Melatonin inhibits the migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell lines involving JNK/MAPK pathway - PubMed (original) (raw)
Melatonin inhibits the migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell lines involving JNK/MAPK pathway
Qiaoyun Zhou et al. PLoS One. 2014.
Abstract
Objective: Melatonin, an indolamine produced and secreted predominately by the pineal gland, exhibits a variety of physiological functions, possesses antioxidant and antitumor properties. But, the mechanisms for the anti-cancer effects are unknown. The present study explored the effects of melatonin on the migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells and its mechanism.
Methods: MTT assay was employed to measure the viability of A549 cells treated with different concentrations of melatonin. The effect of melatonin on the migration of A549 cells was analyzed by wound healing assay. Occludin location was observed by immunofluorescence. The expression of occludin, osteopontin (OPN), myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and phosphorylation of myosin light chain (MLC), JNK were detected by western blots.
Results: After A549 cells were treated with melatonin, the viability and migration of the cells were inhibited significantly. The relative migration rate of A549 cells treated with melatonin was only about 20% at 24 h. The expression level of OPN, MLCK and phosphorylation of MLC of A549 cells were reduced, while the expression of occludin was conversely elevated, and occludin located on the cell surface was obviously increased. The phosphorylation status of JNK in A549 cells was also reduced when cells were treated by melatonin.
Conclusions: Melatonin significantly inhibits the migration of A549 cells, and this may be associated with the down-regulation of the expression of OPN, MLCK, phosphorylation of MLC, and up-regulation of the expression of occludin involving JNK/MAPK pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
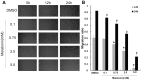
Figure 1. Melatonin inhibits the migration of A549 cells.
(A) The migration of A549 cells at 0.1, 0.75, 2.5, 5.0 mmol/L melatonin groups respectively when A549 cells were treated for 0 h, 12 h and 24 h. (B) Analysis of migration rate (%), compared with control group (DMSO): *P<0.05, #P<0.05.
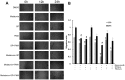
Figure 2. The effect of melatonin, SP600125 and PMA on migration of A549 cells.
(A) The effect of melatonin, SP600125 and PMA on migration of A549 cells after 0 h, 12 h and 24 h. (B) Analysis of migration rate, compared with control group: *P<0.05, #P<0.05; compared with PMA group: ▴P<0.05, △P<0.05.
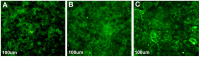
Figure 3. Immunofluorescence detection of tight junction correlated protein occludin in A549 cells.
(A) DMSO control. (B) melatonin (0.1 mmol/L). (C) melatonin (2.0 mmol/L).
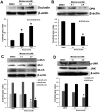
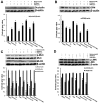
Figure 4. Effect of melatonin on the expression of occludin, OPN, MLCK and phosphorylation of MLC, JNK.
(A) occludin, (B) OPN, (C) MLC and MLCK, (D) JNK. Results are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, in comparison to control group.
Figure 5. The Effect of melatonin, SP600125 and PMA on the expression of occludin, OPN, MLCK and phosphorylation of MLC, JNK.
(A) occludin, (B) OPN, (C) MLC and MLCK, (D) JNK. Results are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, #P<0.05, in comparison to control; ▴P<0.05, △P<0.05, in comparison to PMA group.
Similar articles
- A novel all-trans retinoid acid derivative N-(3-trifluoromethyl- phenyl)- retinamide inhibits lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell migration through down-regulating expression of myosin light chain kinase.
Fan TT, Cheng Y, Wang YF, Gui SY, Chen FH, Zhou Q, Wang Y. Fan TT, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(18):7687-92. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.18.7687. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25292047 - Melatonin inhibits the Migration of Colon Cancer RKO cells by Down-regulating Myosin Light Chain Kinase Expression through Cross-talk with p38 MAPK.
Zou DB, Wei X, Hu RL, Yang XP, Zuo L, Zhang SM, Zhu HQ, Zhou Q, Gui SY, Wang Y. Zou DB, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(14):5835-42. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.14.5835. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 26320459 - New insights into 4-amino-2-tri-fluoromethyl-phenyl ester inhibition of cell growth and migration in the A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line.
Wang H, Gui SY, Chen FH, Zhou Q, Wang Y. Wang H, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(12):7265-70. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.12.7265. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24460286 - Melatonin inhibits colon cancer RKO cell migration by downregulating Rho‑associated protein kinase expression via the p38/MAPK signaling pathway.
Liu Z, Zou D, Yang X, Xue X, Zuo L, Zhou Q, Hu R, Wang Y. Liu Z, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):9383-9392. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7836. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 29152648 Free PMC article. - Melatonin and its ubiquitous anticancer effects.
Bhattacharya S, Patel KK, Dehari D, Agrawal AK, Singh S. Bhattacharya S, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Dec;462(1-2):133-155. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03617-5. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31451998 Review.
Cited by
- Melatonin: an endogenous miraculous indolamine, fights against cancer progression.
Samanta S. Samanta S. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Aug;146(8):1893-1922. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03292-w. Epub 2020 Jun 24. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32583237 Review. - Melatonin and Cancer Hallmarks.
Talib WH. Talib WH. Molecules. 2018 Feb 26;23(3):518. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030518. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29495398 Free PMC article. Review. - XBP1s promotes the development of lung adenocarcinoma via the p‑JNK MAPK pathway.
Jiang H, Jiang Q, He Y, Li X, Xu Y, Liu X. Jiang H, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2022 Mar;49(3):34. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5089. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35059734 Free PMC article. - NT-3 attenuates the growth of human neuron cells through the ERK pathway.
Li R, Wu Y, Jiang D. Li R, et al. Cytotechnology. 2016 Aug;68(4):659-64. doi: 10.1007/s10616-014-9813-1. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Cytotechnology. 2016. PMID: 25501303 Free PMC article. - Melatonin, a Full Service Anti-Cancer Agent: Inhibition of Initiation, Progression and Metastasis.
Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral SA, Tan DX, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Qin L, Yang SF, Xu K. Reiter RJ, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 17;18(4):843. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040843. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28420185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 62: 10–29. - PubMed
- Petty RD, Nicolson MC, Kerr KM, Collie-Duguid E, Murray GI (2004) Gene expression profiling in non-small cell lung cancer: from molecular mechanisms to clinical application. Clinical Cancer Research 10: 3237–3248. - PubMed
- Dziadziuszko R, Hirsch FR (2008) Advances in genomic and proteomic studies of non-small-cell lung cancer: clinical and translational research perspective. Clinical Lung Cancer 9: 78–84. - PubMed
- Weight B, Peterse JL, Van’t Veer LJ (2005) Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nature Reviews Cancer 5: 591–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272399) and Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No. 90413116). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials