. Nutrients. 2018 Nov 5;10(11):1682. doi: 10.3390/nu10111682. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30400635 Free PMC article. Review. - Comparison of Antioxidative Effects of Insect Tea and Its Raw Tea (Kuding Tea) Polyphenols in Kunming Mice.
Zhao X, Song JL, Yi R, Li G, Sun P, Park KY, Suo H. Zhao X, et al. Molecules. 2018 Jan 19;23(1):204. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010204. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29351230 Free PMC article. - Ilex latifolia Thunb protects mice from HFD-induced body weight gain.
Wu H, Chen YL, Yu Y, Zang J, Wu Y, He Z. Wu H, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 7;7(1):14660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15292-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29116160 Free PMC article.
References
- Liu LX, Sun Y, Laura TG, Liang XF, Ye H, Zeng XX. Determination of polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity of kudingcha made from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng. Food Chem. 2009;112:35–41.
- Sun Y, Xu WQ, Zhang WQ, Hu QH, Zeng XX. Optimizing the extraction of phenolic antioxidants from kudingcha made from Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng by using response surface methodology. Sep Purif Technol. 2011;78:311–320.
- Bravo L, Goya L, Lecumberri E. LC/MS characterization of phenolic constituents of mate (Ilex paraguariensis, St. Hil) and its antioxidant activity compared to commonly consumed beverages. Food Res Int. 2007;40:393–405.
- Nakajima Y, Shimazawa M, Mishima S, Hara H. Water extract of propolis and its main constituents, caffeoylquinic acid derivatives, exert neuroprotective effects via antioxidant actions. Life Sci. 2007;80:370–377. - PubMed
- Han J, Miyamae Y, Shigemori H, Isoda H. Neuroprotective effect of 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid on SH-SY5Y cells and senescence-accelerated-prone mice 8 through the up-regulation of phosphoglycerate kinase-1. Neuroscience. 2010;169:1039–1045. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials