When Mad met Bub - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
When Mad met Bub
Katharina Overlack et al. EMBO Rep. 2014 Apr.
Abstract
The faithful segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells is essential for cellular and organismal viability. Errors in this process cause aneuploidy, a hallmark of cancer and several congenital diseases. For proper separation, chromosomes attach to microtubules of the mitotic spindle via their kinetochores, large protein structures assembled on centromeric chromatin. Kinetochores are also crucial for a cell cycle feedback mechanism known as the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). The SAC forces cells to remain in mitosis until all chromosomes are properly attached to microtubules. At the beginning of mitosis, the SAC proteins--Mad1, Mad2, Bub1, Bub3, BubR1, Mps1, and Cdc20--are recruited to kinetochores in a hierarchical and interdependent fashion (Fig 1A). There they monitor, in ways that are not fully clarified, the formation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments. Two studies recently published in EMBO reports by the groups of Silke Hauf and Jakob Nilsson, and a recent study by London and Biggins in Genes & Development, shed new light on the conserved SAC protein Mad1.
Figures
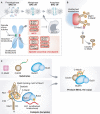
Figure 1
Control of mitotic progression by the SAC. (A) The SAC is active in prometaphase and turns off when chromosomes are bi-oriented (metaphase). Kinetochores are shown as green or red dots, depending on whether or not they are bound to microtubules. SAC proteins are recruited to “red” kinetochores, where they assemble the MCC, which inhibits the APC/C. (B) Mad1/C-Mad2 forms a 2:2 tetramer. Mad1/C-Mad2 at kinetochores acts as a receptor for O-Mad2, facilitating the transformation of O-Mad2 into C-Mad2 bound to Cdc20. (C) Mad2 binds a Mad2-binding motif in Mad1 (green) with the help of its “seatbelt” (red). The CTD of Mad1 is near the Mad2-binding region, and the RLK motif neighbors the CTD. Please see the text for details of our proposed model of how Mad1/C-Mad2 and Bub1/Bub3 catalyze rapid MCC formation. The coloring scheme emphasizes the copy to template relationship of the MCC product with the catalytic platform.
Comment on
- A direct role of Mad1 in the spindle assembly checkpoint beyond Mad2 kinetochore recruitment.
Kruse T, Larsen MS, Sedgwick GG, Sigurdsson JO, Streicher W, Olsen JV, Nilsson J. Kruse T, et al. EMBO Rep. 2014 Mar;15(3):282-90. doi: 10.1002/embr.201338101. Epub 2014 Jan 29. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 24477933 Free PMC article. - Mad1 contribution to spindle assembly checkpoint signalling goes beyond presenting Mad2 at kinetochores.
Heinrich S, Sewart K, Windecker H, Langegger M, Schmidt N, Hustedt N, Hauf S. Heinrich S, et al. EMBO Rep. 2014 Mar;15(3):291-8. doi: 10.1002/embr.201338114. Epub 2014 Jan 29. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 24477934 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Mad1 contribution to spindle assembly checkpoint signalling goes beyond presenting Mad2 at kinetochores.
Heinrich S, Sewart K, Windecker H, Langegger M, Schmidt N, Hustedt N, Hauf S. Heinrich S, et al. EMBO Rep. 2014 Mar;15(3):291-8. doi: 10.1002/embr.201338114. Epub 2014 Jan 29. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 24477934 Free PMC article. - Phosphodependent recruitment of Bub1 and Bub3 to Spc7/KNL1 by Mph1 kinase maintains the spindle checkpoint.
Shepperd LA, Meadows JC, Sochaj AM, Lancaster TC, Zou J, Buttrick GJ, Rappsilber J, Hardwick KG, Millar JB. Shepperd LA, et al. Curr Biol. 2012 May 22;22(10):891-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.051. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22521786 Free PMC article. - MPS1/Mph1 phosphorylates the kinetochore protein KNL1/Spc7 to recruit SAC components.
Yamagishi Y, Yang CH, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y. Yamagishi Y, et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Jun 3;14(7):746-52. doi: 10.1038/ncb2515. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22660415 - Microtubule attachment and spindle assembly checkpoint signalling at the kinetochore.
Foley EA, Kapoor TM. Foley EA, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;14(1):25-37. doi: 10.1038/nrm3494. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23258294 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A molecular basis for the differential roles of Bub1 and BubR1 in the spindle assembly checkpoint.
Overlack K, Primorac I, Vleugel M, Krenn V, Maffini S, Hoffmann I, Kops GJ, Musacchio A. Overlack K, et al. Elife. 2015 Jan 22;4:e05269. doi: 10.7554/eLife.05269. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25611342 Free PMC article. - Mps1Mph1 Kinase Phosphorylates Mad3 to Inhibit Cdc20Slp1-APC/C and Maintain Spindle Checkpoint Arrests.
Zich J, May K, Paraskevopoulos K, Sen O, Syred HM, van der Sar S, Patel H, Moresco JJ, Sarkeshik A, Yates JR 3rd, Rappsilber J, Hardwick KG. Zich J, et al. PLoS Genet. 2016 Feb 16;12(2):e1005834. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005834. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 26882497 Free PMC article. - An actin-dependent spindle position checkpoint ensures the asymmetric division in mouse oocytes.
Metchat A, Eguren M, Hossain JM, Politi AZ, Huet S, Ellenberg J. Metchat A, et al. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 15;6:7784. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8784. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26174204 Free PMC article. Retracted. - Stressing mitosis to death.
Burgess A, Rasouli M, Rogers S. Burgess A, et al. Front Oncol. 2014 Jun 4;4:140. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00140. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24926440 Free PMC article. Review. - Gene signatures and prognostic analyses of the Tob/BTG pituitary tumor-transforming gene (PTTG) family in clinical breast cancer patients.
Wu CC, Ekanem TI, Phan NN, Loan DTT, Hou SY, Lee KH, Wang CY. Wu CC, et al. Int J Med Sci. 2020 Oct 22;17(18):3112-3124. doi: 10.7150/ijms.49652. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33173433 Free PMC article.
References
- Lara-Gonzalez P, Westhorpe FG, Taylor SS. Curr Biol. 2012;22:R966–R980. - PubMed
- De Antoni A, Pearson CG, Cimini D, et al. Curr Biol. 2005;15:214–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous