Estimation of 24-hour urinary sodium excretion using spot urine samples - PubMed (original) (raw)
Estimation of 24-hour urinary sodium excretion using spot urine samples
Moo-Yong Rhee et al. Nutrients. 2014.
Abstract
The present study evaluated the reliability of equations using spot urine (SU) samples in the estimation of 24-hour urine sodium excretion (24-HUNa). Equations estimating 24-HUNa from SU samples were derived from first-morning SU of 101 participants (52.4 ± 11.1 years, range 24-70 years). Equations developed by us and other investigators were validated with SU samples from a separate group of participants (n = 224, 51.0 ± 10.9 years, range 24-70 years). Linear, quadratic, and cubic equations were derived from first-morning SU samples because these samples had a sodium/creatinine ratio having the highest correlation coefficient for 24-HUNa/creatinine ratio (r = 0.728, p < 0.001). In the validation group, the estimated 24-HUNa showed significant correlations with measured 24-HUNa values. The estimated 24-HUNa by the linear, quadratic, and cubic equations developed from our study were not significantly different from measured 24-HUNa, while estimated 24-HUNa by previously developed equations were significantly different from measured 24-HUNa values. The limits of agreement between measured and estimated 24-HUNa by six equations exceeded 100 mmol/24-hour in the Bland-Altman analysis. All equations showed a tendency of under- or over-estimation of 24-HUNa, depending on the level of measured 24-HUNa. Estimation of 24-HUNa from single SU by equations as tested in the present study was found to be inadequate for the estimation of an individual's 24-HUNa.
Figures
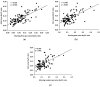
Figure 1
Relationship between (a) 24-hour urine sodium/creatinine (Na/Cr) ratio vs. first-morning spot urine Na/Cr ratio; (b) 24-hour urine Na/Cr ration vs. evening spot urine Na/Cr ratio; and (c) 24-hour urine Na/Cr ration vs. random morning spot urine Na/Cr ratio in 101 subjects.
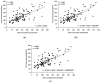
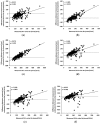
Figure 2
Development of equations by curve fitting from 101 subjects. (a) Linear equation association; (b) quadratic equation association and (c) cubic equation association. Each equations and their correlation coefficient are showed. Equation XNa = (spot urine sodium/spot urine creatinine) × predicted 24-hour urine creatinine excretion.
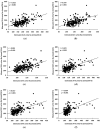
Figure 3
Relationship between measured and estimated 24-hour urine sodium obtained by six equations. (a) Kawasaki’s equation; (b) Tanaka’s equation; (c) INTERSALT equation; (d) linear equation; (e) quadratic equation; and (f) cubic equation.
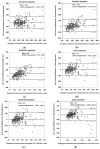
Figure 4
Bland-Altman analysis for agreement of the six equations. (a) Kawasaki’s equation; (b) Tanaka’s equation; (c) INTERSALT equation; (d) linear equation; (e) quadratic equation; (f) cubic equation.
Figure 5
Relationship between the differences of measured and estimated 24-hour urine sodium against measured 24-hour urine sodium. (a) Kawasaki’s equation; (b) Tanaka’s equation; (c) INTERSALT equation; (d) linear equation; (e) quadratic equation; and (f) cubic equation.
Similar articles
- Estimating sodium intake from spot urine samples at population level: a validation and application study in French adults.
Emeville E, Lassale C, Castetbon K, Deschamps V, Salanave B, Vernay M, Guergour D, Faure P, Hercberg S, Galan P, Kesse-Guyot E, Verdot C. Emeville E, et al. Br J Nutr. 2019 Jul 28;122(2):186-194. doi: 10.1017/S0007114519000886. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Br J Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31006386 - Estimating 24-Hour Sodium Excretion from Spot Urine Samples in Chinese Adults: Can Spot Urine Substitute 24-Hour Urine Samples?
Xu J, Zhang J, Liu M, Bai Y, Guo X, Dong J, Xu A, Wu J. Xu J, et al. Nutrients. 2020 Mar 18;12(3):798. doi: 10.3390/nu12030798. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32197398 Free PMC article. - Validity of predictive equations for 24-h urinary sodium excretion at the population and individual levels among Chinese adults aged 18-69 years.
Du X, Fang L, Guo J, Chen X, Su S, Zhang J. Du X, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 17;11(1):22404. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00513-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34789756 Free PMC article. - Estimation of sodium consumption by novel formulas derived from random spot and 12-hour urine collection.
Sonuch P, Kantachuvesiri S, Vathesatogkit P, Lappichetpaiboon R, Chailimpamontri W, Thokanit NS, Aekplakorn W. Sonuch P, et al. PLoS One. 2021 Dec 2;16(12):e0260408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260408. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34855776 Free PMC article. - Systematic review of studies evaluating urinary iodine concentration as a predictor of 24-hour urinary iodine excretion for estimating population iodine intake.
Ji C, Lu T, Dary O, Legetic B, Campbell NR, Cappuccio FP; Sub-Group for Research and Surveillance of the PAHO–WHO Regional Expert Group for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention through Population-wide Dietary Salt Reduction. Ji C, et al. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2015 Jul;38(1):73-81. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2015. PMID: 26506324 Review.
Cited by
- Self-monitoring urinary salt excretion device can be used for controlling hypertension for developing countries.
Jahan Y, Moriyama M, Rahman MM, Rahman A. Jahan Y, et al. Clin Hypertens. 2019 Mar 15;25:3. doi: 10.1186/s40885-019-0109-9. eCollection 2019. Clin Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30923632 Free PMC article. Review. - Development and application of the sodium index to estimate and assess sodium intake for Korean adults.
Lee YK, Hyun T, Ro H, Heo YR, Choi MK. Lee YK, et al. Nutr Res Pract. 2022 Jun;16(3):366-378. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2022.16.3.366. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Nutr Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35663439 Free PMC article. - Validation and Assessment of Three Methods to Estimate 24-h Urinary Sodium Excretion from Spot Urine Samples in High-Risk Elder Patients of Stroke from the Rural Areas of Shaanxi Province.
Ma W, Yin X, Zhang R, Liu F, Yang D, Fan Y, Rong J, Tian M, Yu Y. Ma W, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Oct 11;14(10):1211. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14101211. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29019912 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Assessment and validation of spot urine in estimating the 24-h urinary sodium, potassium, and sodium/potassium ratio in Chinese adults.
Xu J, Du X, Bai Y, Fang L, Liu M, Ji N, Zhong J, Yu M, Wu J. Xu J, et al. J Hum Hypertens. 2020 Feb;34(2):184-192. doi: 10.1038/s41371-019-0274-z. Epub 2019 Oct 28. J Hum Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 31659230 Free PMC article.
References
- World Health Organization . Report of a Who Forum and Technical Meeting, Paris, France, 5–7 October 2006. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2007. Reducing salt intake in populations; pp. 1–56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources