Review article: the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Review article: the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases
Aleksandra Piechota-Polanczyk et al. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014 Jul.
Abstract
In this review, we focus on the role of oxidative stress in the aetiology of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and colitis-associated colorectal cancer and discuss free radicals and free radical-stimulated pathways as pharmacological targets for anti-IBD drugs. We also suggest novel anti-oxidative agents, which may become effective and less-toxic alternatives in IBD and colitis-associated colorectal cancer treatment. A Medline search was performed to identify relevant bibliography using search terms including: 'free radicals,' 'antioxidants,' 'oxidative stress,' 'colon cancer,' 'ulcerative colitis,' 'Crohn's disease,' 'inflammatory bowel disease.' Several therapeutics commonly used in IBD treatment, among which are immunosuppressants, corticosteroids and anti-TNF-α antibodies, could also affect the IBD progression by interfering with cellular oxidative stress and cytokine production. Experimental data shows that these drugs may effectively scavenge free radicals, increase anti-oxidative capacity of cells, influence multiple signalling pathways, e.g. MAPK and NF-kB, and inhibit pro-oxidative enzyme and cytokine concentration. However, their anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effectiveness still needs further investigation. A highly specific antioxidative activity may be important for the clinical treatment and relapse of IBD. In the future, a combination of currently used pharmaceutics, together with natural and synthetic anti-oxidative compounds, like lipoic acid or curcumine, could be taken into account in the design of novel anti-IBD therapies.
Figures
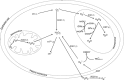
Fig. 1
Formation of ROS and anti-oxidant defence system in intestinal epithelial cells. CAT catalase, GRd glutathione reductase, GSH reduced glutathione, GSSG oxidised glutathione, GPx glutathione peroxidise, H 2 O 2 hydrogen peroxide, NO • nitric oxide, NOX NADPH oxidase, ONOO − peroxynitrate, O 2 •− superoxide anion, OH • hydroxyl radical, SOD1 cooper/zinc superoxide dismutase, SOD2 mitochondrial superoxide dismutase, SOD3 extracellular superoxide dismutase, XO xanthine oxidase. Numbers corresponds to reactions catalysed by representative enzymes and presented in Table 2
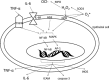
Fig. 2
The influence of ROS and cytokines on signalling pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. AGE advanced glycation end products, AP-1 activator protein 1, ICAM intracellular adhesion molecule, IL-6 interleukin 6, IL-6R interleukin 6 receptor, iNOS inducible nitric oxide synthase, NF-kB nuclear factor-kappa B, NOX NADPH oxidase, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinases, OCl − hypochlorite ion, SOD3 extracellular superoxide dismutase, TNF-α tumour necrosis factor alpha, TNFR tumour necrosis factor receptor
Similar articles
- The implications of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical aspects and animal models.
Balmus IM, Ciobica A, Trifan A, Stanciu C. Balmus IM, et al. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan-Feb;22(1):3-17. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.173753. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26831601 Free PMC article. Review. - Pathomechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Potential Antioxidant Therapies.
Tian T, Wang Z, Zhang J. Tian T, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:4535194. doi: 10.1155/2017/4535194. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28744337 Free PMC article. Review. - The emerging role of oxidative stress in inflammatory bowel disease.
Muro P, Zhang L, Li S, Zhao Z, Jin T, Mao F, Mao Z. Muro P, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 15;15:1390351. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1390351. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39076514 Free PMC article. Review. - Oxidative stress and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: an epiphenomenon or the cause?
Rezaie A, Parker RD, Abdollahi M. Rezaie A, et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2007 Sep;52(9):2015-21. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9622-2. Epub 2007 Apr 3. Dig Dis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17404859 Review. - Marine Algae and Deriving Biomolecules for the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Potential Clinical Therapeutics to Decrease Gut Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers?
Repici A, Hasan A, Capra AP, Scuderi SA, Paterniti I, Campolo M, Ardizzone A, Esposito E. Repici A, et al. Mar Drugs. 2024 Jul 25;22(8):336. doi: 10.3390/md22080336. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39195452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- New Class of Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutics Based on Gold (III) Complexes in Intestinal Inflammation-Proof of Concept Based on In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.
Krajewska JB, Włodarczyk J, Jacenik D, Kordek R, Taciak P, Szczepaniak R, Fichna J. Krajewska JB, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 18;22(6):3121. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063121. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803793 Free PMC article. - Narrative Review of _n_-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation upon Immune Functions, Resolution Molecules and Lipid Peroxidation.
Zaloga GP. Zaloga GP. Nutrients. 2021 Feb 18;13(2):662. doi: 10.3390/nu13020662. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33670710 Free PMC article. Review. - Consumption of dental treatment in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, a register study.
Johannsen A, Fored MC, Håkansson J, Ekbom A, Gustafsson A. Johannsen A, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Aug 12;10(8):e0134001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134001. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26267797 Free PMC article. - Intestinal barrier dysfunction orchestrates the onset of inflammatory host-microbiome cross-talk in a human gut inflammation-on-a-chip.
Shin W, Kim HJ. Shin W, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10539-E10547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810819115. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30348765 Free PMC article. - Coriolus Versicolor Downregulates TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Cascade in Dinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid-Treated Mice: A Possible Mechanism for the Anti-Colitis Effect.
Impellizzeri D, Fusco R, Genovese T, Cordaro M, D'Amico R, Trovato Salinaro A, Ontario ML, Modafferi S, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R, Calabrese V, Siracusa R. Impellizzeri D, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Feb 17;11(2):406. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020406. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204289 Free PMC article.
References
- Abdel-Aziz H, Wadie W, Abdallah DM, Lentzen G, Khayyal MT (2013) Novel effects of ectoine, a bacteria-derived natural tetrahydropyrimidine, in experimental colitis. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology - PubMed
- Agnholt J, Kaltoft K. Infliximab downregulates interferon-gamma production in activated gut T-lymphocytes from patients with Crohn's disease. Cytokine. 2001;15:212–222. - PubMed
- Ancha HR, Kurella RR, McKimmey CC, Lightfoot S, Harty RF. Effects of N-acetylcysteine plus mesalamine on prostaglandin synthesis and nitric oxide generation in TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54:758–766. - PubMed
- Arijs I, De Hertogh G, Machiels K, Van Steen K, Lemaire K, Schraenen A, Van Lommel L, Quintens R, Van Assche G, Vermeire S, Schuit F, Rutgeerts P. Mucosal gene expression of cell adhesion molecules, chemokines, and chemokine receptors in patients with inflammatory bowel disease before and after infliximab treatment. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:748–761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources