TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways
Guadalupe Sabio et al. Semin Immunol. 2014 Jun.
Abstract
The binding of tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) to cell surface receptors engages multiple signal transduction pathways, including three groups of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases: extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERKs); the cJun NH2-terminal kinases (JNKs); and the p38 MAP kinases. These MAP kinase signalling pathways induce a secondary response by increasing the expression of several inflammatory cytokines (including TNFα) that contribute to the biological activity of TNFα. MAP kinases therefore function both upstream and down-stream of signalling by TNFα receptors. Here we review mechanisms that mediate these actions of MAP kinases during the response to TNFα.
Keywords: ERK; JNK; MAP kinase; TNF; p38 MAP kinase.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
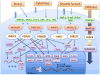
Figure 1. MAP kinase pathways
A general feature of MAPK pathways is a canonical cascade consisting of a MAPK kinase kinases (MAP3K), a MAPK kinase (MAP2K) and a MAPK. Three groups of MAP kinases can be defined: ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase); JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase); and p38 MAP kinases. These pathways can be activated by many stimuli, including growth factors, inflammatory cytokines, and a wide spectrum of cellular stresses. The MAP kinases can phosphorylate downstream targets, including protein kinases, cytosolic substrates, and transcription factors.
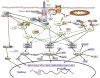
Figure 2. Activation of MAP kinases by TNFα
TNFα causes the activation of ERK, JNK, and p38 MAP kinases. TNFα-stimulated ERK activation is primarily mediated by the TAK1-IKK2-TPL2 pathway. In contrast, TNFα-stimulated activation of stress-activated MAP kinases (p38 and JNK) is mediated by multiple pathways, including those engaged by ASK1, MLK, TAK1, and TPL2.
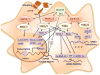
Figure 3. MAP kinases control of TNFα biosynthesis
MAPK regulates TNFα expression by several mechanisms. Tnfα gene transcription can be regulated by ERK, JNK and p38α MAP kinases (and by down-stream protein kinases, including MSK1/2). In addition, the ERK pathway regulates Tnfα mRNA export to the cytoplasm, Tnfα mRNA stability, Tnfα mRNA translation initiation (mediated by MNK), and TNFα shedding by TACE phosphorylation. The p38α MAP kinase pathway regulates Tnfα mRNA translation initiation and Tnfα mRNA stability (mediated by the MNK and MK2/3 pathways). Moreover, the p38γ/δ MAP kinase pathway controls TNFα translation elongation by phosphorylation and inactivation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 Kinase (eEF2K).
Similar articles
- Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades during priming of human neutrophils by TNF-alpha and GM-CSF.
McLeish KR, Knall C, Ward RA, Gerwins P, Coxon PY, Klein JB, Johnson GL. McLeish KR, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Oct;64(4):537-45. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9766635 - Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases.
Johnson GL, Lapadat R. Johnson GL, et al. Science. 2002 Dec 6;298(5600):1911-2. doi: 10.1126/science.1072682. Science. 2002. PMID: 12471242 Review. - Stress and vascular responses: atheroprotective effect of laminar fluid shear stress in endothelial cells: possible role of mitogen-activated protein kinases.
Yoshizumi M, Abe J, Tsuchiya K, Berk BC, Tamaki T. Yoshizumi M, et al. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Mar;91(3):172-6. doi: 10.1254/jphs.91.172. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12686737 Review.
Cited by
- Comparing the functions of equine and canine influenza H3N8 virus PA-X proteins: Suppression of reporter gene expression and modulation of global host gene expression.
Feng KH, Sun M, Iketani S, Holmes EC, Parrish CR. Feng KH, et al. Virology. 2016 Sep;496:138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27314620 Free PMC article. - Parkia speciosa empty pod extract exerts anti-inflammatory properties by modulating NFκB and MAPK pathways in cardiomyocytes exposed to tumor necrosis factor-α.
Gui JS, Jalil J, Jubri Z, Kamisah Y. Gui JS, et al. Cytotechnology. 2019 Feb;71(1):79-89. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0267-8. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Cytotechnology. 2019. PMID: 30600464 Free PMC article. - High-Dose Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) Displays Strong Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Monocytes.
Mikkelsen K, Dargahi N, Fraser S, Apostolopoulos V. Mikkelsen K, et al. Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 19;11(9):2578. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092578. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761018 Free PMC article. - Tristetraprolin regulates necroptosis during tonic Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling in murine macrophages.
Ariana A, Alturki NA, Hajjar S, Stumpo DJ, Tiedje C, Alnemri ES, Gaestel M, Blackshear PJ, Sad S. Ariana A, et al. J Biol Chem. 2020 Apr 3;295(14):4661-4672. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011633. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32094226 Free PMC article. - Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sulforaphane on LPS-Activated Microglia Potentially through JNK/AP-1/NF-κB Inhibition and Nrf2/HO-1 Activation.
Subedi L, Lee JH, Yumnam S, Ji E, Kim SY. Subedi L, et al. Cells. 2019 Feb 22;8(2):194. doi: 10.3390/cells8020194. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30813369 Free PMC article.
References
- Janes KA, Gaudet S, Albeck JG, Nielsen UB, Lauffenburger DA, Sorger PK. The response of human epithelial cells to TNF involves an inducible autocrine cascade. Cell. 2006;124:1225–39. - PubMed
- Nebreda AR, Porras A. p38 MAP kinases: beyond the stress response. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:257–60. - PubMed
- Schieven GL. The biology of p38 kinase: a central role in inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem. 2005;5:921–8. - PubMed
- Manning AM, Davis RJ. Targeting JNK for therapeutic benefit: from junk to gold? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:554–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 260464/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- P01 AI046629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK090963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous